Содержание
- 2. The Aztec people were certain ethnic groups of central Mexico, who spoke the Nahuatl language and
- 3. Aztec (Aztecatl) is the Nahuatl word for "people from Aztlan", a mythological place for the Nahuatl-speaking
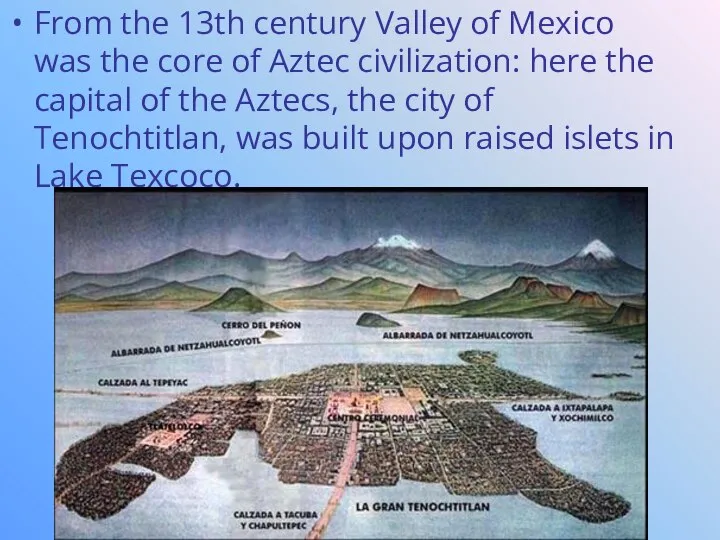
- 4. From the 13th century Valley of Mexico was the core of Aztec civilization: here the capital
- 5. At its pinnacle Aztec culture had rich and complex mythological and religious traditions, as well as
- 6. In 1521, Hernán Cortés, along with a large number of Nahuatl speaking indigenous allies, conquered Tenochtitlan
- 7. The Spanish founded the new settlement of Mexico City on the site of the ruined Aztec
- 9. Aztec culture and history is primarily known through archaeological evidence found in excavations such as that
- 10. We know some facts from 16th and 17th century descriptions of Aztec culture and history written
- 12. Скачать презентацию








 Аттестационная работа. Проектно-исследовательская деятельность на уроках английского языка в начальной и средней школе
Аттестационная работа. Проектно-исследовательская деятельность на уроках английского языка в начальной и средней школе Презентация к уроку английского языка "School uniform in different countries" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "School uniform in different countries" - скачать бесплатно Writing
Writing Основание краеведческого музея в п. Харик. Февраль 1986 года. Первая экскурсия – 9 мая 1986 года.
Основание краеведческого музея в п. Харик. Февраль 1986 года. Первая экскурсия – 9 мая 1986 года. There are a lot of countries in the world
There are a lot of countries in the world Герундий Функции герундия в предложении
Герундий Функции герундия в предложении English Grammar (Lesson 1)
English Grammar (Lesson 1) The problem of Singular and Plural Semantics of Different groups of Nouns
The problem of Singular and Plural Semantics of Different groups of Nouns Hotel “Golden Crown”
Hotel “Golden Crown”  Grammar practice
Grammar practice Jane Eyre. Chapter 1
Jane Eyre. Chapter 1 AMERICAN HOLIDAYS by Sergey Andronaki
AMERICAN HOLIDAYS by Sergey Andronaki Australian Animals Spotlight – 5 (module 5) School #1694, Moscow, Russia Class 5b Teacher: Elena Makhovikova Creative team: Semyon Vozenkov, Vadim Minayev, Anna Tolkunova, Elena Matsal, Maria Popova 2009\2010 school year
Australian Animals Spotlight – 5 (module 5) School #1694, Moscow, Russia Class 5b Teacher: Elena Makhovikova Creative team: Semyon Vozenkov, Vadim Minayev, Anna Tolkunova, Elena Matsal, Maria Popova 2009\2010 school year School is fun, isn’t it?
School is fun, isn’t it?  Control test 3. Preparation
Control test 3. Preparation Презентация к уроку английского языка "History of the USA" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "History of the USA" - скачать  Queen
Queen Презентация к уроку английского языка "My Scotland" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "My Scotland" - скачать  Актуальные вопросы преподавания английского языка
Актуальные вопросы преподавания английского языка «Океанский прибой, вечно бьющийся в берега жизни» Чингиз Айтматов.
«Океанский прибой, вечно бьющийся в берега жизни» Чингиз Айтматов. Презентация к уроку английского языка "Сountables and uncountables" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Сountables and uncountables" - скачать  Irregular verbs Part 1
Irregular verbs Part 1 Family
Family ГБОУ СОШ 1387 Айрапетян Мелине Аванесовна . Учитель английского языка Тема: Irregular verbs Класс – 5
ГБОУ СОШ 1387 Айрапетян Мелине Аванесовна . Учитель английского языка Тема: Irregular verbs Класс – 5  Rock groups of America
Rock groups of America  English game
English game Презентация к уроку английского языка "Frederik Frantsisk Shopen" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Frederik Frantsisk Shopen" - скачать  What is it?
What is it?