Содержание
- 2. FOOD A nutrient is a substance required by the body for energy, growth, repair, and maintenance.
- 4. Energy and Building Materials Each nutrient plays a different role in maintaining a healthy body. Carbohydrates,
- 5. NUTRIENTS
- 6. Carbohydrates Carbohydrates that exist as single sugar molecules are called monosaccharides or simple carbohydrates. Carbohydrates made
- 7. Proteins Amino acids from proteins are used by the body for making additional proteins. Extra amino
- 8. Lipids The body uses lipids to make steroid hormones and cell membranes and to store energy.
- 9. NUTRIENTS
- 10. Vitamins, Minerals, and Water Vitamins are organic substances that occur in foods in small amounts. They
- 11. VITAMINS
- 12. MINERALS
- 13. WATER
- 14. DIGESTION Organisms must break down their foodstuffs into their components for passing through the cell membrane.
- 15. There are two types of digestion. These are; Mechanical digestion Chemical digestion TYPES OF DIGESTION
- 16. MECHANICAL DIGESTION Pieces of food are firstly cut, crushed, or broken into smaller particles without being
- 17. MECHANICAL DIGESTION
- 18. Chemical digestion is series of reactions in which foods are hydrolyzed, aided by water and enzymes.
- 19. CHEMICAL DIGESTION
- 20. TYPES OF DIGESTION ACCORDING TO THE THEIR MEDIUM There are two types digestion according to the
- 21. INTRACELLULAR DIGESTION In unicellular organisms foodstuffs are digested within food vacuoles in the cytoplasm. They are
- 22. EXTRACELLULAR DIGESTION In this process, digestion of food takes place within an area external to the
- 24. HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system is made up of highly specialized digestive tube and several
- 26. DIGESTIVE ORGANS
- 28. HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
- 29. MOUTH Food enters the body through the mouth. Mechanical and chemical digestion occur in mouth. Teeth
- 30. SALIVARY GLANDS
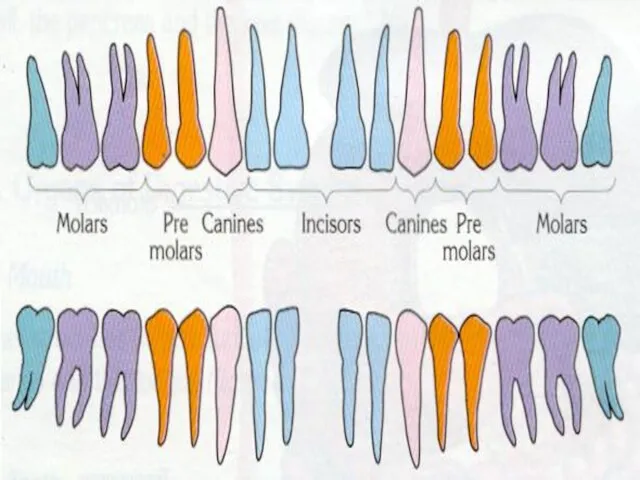
- 31. TEETH Teeth are adapted for mechanical digestion of food. Each tooth is composed of crown and
- 36. TYPES OF TEETH There are 4 types of teeth. These are 1- Molars 12 2- Pre
- 41. ESOPHAGUS After chewing of food, it is pushed by the tongue to the esophagus. The esophagus
- 44. PERISTALSIS
- 45. STOMACH Food is stored temporarily in the stomach. Mechanical and chemical digestion occur in mouth. Food
- 46. STOMACH
- 48. STOMACH
