Содержание
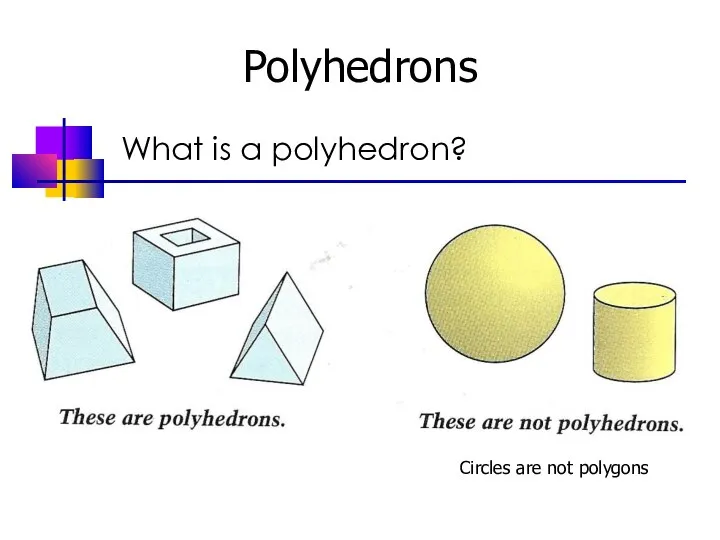
- 2. Polyhedrons What is a polyhedron? Circles are not polygons
- 3. Identifying Polyhedrons A polyhedron is a solid that is bounded by polygons, called faces, that enclose
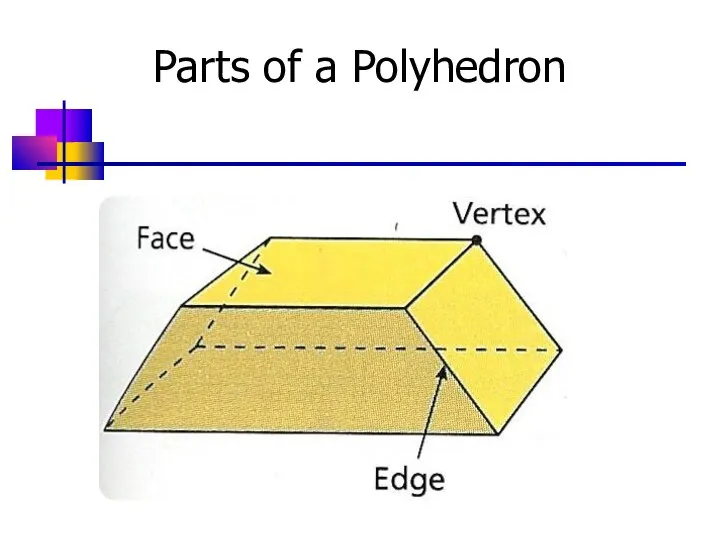
- 4. Parts of a Polyhedron
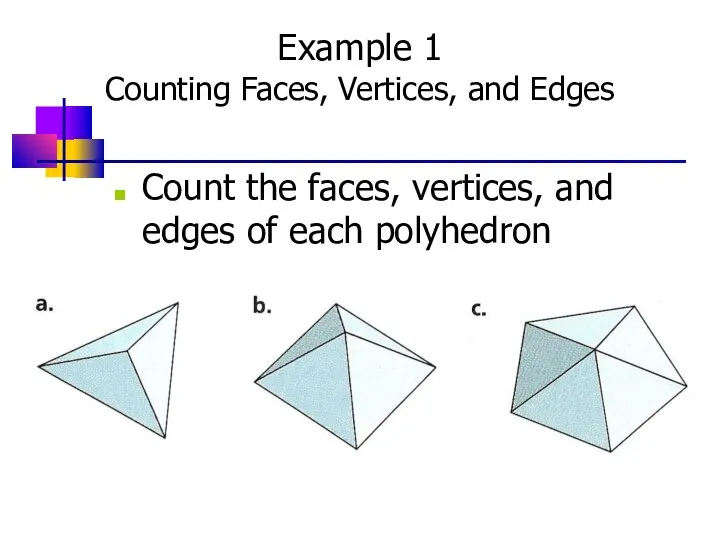
- 5. Example 1 Counting Faces, Vertices, and Edges Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron
- 6. Example 1A Counting Faces Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 4 faces
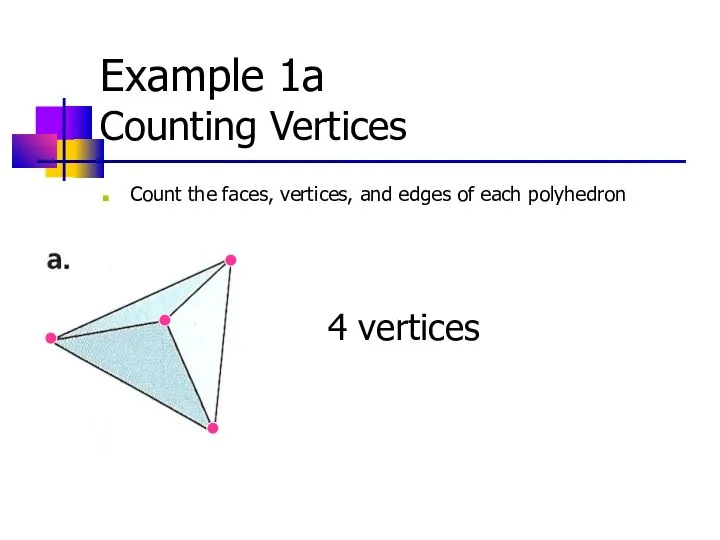
- 7. Example 1a Counting Vertices Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 4 vertices
