Содержание
- 4. Course reading / learning material Kotler’s 6th edition: Chapter 8: products , services and brands Chapter
- 5. Examples Frozen Yogurt 1993: - taste strawberry of “I Can’t Believe It’s Yogurt” in the Netherlands
- 6. Introduction: Product To marketers, products are bundles of benefits delivered to the customer. The form in
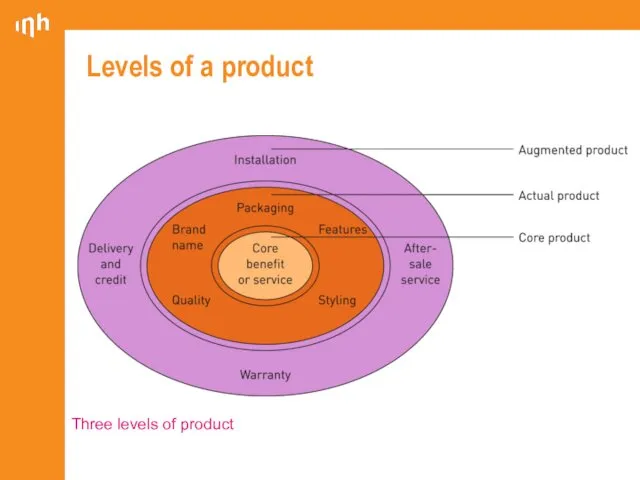
- 7. Levels of a product Three levels of product
- 8. Levels of a product Core product problem solving service or core benefits that consumers are really
- 9. Product classifications Products can be classified according to their durability and tangibility. Non-durable products are goods
- 10. Consumer products Bought to satisfy personal and family needs. Classified according to consumer shopping habits: -
- 11. Consumer products Bought to satisfy personal and family needs. Classified according to consumer shopping habits: -
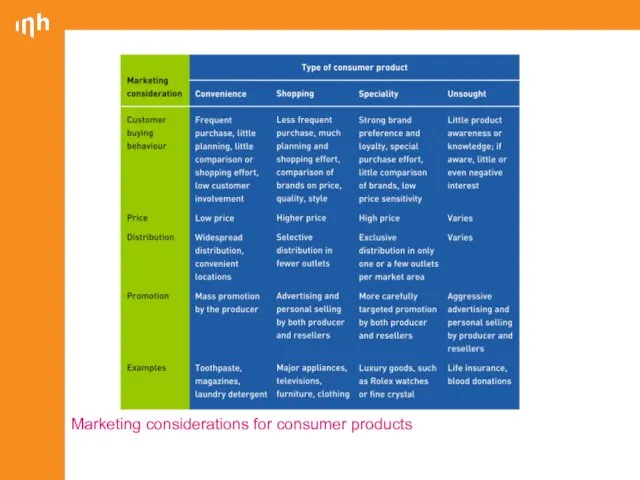
- 12. Marketing considerations for consumer products
- 13. What type of product is … for you? Mobile phone School books French fries with mayonaise
- 14. Industrial products Products bought for further processing or the purposes of resale. Distinction based upon the
- 15. Organisations, persons, places and ideas Marketers have broadened the concept of product to include other marketable
- 16. Examples: Kim Kardashian Tower Bridge London https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QdpDIE8tTw8
- 17. Product decisions Marketers make product decisions at three levels: individual product decisions product line decisions product
- 18. Individual product decisions Product decisions are focused around the development and marketing of Product attributes; Branding;
- 19. Product attributes Define the benefits offered to the customer Product quality Conformance and Customer driven quality
- 20. Branding A name, term, sign, symbol or design, or a combination of these, intended to identify
- 21. Branding: benefits for consumers Brand names tell the buyer about the quality of the product. Brand
- 22. Branding: supplier advantage Brand name makes it easier for the supplier to process orders and track
- 24. Branding: powerful marketing mechanism Leads to higher and more consistent product quality. Increases innovation by giving
- 25. Packaging Innovative and attractive packaging to gain the attention of the consumer. Packaging is central to
- 26. Labelling Identifies the product Conforms to legal requirements as in the case of medical products Describes
- 27. Product support services Customer service is an essential element of the product strategy, and can play
- 28. Product line considerations The product line is comprised of a group of products that are closely
- 29. Product line length decisions The product line length involves the number of items in the product
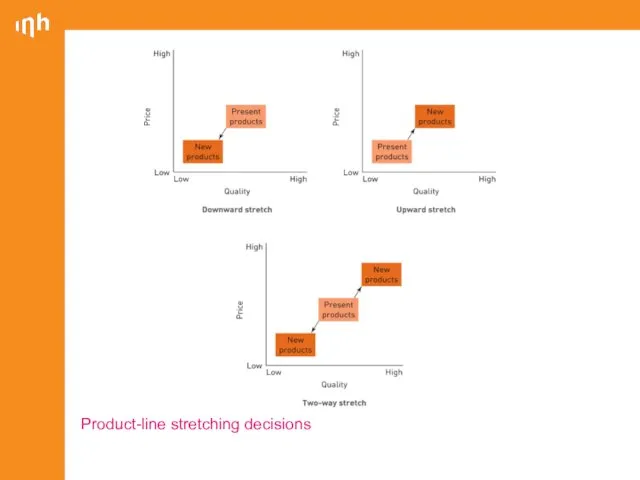