- 49. STOMACH
- 50. Most digestion and absorption occur in small intestine. Most chemical digestion and all absorption occur in
- 51. SMALL INTESTINE
- 53. SMALL INTESTINE
- 54. SMALL INTESTINE
- 55. SMALL INTESTINE
- 56. Undigested materials pass from the small intestine into the large intestine. There is no digestion in
- 57. FUNCTIONS OF LARGE INTESTINE Reabsorption of water Absoption of vitamins Eliminations of undigested materials
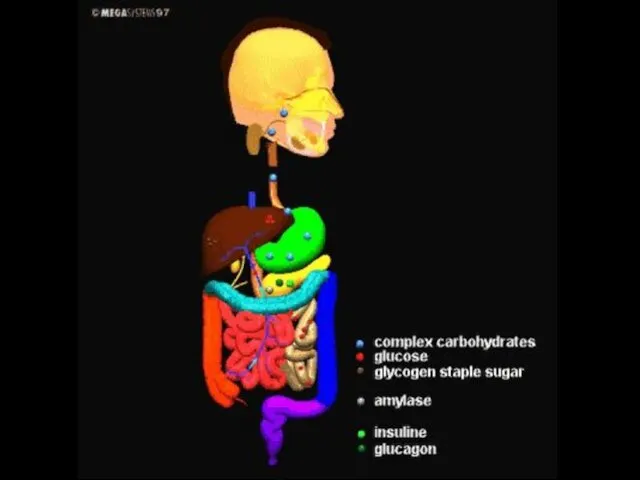
- 59. DIGESTION OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE MOUTH Chemical digestion of carbohydrate starts in mouth. Salivary glands secrete
- 60. Stomach is an acidic area. Amylase can not work in acidic region. Therefore chemical digestion of
- 61. When food passes into the small intestine from stomach, it stimulates cells of small intestine. Than
- 62. They stimulate pancreas and it secretes pancreatic enzymes to small intestine. Enzymes act on every types
- 64. Digestion of carbohydrates is completed in small intestine. Dextrin + H2O Glucose + Glucose +…… Amylase
- 65. CARBOHYDRATE DIGESTINE
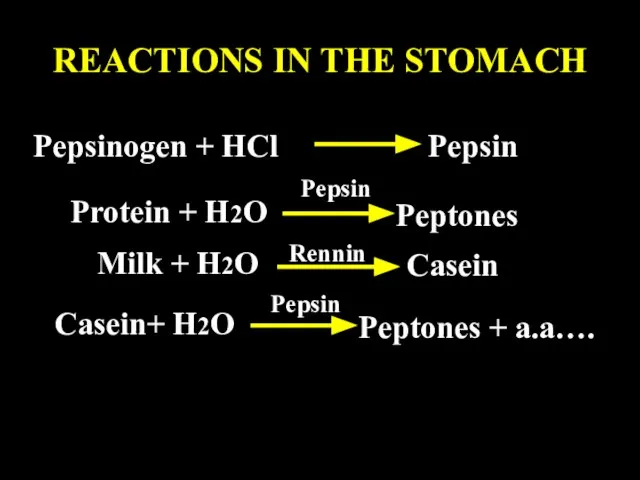
- 66. DIGESTION OF PROTEINS Digestion of protein starts in stomach and complete in small intestine. When food
- 67. REACTIONS IN THE STOMACH Pepsinogen + HCl Pepsin Protein + H2O Peptones Pepsin Milk + H2O
- 68. DIGESTION OF PROTEINS IN THE INTESTINE Tripsinogen and Chymotripsinogen take role in the digestion of proteins
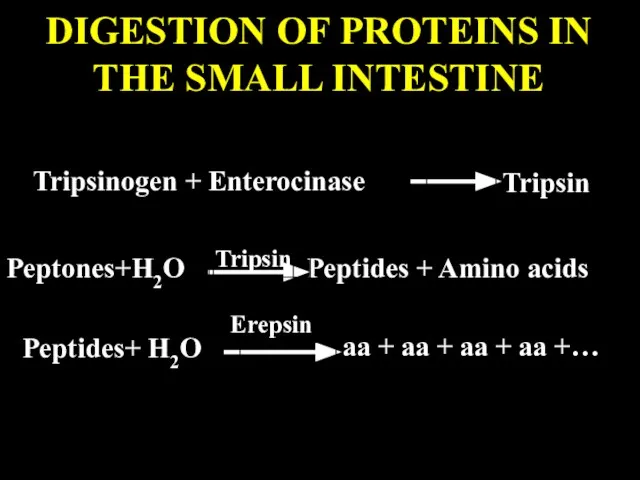
- 69. DIGESTION OF PROTEINS IN THE SMALL INTESTINE Tripsinogen + Enterocinase Tripsin Peptones+H2O Peptides + Amino acids
- 70. PROTEIN DIGESTINE
- 71. DIGESTION OF LIPIDS Digestion of lipid occurs only in small intestine. The cells of the liver
- 72. Bile does not contain enzyme but it aids mechanical digestion of lipid. This process is called
- 75. Lipase is secreted from pancreas. Lipase breaks down lipid molecules into fatty acids and glycerol. Lipid
- 76. LIPID DIGESTINE
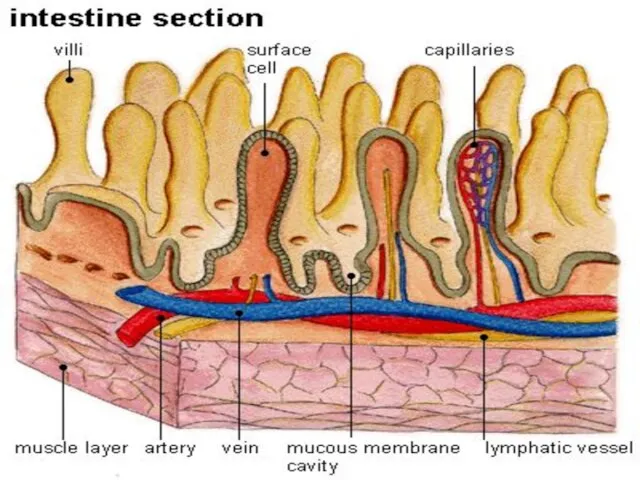
- 77. ABSORBTION There are many finger like projections in lining of small intestine.They are called VILLI. Villi
- 80. Скачать презентацию







































































 Сведения о деятельности подразделений медицинской организации, оказывающих медицинскую помощь в стационарных условиях. Форма №14