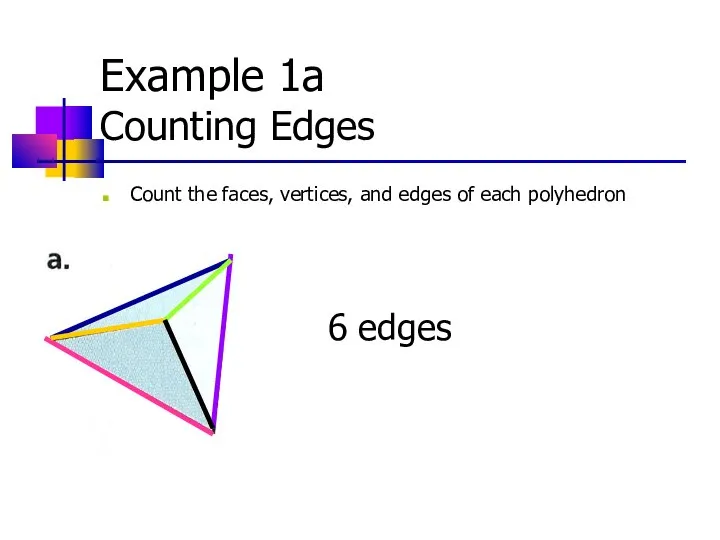
- 8. Example 1a Counting Edges Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 6 edges
- 9. Example 1b Counting Faces Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 5 faces
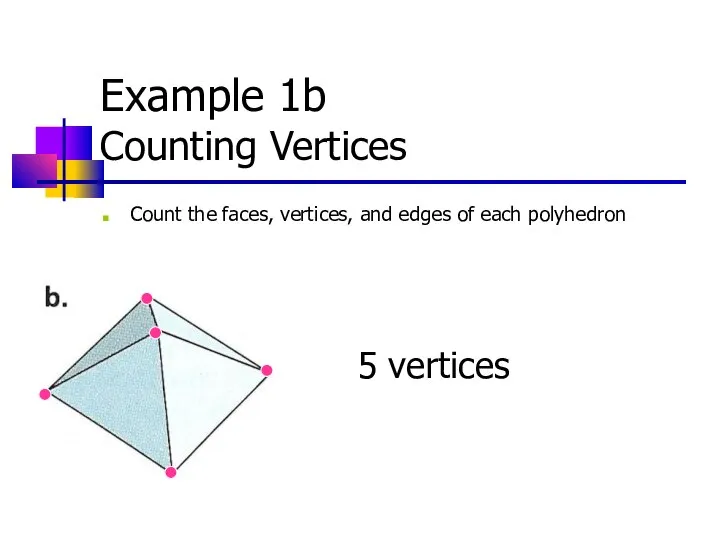
- 10. Example 1b Counting Vertices Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 5 vertices
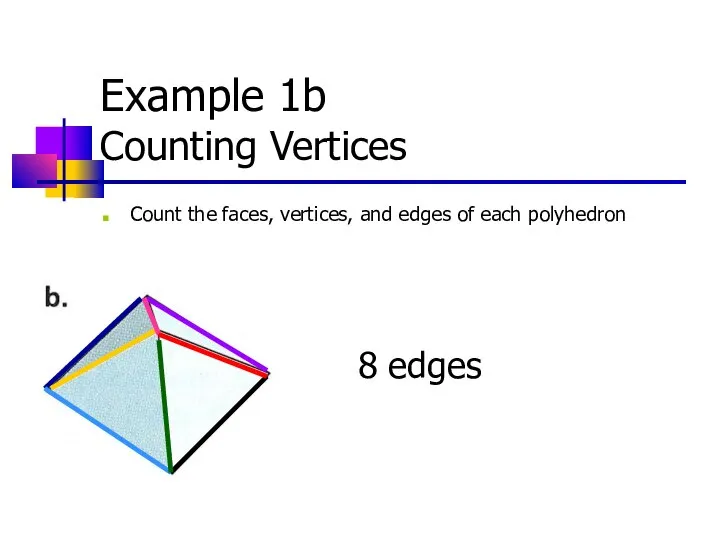
- 11. Example 1b Counting Vertices Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 8 edges
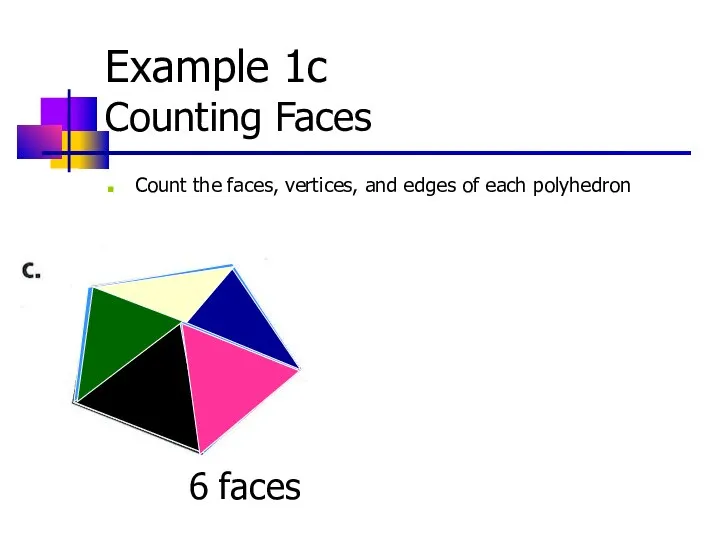
- 12. Example 1c Counting Faces Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 6 faces
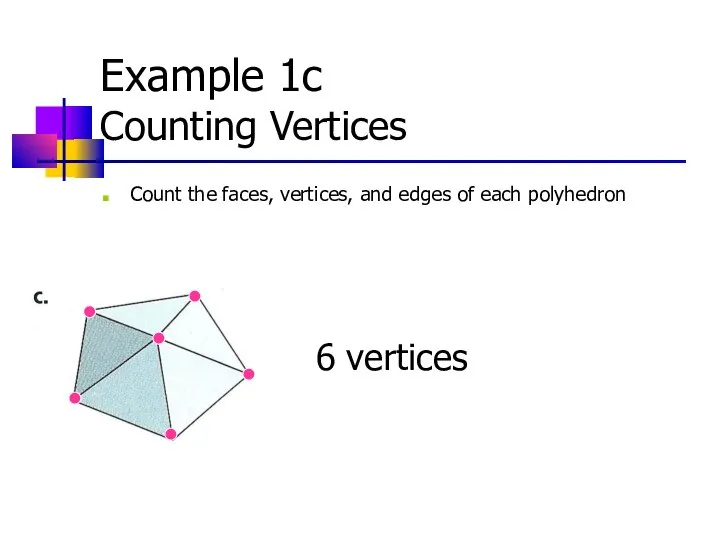
