Содержание
- 2. Review Define volatile and none-volatile State what components connect to the North and South Bridge Define
- 3. Objectives Understand static electricity List reasons why we take precautions from static electricity State precautions we
- 4. The movement and contact of the human body can accumulate energy in the form of electrostatic
- 5. “Electro static discharge (ESD) is the transfer of an electrostatic charge between two objects. This is
- 6. Tribo-electrification Static electricity must build up a charge greater than 1000 V before we may notice
- 7. ESD is more likely to exist in work places which are humid, the use of a
- 8. ESD Symbols Fig 1 ESD Susceptibility Fig 2 ESD Protective Indicates that the device is susceptible
- 9. ESD protective devices A range of ESD protective devices are available to protect the computer from
- 10. Working inside a computer When working on the internals of a computer you must… Always connect
- 11. Good uses of ESD ESD is used to apply toner to paper in photocopy machines and
- 12. Electrostatic discharge can cause damage to integrated circuits such as the CMOS and other memory chips.
- 13. Static Electricity Video Testing for Static Electricity Electrostatic Charge at a Petrol Station Pauls guide to
- 14. Follow the safety rules Be prepared: have the right tools at hand Obey the dress code:
- 15. This highly magnified picture shows the damage that can be done to an IC by Electrostatic
- 16. Anti-static Wrist Strap Wrist straps safely remove static charge from individuals who handle static sensitive devices
- 17. How do you know if its working? Anti-static wrist straps can fail to perform their intended
- 18. Testing your wrist band Firstly check your multi-meter is working correctly by setting the 2M-ohms. Have
- 19. Motherboards The Main Printed Circuit Board Inside The PC That Contains and Controls The Components That
- 20. Motherboard is… Multi-layered printed circuit board Copper circuit paths called traces carry signals and voltages across
- 21. Think of a Motherboard as: Futuristic City with many modular plug-in buildings, using power from a