Сведения о деятельности подразделений медицинской организации, оказывающих медицинскую помощь в стационарных условиях. Форма №14 Диссеминированный туберкулез легких
Диссеминированный туберкулез легких Ионизирующие излучение и его последствия
Ионизирующие излучение и его последствия Бронхиальная астма
Бронхиальная астма Методы исследования пародонтологических больных
Методы исследования пародонтологических больных Современный взгляд на принцип функционирования центра терморегуляции
Современный взгляд на принцип функционирования центра терморегуляции Человек и его ближайшее окружение. Межличностные отношения. Общение
Человек и его ближайшее окружение. Межличностные отношения. Общение Выделительная система
Выделительная система Жүрек гликозидтері мен АПФ ингибиторлары
Жүрек гликозидтері мен АПФ ингибиторлары Лучевая диагностика заболеваний предстательной железы
Лучевая диагностика заболеваний предстательной железы Променева хвороба
Променева хвороба Нарушение диуреза
Нарушение диуреза Подготовка к иструментальным методам исследования
Подготовка к иструментальным методам исследования Полтавченко СИ 71310 Ангиография
Полтавченко СИ 71310 Ангиография Методы исследования в микробиологии
Методы исследования в микробиологии Аномалии конституции (диатез) у детей
Аномалии конституции (диатез) у детей Лабораторные методы исследования кала в гастроэнтерологии
Лабораторные методы исследования кала в гастроэнтерологии Адренергиялық заттар
Адренергиялық заттар Психомоторное развитие ребенка и его оценка. Теории психического и духовного развития. Поведение детей
Психомоторное развитие ребенка и его оценка. Теории психического и духовного развития. Поведение детей Аборт и его осложнения
Аборт и его осложнения Денсаулық жағдайының ауытқулары мен даму ақаулары бар балалар мен жасөспірімдерге арналған мекемелерде
Денсаулық жағдайының ауытқулары мен даму ақаулары бар балалар мен жасөспірімдерге арналған мекемелерде Патологиялық анатомия
Патологиялық анатомия Лечение наркомании
Лечение наркомании Тістерді егеуге қолданылатын абразивті материалдар
Тістерді егеуге қолданылатын абразивті материалдар Групповые методы психологического воздействия
Групповые методы психологического воздействия Общая психопатология
Общая психопатология Медицинская реабилитация при пневонии
Медицинская реабилитация при пневонии Проявление туберкулеза, сифилиса, дифтерии, ВИЧ-инфекции в полости рта
Проявление туберкулеза, сифилиса, дифтерии, ВИЧ-инфекции в полости рта