- 13. Example 1c Counting Vertices Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 6 vertices
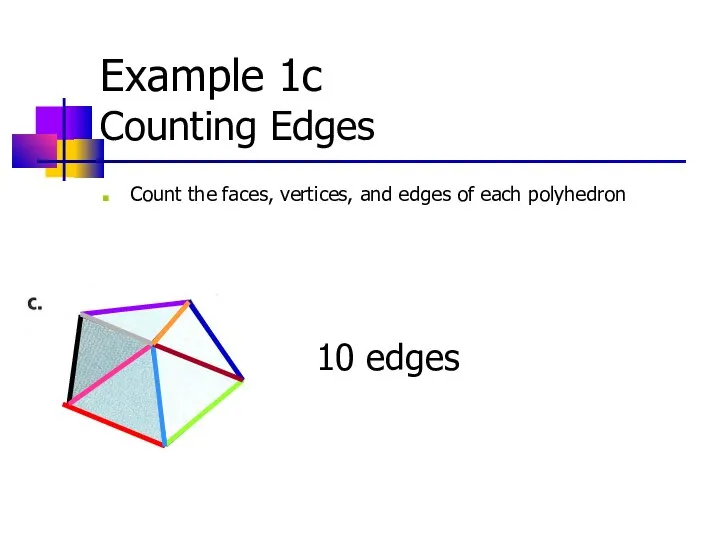
- 14. Example 1c Counting Edges Count the faces, vertices, and edges of each polyhedron 10 edges
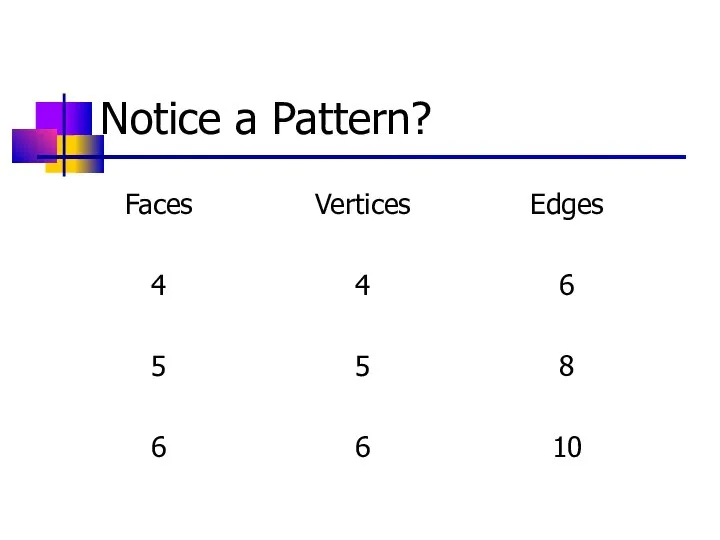
- 15. Notice a Pattern?
- 16. Theorem 12.1 Euler's Theorem The number of faces (F), vertices (V), and edges (E) of a
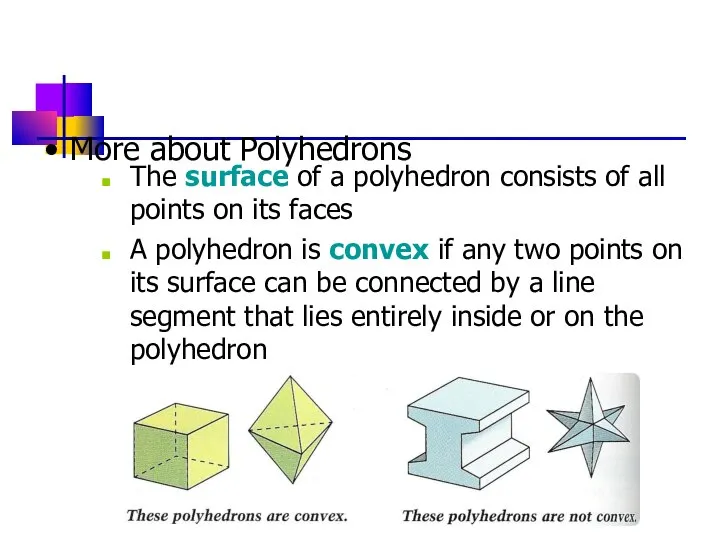
- 17. The surface of a polyhedron consists of all points on its faces A polyhedron is convex
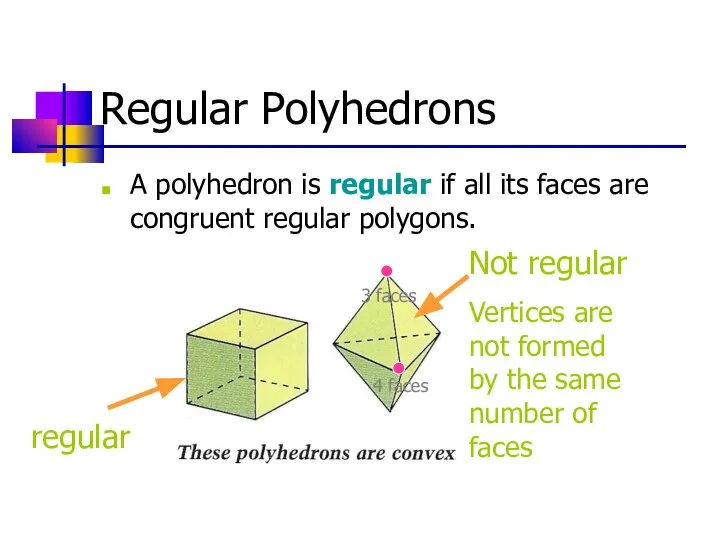
- 18. Regular Polyhedrons A polyhedron is regular if all its faces are congruent regular polygons. regular Not