- 22. Motherboard MD Definition Research Activity MD Component identification and function How to install a motherboard
- 23. Basic Motherboard Chipset and Functions Different chips integrated to a single chip called the chipset. The
- 24. Motherboard Determines: CPU type and speed Chipset Types & number of connection slots Type of memory
- 25. Form Factors Form factor means the size and shape of the actual motherboard 3 most common
- 26. What other features do modern Motherboards include? In groups spend ten minutes look at recent motherboard
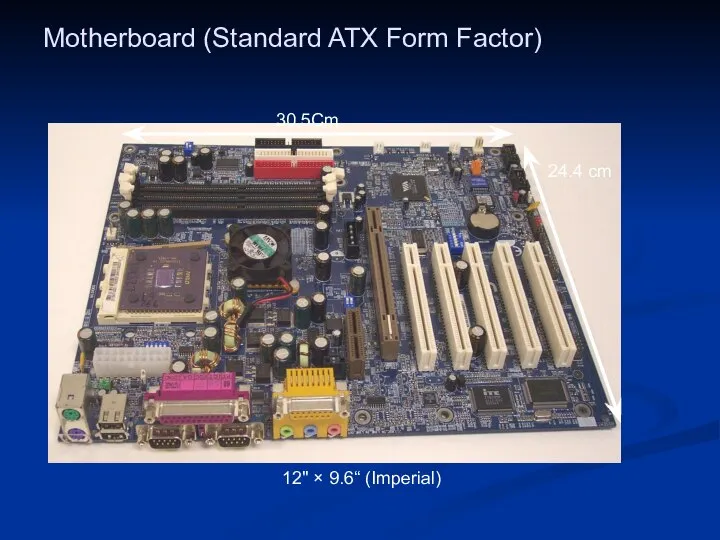
- 27. Motherboard (Standard ATX Form Factor) 12" × 9.6“ (Imperial) 30.5Cm 24.4 cm
- 28. A. Processor (Intel & AMD)
- 29. B. North Bridge "North Bridge: The Intel term for the main portion of the motherboard chipset
- 30. I. South Bridge "South Bridge: The Intel term for the lower-speed component in the chipset that
- 31. C. USB Ports
- 32. D. PCI Slots (32 Bit)
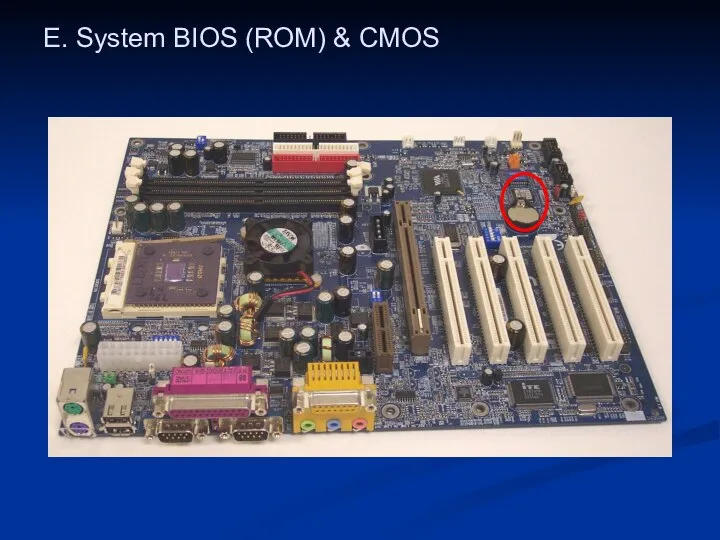
- 33. E. System BIOS (ROM) & CMOS
- 34. F. Memory (RAM)
- 35. G. Parallel Port (25 pin female D-plug)
- 36. H. CMOS Battery
- 37. J. Power Connector (24 Pin Molex) P1
- 38. K. IDE Connections (4 channels, 2 per slot)
- 39. L. ISA Slot (Legacy)
- 40. M. Serial Ports
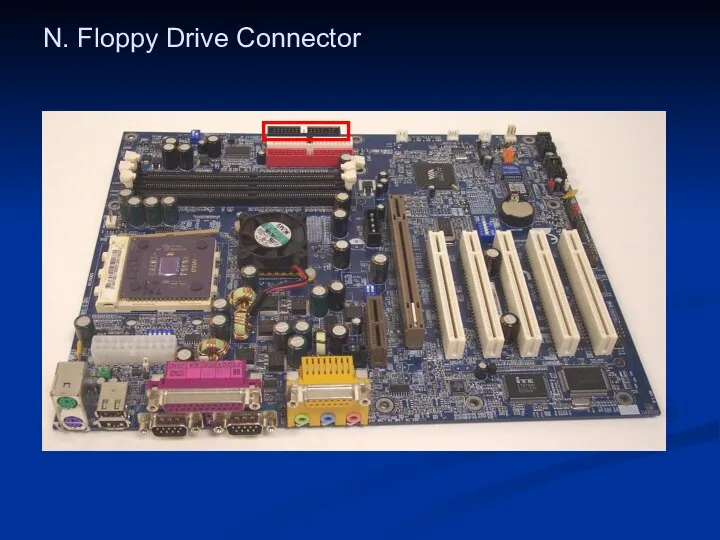
- 41. N. Floppy Drive Connector
- 42. O. PS/2 Connections for mouse/keyboard
- 43. P. AGP Slot (32 bit)
- 44. P. AMR Slot
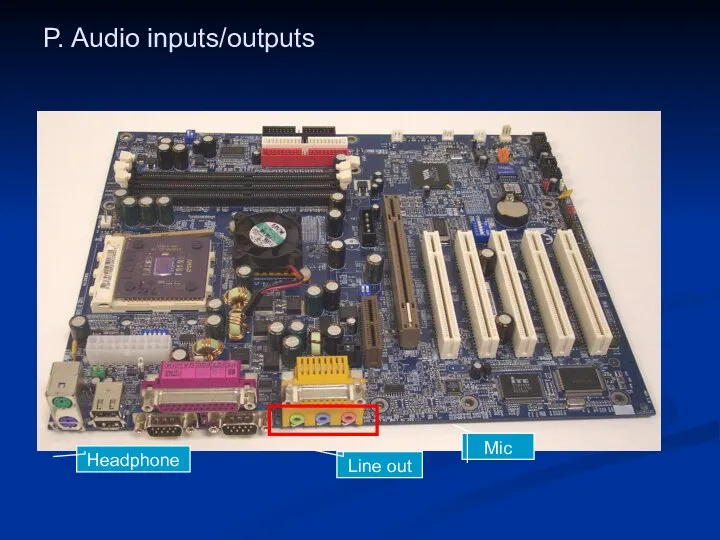
- 45. P. Audio inputs/outputs Mic Headphone Line out
- 46. P. VGA (15 Pin D-Plug Female)
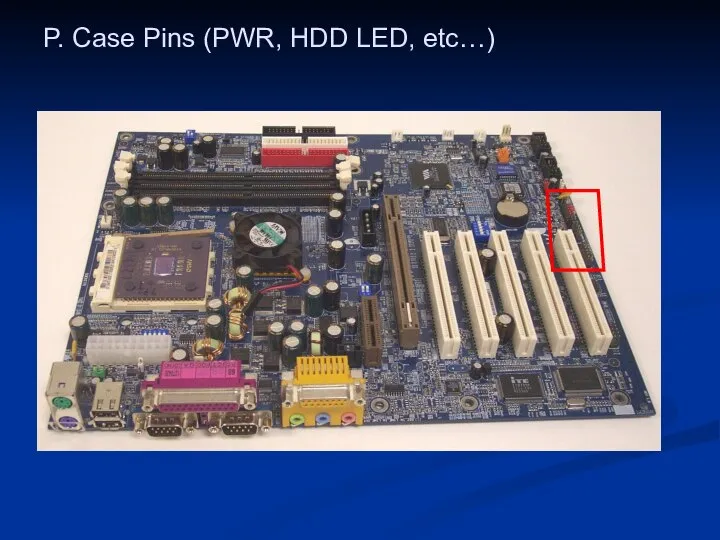
- 47. P. Case Pins (PWR, HDD LED, etc…)
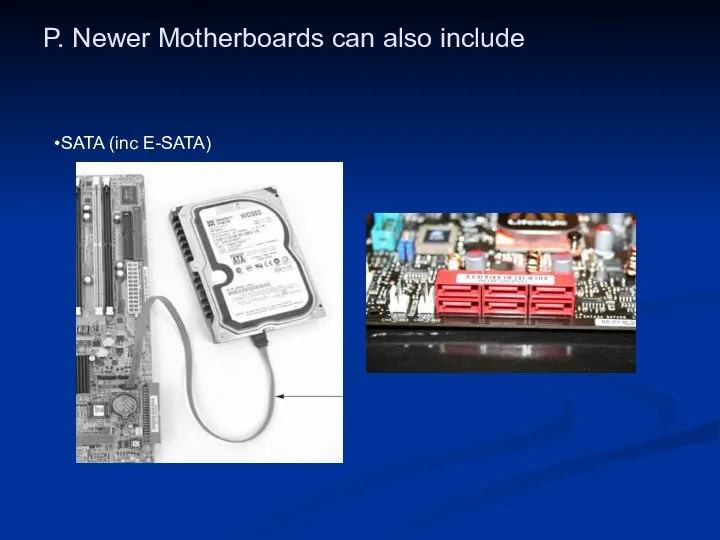
- 48. P. Newer Motherboards can also include SATA (inc E-SATA)
- 49. P. Newer Motherboards can also include Passive Cooling
- 50. P. Newer Motherboards can also include Water cooled systems
- 51. P. Newer Motherboards can also include DDR3 (green slots)
- 52. Video Summary Form Factors Installing and configuring motherboards
- 53. Specialised Cards – Graphics Card What is it? A video card is a hardware component whose
- 54. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) A GPU is a dedicated graphics processor optimized for floating point calculations
