Содержание
- 2. Thrust is the pulling or pushing force developed by an aircraft engine. Aircraft need thrust to
- 3. The piston engine A simple piston engine works on a four-stroke cycle, consisting of induction, compression,
- 4. The ramjet But air flows straight through a jet engine. Yet a jet engine has the
- 5. The gas turbine engine The gas turbine engine draws air from the atmosphere and, after compressing
- 6. The turbojet engine The turbojet engine is most suitable for high forward speeds. At aircraft speeds
- 7. The turboprop engine The advantages of the turboprop engine have to some extent been offset by
- 9. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Thrust is the pulling or pushing force developed by an aircraft
Thrust is the pulling or pushing force developed by an aircraft
engine. Aircraft need thrust to propel them through air. The required thrust may be developed by rotating pulling or pushing propellers by means of piston or reciprocating engines, or by throwing back masses of air by means of gas turbine engines.
Слайд 3
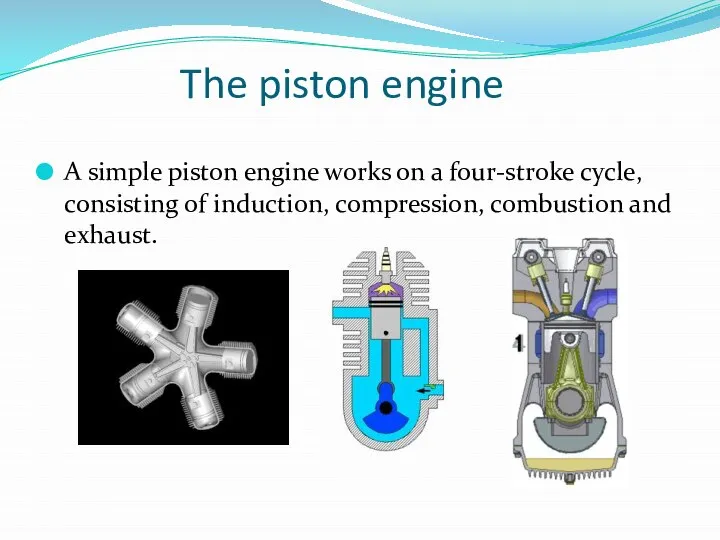
The piston engine
A simple piston engine works on a four-stroke cycle,
The piston engine
A simple piston engine works on a four-stroke cycle,
consisting of induction, compression, combustion and exhaust.
Слайд 4
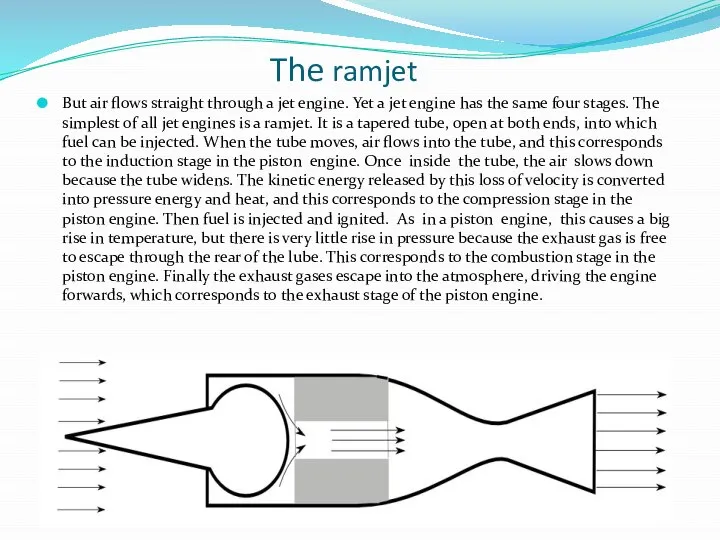
The ramjet
But air flows straight through a jet engine. Yet
The ramjet
But air flows straight through a jet engine. Yet
a jet engine has the same four stages. The simplest of all jet engines is a ramjet. It is a tapered tube, open at both ends, into which fuel can be injected. When the tube moves, air flows into the tube, and this corresponds to the induction stage in the piston engine. Once inside the tube, the air slows down because the tube widens. The kinetic energy released by this loss of velocity is converted into pressure energy and heat, and this corresponds to the compression stage in the piston engine. Then fuel is injected and ignited. As in a piston engine, this causes a big rise in temperature, but there is very little rise in pressure because the exhaust gas is free to escape through the rear of the lube. This corresponds to the combustion stage in the piston engine. Finally the exhaust gases escape into the atmosphere, driving the engine forwards, which corresponds to the exhaust stage of the piston engine.