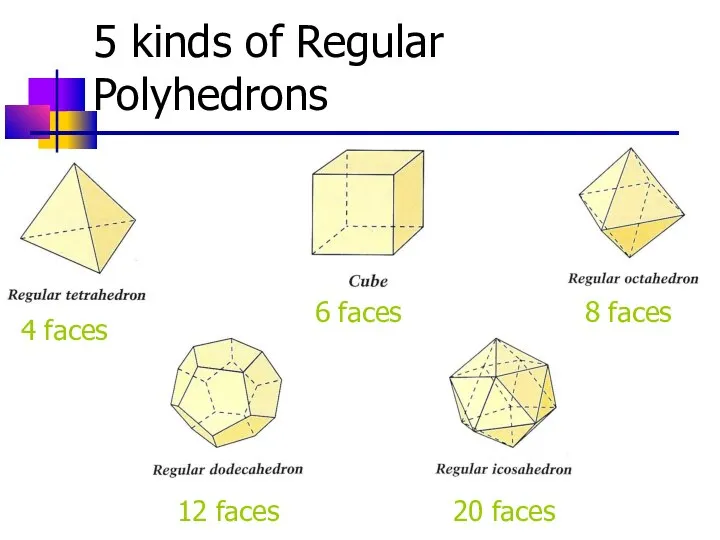
- 19. 5 kinds of Regular Polyhedrons 4 faces 6 faces 8 faces 12 faces 20 faces
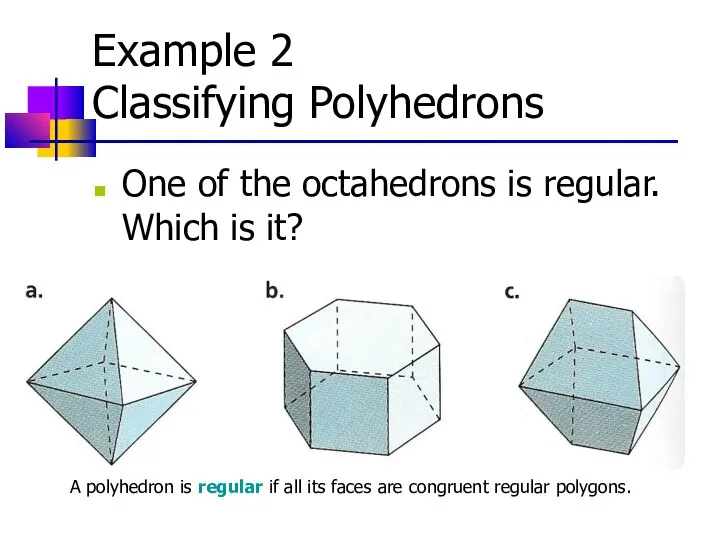
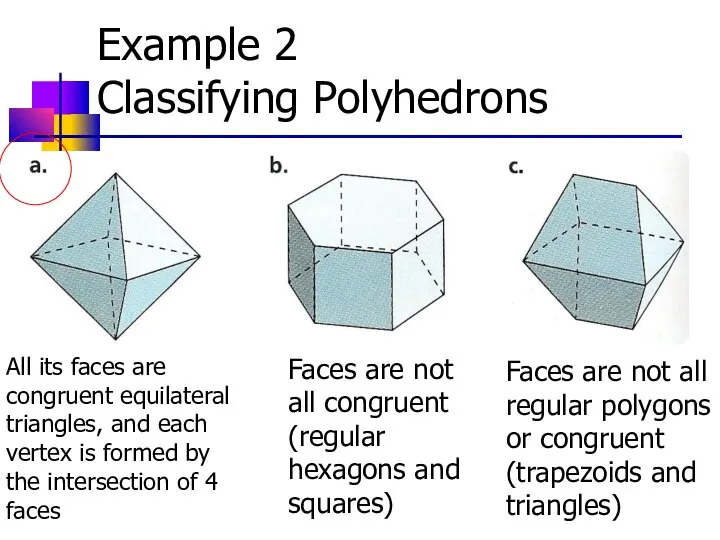
- 20. Example 2 Classifying Polyhedrons One of the octahedrons is regular. Which is it? A polyhedron is
- 21. Example 2 Classifying Polyhedrons All its faces are congruent equilateral triangles, and each vertex is formed
- 22. Example 3 Counting the Vertices of a Soccer Ball A soccer ball has 32 faces: 20
- 23. Example 3 Counting the Vertices of a Soccer Ball A soccer ball has 32 faces: 20
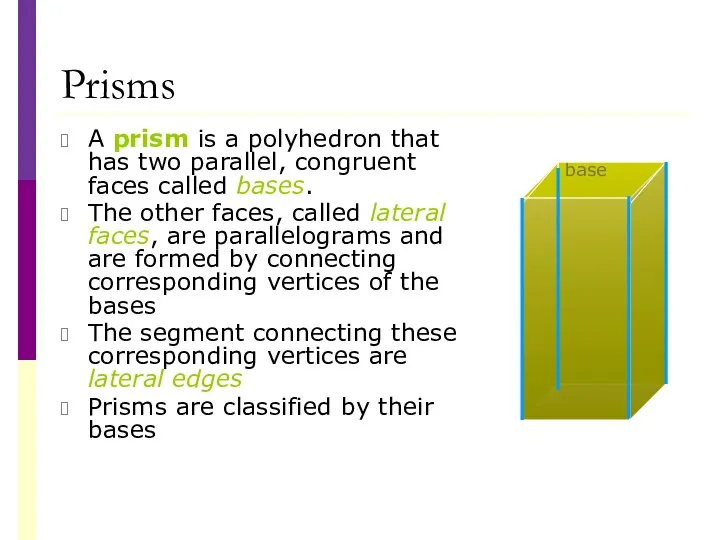
- 24. Prisms A prism is a polyhedron that has two parallel, congruent faces called bases. The other