- 55. Video BIOS This contains the basic program that governs the video card’s operations and provides the
- 56. Video Memory While a Video Card will have its own video memory called video RAM The
- 57. Outputs There are the connection systems which connects the displays with the video card Some different
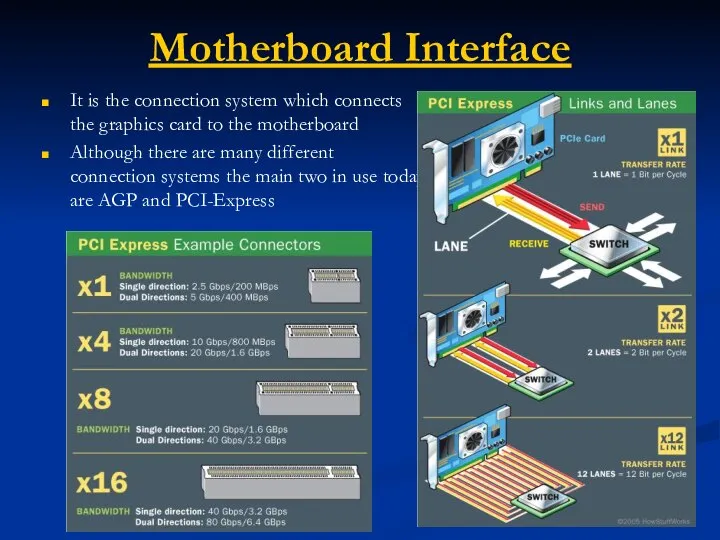
- 58. Motherboard Interface It is the connection system which connects the graphics card to the motherboard Although
- 59. Cooling Device Video cards may use a lot of electricity which is converted into heat If
- 60. Power Demand Fast Video Cards consume a great deal of power Power demands of GPU are
- 61. Advantages of Graphics Cards Anti-Aliasing: This is a technique used to counter distortion caused by aliasing
- 62. Without Graphics Card Distorted Edges.. No anti-Aliasing No reflection detail (No Fresnel Effect) Poor level of
- 63. With Graphics Card Smooth Motion Blur & Depth of field Better level of detail Car Reflection
- 64. Objectives Plenary Understand static electricity List reasons why we take precautions from static electricity State precautions
- 66. Скачать презентацию
























































 Электричество в быту
Электричество в быту Смесительные и детекторные диоды
Смесительные и детекторные диоды Презентация Интеграционные процессы в рамках СНГ. Таможенный союз Белоруссии, России и Казахстана. Формирование Единого экономич
Презентация Интеграционные процессы в рамках СНГ. Таможенный союз Белоруссии, России и Казахстана. Формирование Единого экономич Идентификация минеральных вод с использованием импедансометрического «электронного языка»
Идентификация минеральных вод с использованием импедансометрического «электронного языка» Телемаркетинг Внедрение активных продаж и...
Телемаркетинг Внедрение активных продаж и...  Организация системы внеурочной, внешкольной деятельности по продвижению физической культуры и спорта
Организация системы внеурочной, внешкольной деятельности по продвижению физической культуры и спорта Le park Sofiivka a Ouman
Le park Sofiivka a Ouman Фестиваль исследовательских и творческих работ учащихся «Портфолио» «Дед Мороз шагает по планете» Выполнили: ученик