Слайд 5
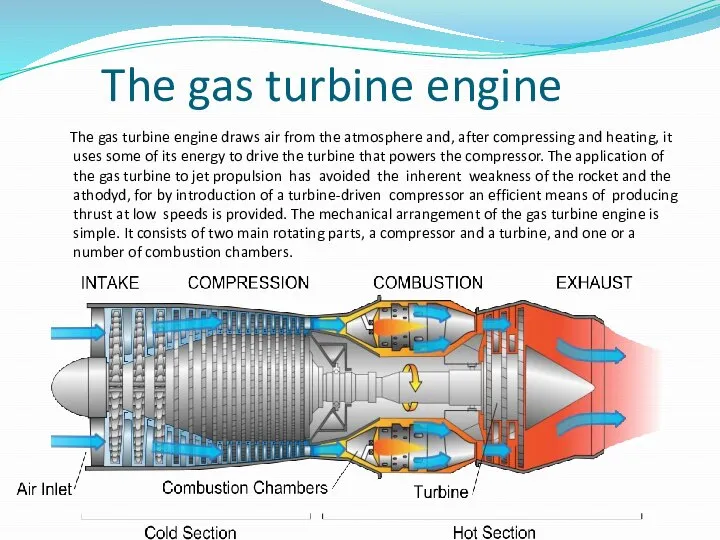
The gas turbine engine
The gas turbine engine draws air from
The gas turbine engine
The gas turbine engine draws air from
the atmosphere and, after compressing and heating, it uses some of its energy to drive the turbine that powers the compressor. The application of the gas turbine to jet propulsion has avoided the inherent weakness of the rocket and the athodyd, for by introduction of a turbine-driven compressor an efficient means of producing thrust at low speeds is provided. The mechanical arrangement of the gas turbine engine is simple. It consists of two main rotating parts, a compressor and a turbine, and one or a number of combustion chambers.
Слайд 6
The turbojet engine
The turbojet engine is most suitable for high forward
The turbojet engine
The turbojet engine is most suitable for high forward
speeds. At aircraft speeds below 450 miles per hour the jet engine is less efficient than a propeller-type engine.
Слайд 7
The turboprop engine
The advantages of the turboprop engine have to some
The turboprop engine
The advantages of the turboprop engine have to some
extent been offset by the introduction of the bypass and ducted fan engines. These engines deal with larger comparative airflows and lower jet velocities than pure jet engines, thus giving a propulsive efficiency which is comparable to that of the turboprop and exceeds that of the pure jet engine.



 ЕГЭ физика 2005 год
ЕГЭ физика 2005 год Дослідження фізичних основ судноплавання
Дослідження фізичних основ судноплавання Механическое движение. Физика 7 класс
Механическое движение. Физика 7 класс Испытания композитных материалов и конструкций
Испытания композитных материалов и конструкций Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа внеурочной деятельности по физике Физика в экспериментах
Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа внеурочной деятельности по физике Физика в экспериментах Колебания и волны. Квантовая физика
Колебания и волны. Квантовая физика Средства тепловой диагностики, обработка и представление результатов измерений
Средства тепловой диагностики, обработка и представление результатов измерений Истечение из сопел. Дросселирование. (Лекция 6)
Истечение из сопел. Дросселирование. (Лекция 6) Классификация химических методов
Классификация химических методов Закони електричного подразнення
Закони електричного подразнення Северное сияние
Северное сияние Аттестационная работа. Программа элективного курса по физике Физические величины и их измерение. 7 класс
Аттестационная работа. Программа элективного курса по физике Физические величины и их измерение. 7 класс Частица в одномерной глубокой потенциальной яме. Прохождение частицы через потенциальный барьер. Туннельный эффект. (Лекция 5)
Частица в одномерной глубокой потенциальной яме. Прохождение частицы через потенциальный барьер. Туннельный эффект. (Лекция 5) Защита картера и КПП CHERY T19
Защита картера и КПП CHERY T19 Эмилий Христианович Ленц
Эмилий Христианович Ленц Давление газа. Уравнение состояния идеального газа. Изопроцессы
Давление газа. Уравнение состояния идеального газа. Изопроцессы Виды критериев прочности материала
Виды критериев прочности материала Сила. Решение задач по теме «Виды сил»
Сила. Решение задач по теме «Виды сил» Первое начало термодинамики. Теплота и работа
Первое начало термодинамики. Теплота и работа Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа внеурочной деятельности по физике« Юный исследователь»
Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа внеурочной деятельности по физике« Юный исследователь» Тепловые явления. 8 классе
Тепловые явления. 8 классе Механика жидкости и газа
Механика жидкости и газа Закон Ома для участка цепи
Закон Ома для участка цепи Закон сохранения момента импульса системы материальных точек
Закон сохранения момента импульса системы материальных точек Приборы и методы радиометрических измерений
Приборы и методы радиометрических измерений Взаимодействие рентгеновского излучения с веществом
Взаимодействие рентгеновского излучения с веществом Электрическое поле в проводниках и дилектриках
Электрическое поле в проводниках и дилектриках Ракетные двигатели
Ракетные двигатели