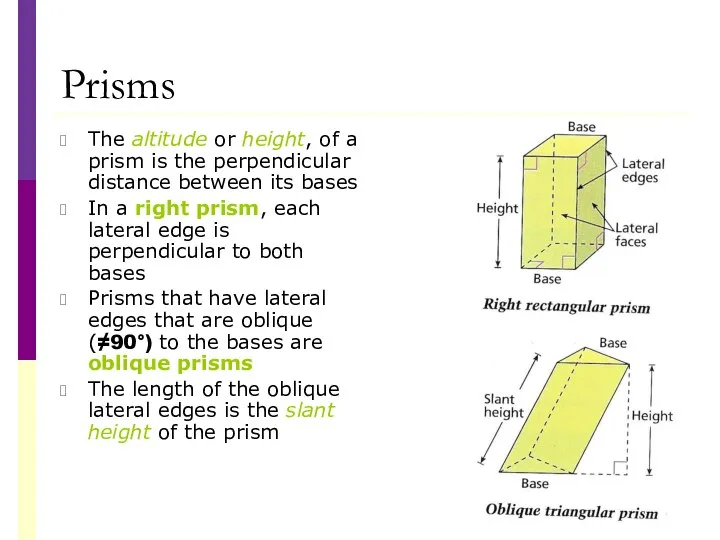
- 25. Prisms The altitude or height, of a prism is the perpendicular distance between its bases In
- 26. Surface Area of a Prism The surface area of a polyhedron is the sum of the
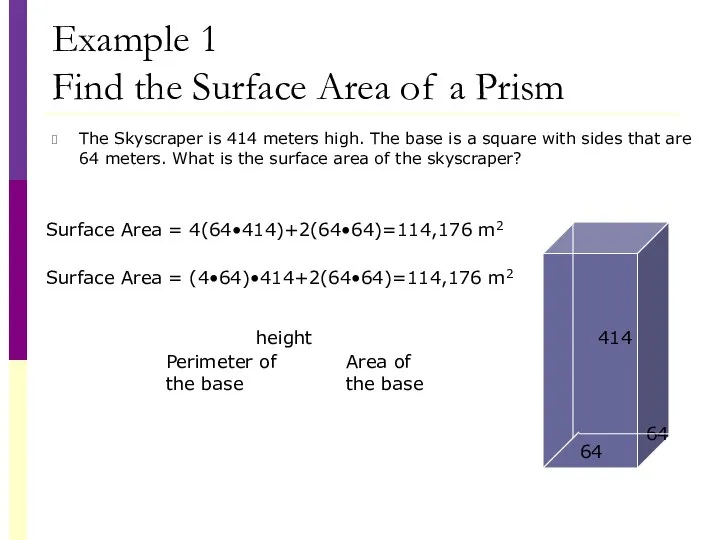
- 27. Example 1 Find the Surface Area of a Prism The Skyscraper is 414 meters high. The
- 28. Example 1 Find the Surface Area of a Prism The Skyscraper is 414 meters high. The
- 29. Example 1 Find the Surface Area of a Prism The Skyscraper is 414 meters high. The
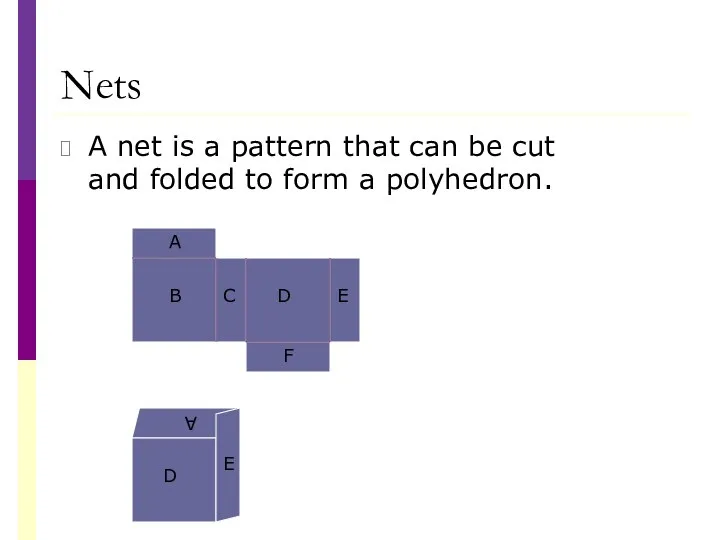
- 30. Nets A net is a pattern that can be cut and folded to form a polyhedron.