- 30. Product line stretching Downward stretch Company initially located at the top end of the market and
- 31. Product-line stretching decisions
- 32. Product line filling Increasing the product line by adding more items within the present range of
- 33. Product mix decisions Product mix or product assortment consists of all the product lines and items
- 34. Four dimensions of the product mix Breadth or width Wide product mix containing many different product
- 36. Скачать презентацию



























 Отчет директора филиала Лебяжинского района Палаты предпринимателей Павлодарской области
Отчет директора филиала Лебяжинского района Палаты предпринимателей Павлодарской области Бизнес-план. Структура бизнес-плана
Бизнес-план. Структура бизнес-плана Бизнес-модель и тестирование гипотез
Бизнес-модель и тестирование гипотез The Travel and Tourism Industry in Perspective
The Travel and Tourism Industry in Perspective Технология мотивационного рекрутирования
Технология мотивационного рекрутирования Система ДОП
Система ДОП Бизнес-план разведения перепелов в условиях семейной фермы КФХ Птицевод за счет реконструкции помещения
Бизнес-план разведения перепелов в условиях семейной фермы КФХ Птицевод за счет реконструкции помещения Социальная парикмахерская
Социальная парикмахерская Бизнес-концепция
Бизнес-концепция Бизнес - школа дизайнеров
Бизнес - школа дизайнеров Деловая игра по развитию бизнеса
Деловая игра по развитию бизнеса Инструменты успешного предпринимателя
Инструменты успешного предпринимателя Индитекс — мировой лидер в сфере розничной торговли одеждой
Индитекс — мировой лидер в сфере розничной торговли одеждой Підприємство як суб'єкт господарювання. Тема 1
Підприємство як суб'єкт господарювання. Тема 1 Коммерческие операции во ВЭД, их сущность и содержание
Коммерческие операции во ВЭД, их сущность и содержание Как создать свой бизнес?
Как создать свой бизнес? Подбор тура по запросу клиента
Подбор тура по запросу клиента Изготовление моделей мебели для детской игровой зоны. Проект
Изготовление моделей мебели для детской игровой зоны. Проект Группа компаний ОСМ. Лифты, эскалаторы. Структура и направления бизнеса
Группа компаний ОСМ. Лифты, эскалаторы. Структура и направления бизнеса Business cycle
Business cycle План 2017
План 2017 Бизнес-план Детская игровая комната Солнышко
Бизнес-план Детская игровая комната Солнышко Кастомизация. Целевой сегмент
Кастомизация. Целевой сегмент Модель 7С
Модель 7С Контрольная работа №3 .Резюме бизнес-плана (первоначальный(учебный) вариант)
Контрольная работа №3 .Резюме бизнес-плана (первоначальный(учебный) вариант) Образовательная программа для реализации проекта или бизнес - идеи
Образовательная программа для реализации проекта или бизнес - идеи Ресторан: Ниагара
Ресторан: Ниагара Обоснование спроса на услуги автосервиса
Обоснование спроса на услуги автосервиса