Фестиваль исследовательских и творческих работ учащихся «Портфолио» «Дед Мороз шагает по планете» Выполнили: ученик Презентация Документы по платежно-банковским операциям
Презентация Документы по платежно-банковским операциям Презентация "Культура античности.Эгейское искусство" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Культура античности.Эгейское искусство" - скачать презентации по МХК Интеллектуальные информационные системы. Искусственный интеллект
Интеллектуальные информационные системы. Искусственный интеллект Державна служба України (регіональний аспект)
Державна служба України (регіональний аспект) Тема 10. Коммуникации в системе управления фирмой
Тема 10. Коммуникации в системе управления фирмой  Биография Мартина Лютера
Биография Мартина Лютера Адаптация первоклассников
Адаптация первоклассников Место и роль закона в системе общего права
Место и роль закона в системе общего права Palabras en español
Palabras en español Справедливость как философская проблема Горбатов В.В. НИУ ВШЭ, 2012
Справедливость как философская проблема Горбатов В.В. НИУ ВШЭ, 2012 Вегетативная нервная система: Симпатическая и Парасимпатическая нервная система
Вегетативная нервная система: Симпатическая и Парасимпатическая нервная система Машины переменного тока. Синхронные машины (СМ). Параллельная работа СГ с сетью бесконечно большой мощности
Машины переменного тока. Синхронные машины (СМ). Параллельная работа СГ с сетью бесконечно большой мощности Презентация "Соответствие проектов команд критерию судейства SIFE" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Соответствие проектов команд критерию судейства SIFE" - скачать презентации по Экономике Массивы в Паскале. Одномерные массивы. (9 класс)
Массивы в Паскале. Одномерные массивы. (9 класс) V- X Олимпийские игры
V- X Олимпийские игры Классифиция и виды обоев
Классифиция и виды обоев Спортивная семья
Спортивная семья Жұдырықшалы механизмдер
Жұдырықшалы механизмдер Аппаратная поддержка порядка операций обращения в память в системе на кристалле «Эльбрус-2S»
Аппаратная поддержка порядка операций обращения в память в системе на кристалле «Эльбрус-2S» Індивідуальне завдання
Індивідуальне завдання