- 31. Surface Area of a Right Prism The surface area, S, of a right prism is S
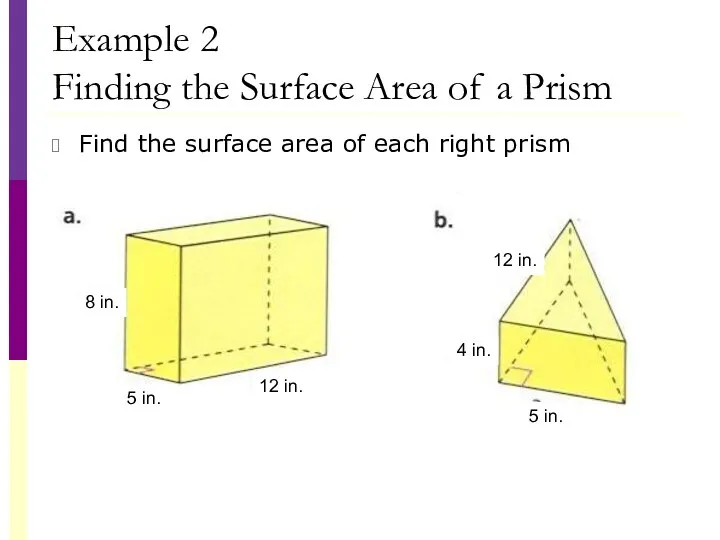
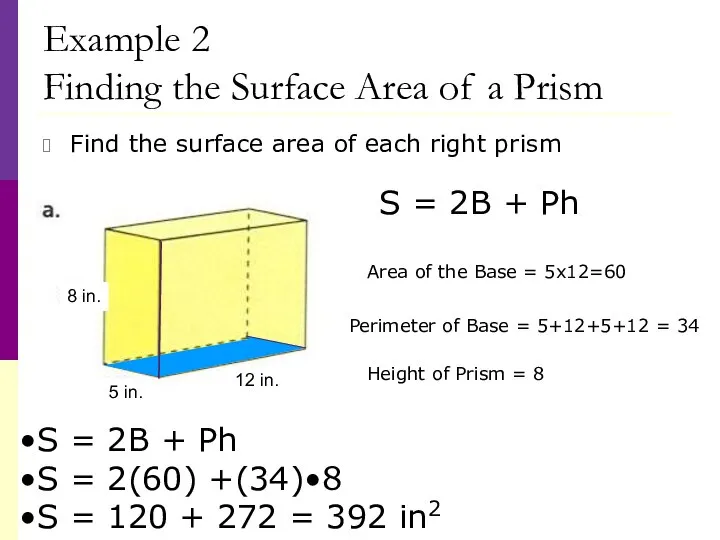
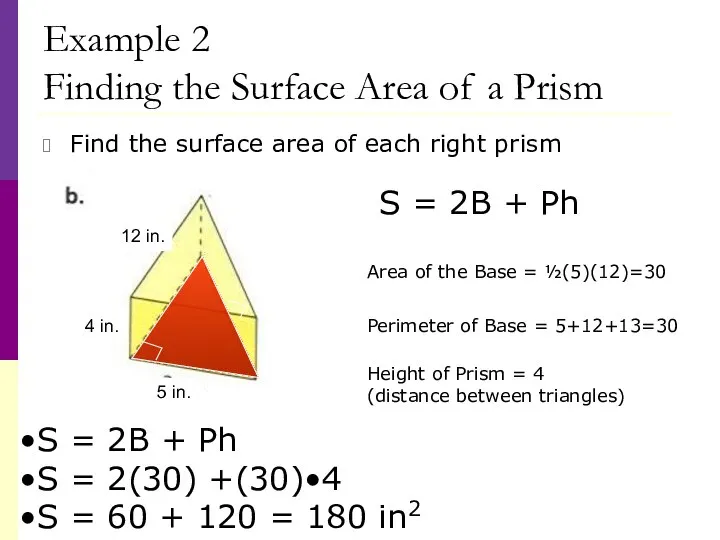
- 32. Example 2 Finding the Surface Area of a Prism Find the surface area of each right
- 33. Example 2 Finding the Surface Area of a Prism Find the surface area of each right
- 34. Example 2 Finding the Surface Area of a Prism Find the surface area of each right
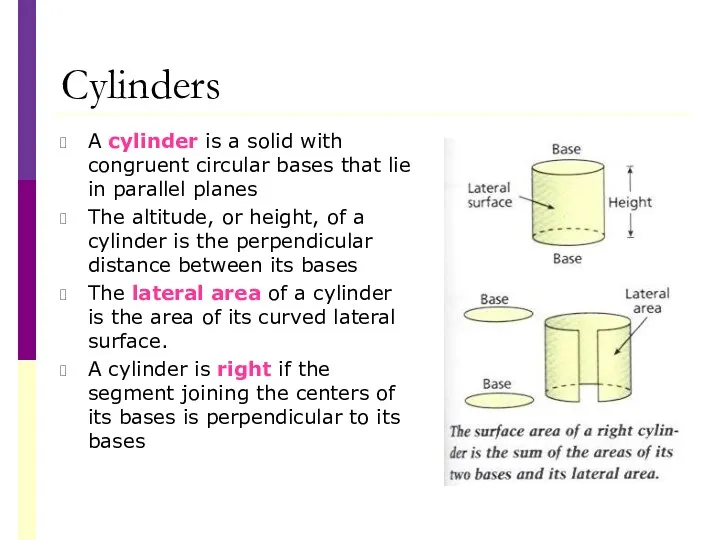
- 35. Cylinders A cylinder is a solid with congruent circular bases that lie in parallel planes The
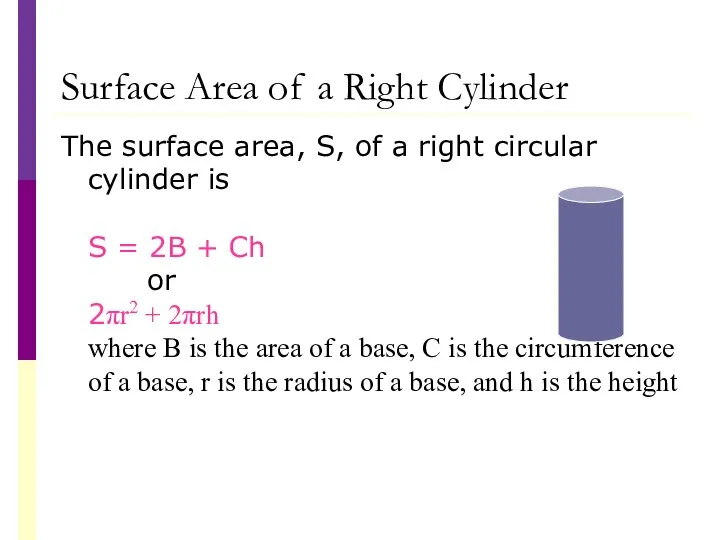
- 36. Surface Area of a Right Cylinder The surface area, S, of a right circular cylinder is
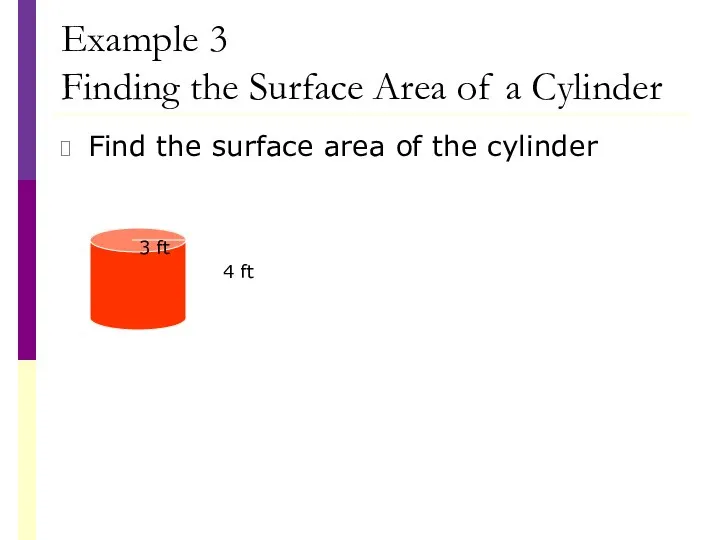
- 37. Example 3 Finding the Surface Area of a Cylinder Find the surface area of the cylinder
- 38. Example 3 Finding the Surface Area of a Cylinder Find the surface area of the cylinder
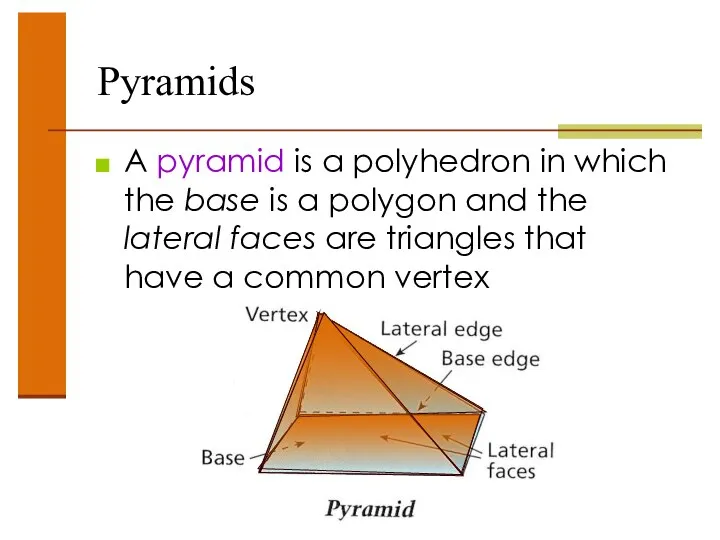
- 39. Pyramids A pyramid is a polyhedron in which the base is a polygon and the lateral
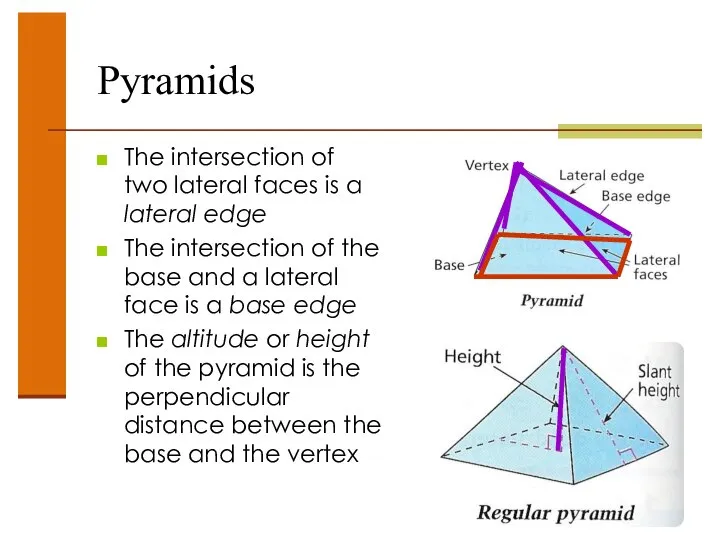
- 40. Pyramids The intersection of two lateral faces is a lateral edge The intersection of the base
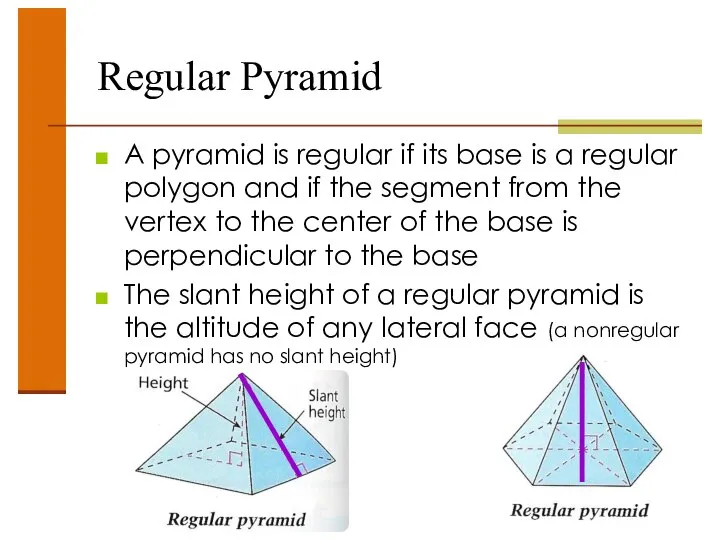
- 41. Regular Pyramid A pyramid is regular if its base is a regular polygon and if the
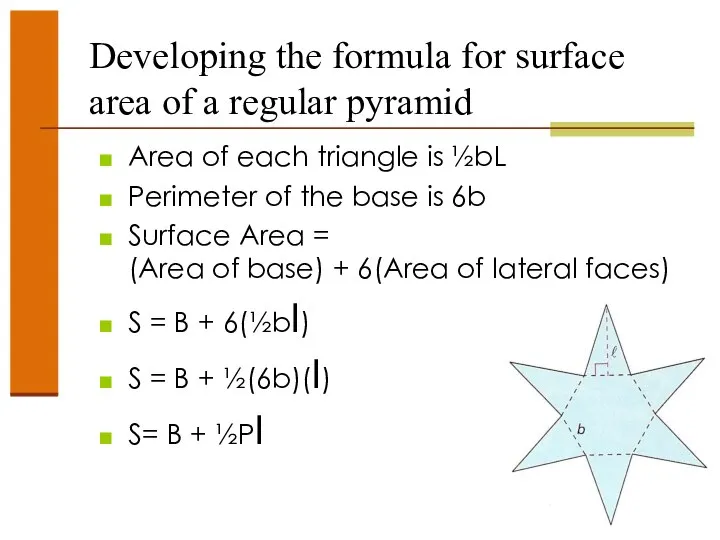
- 42. Developing the formula for surface area of a regular pyramid Area of each triangle is ½bL
- 43. Surface Area of a Regular Pyramid The surface area, S, of a regular pyramid is S
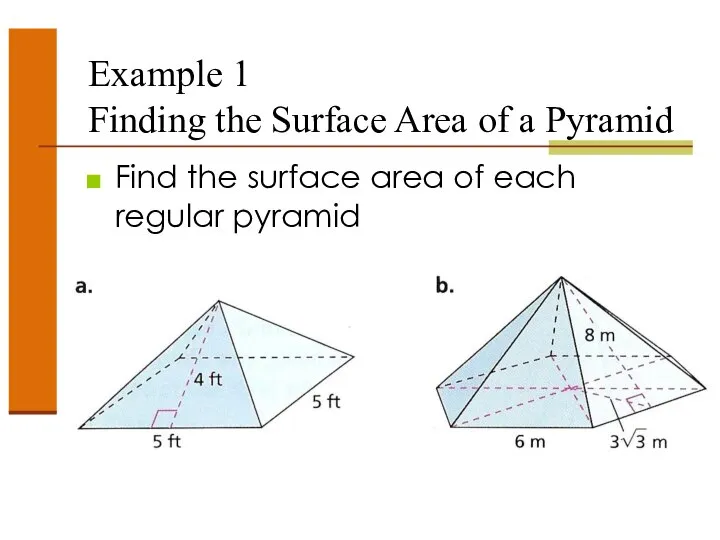
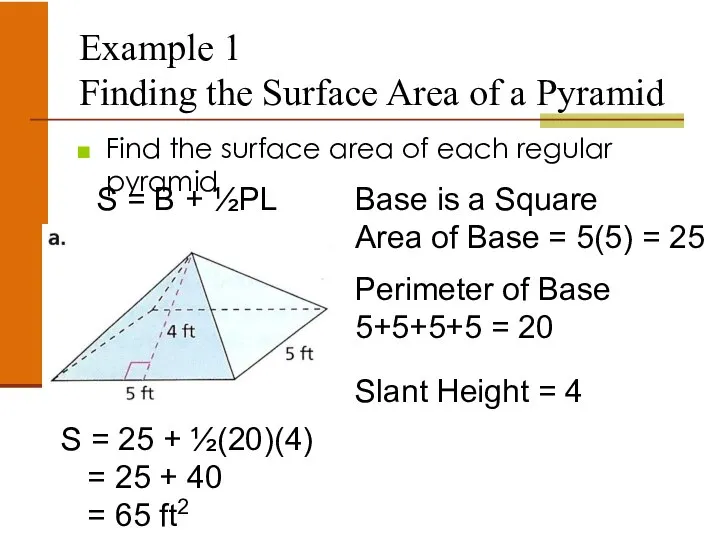
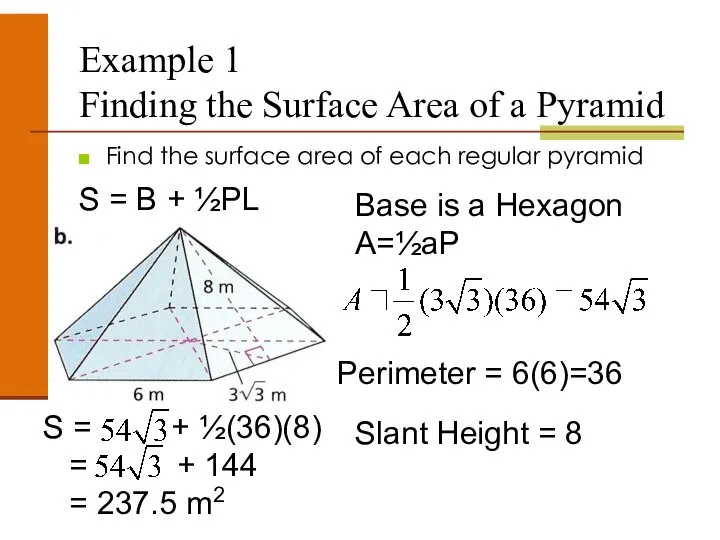
- 44. Example 1 Finding the Surface Area of a Pyramid Find the surface area of each regular
- 45. Example 1 Finding the Surface Area of a Pyramid Find the surface area of each regular
- 46. Example 1 Finding the Surface Area of a Pyramid Find the surface area of each regular
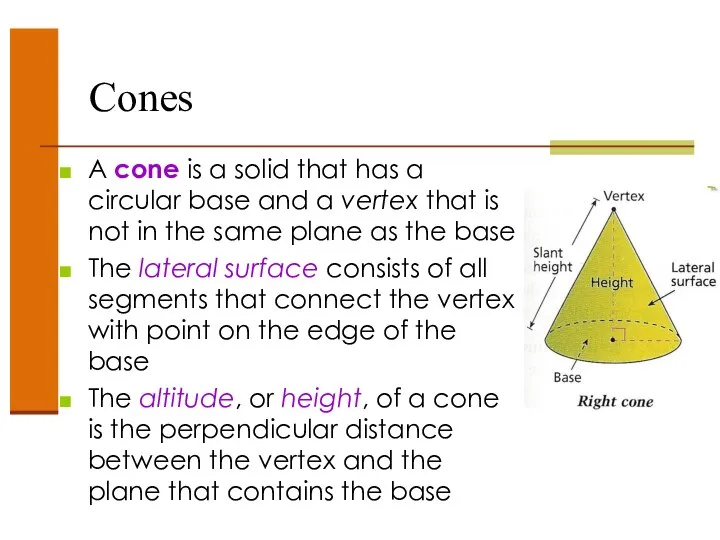
- 47. Cones A cone is a solid that has a circular base and a vertex that is
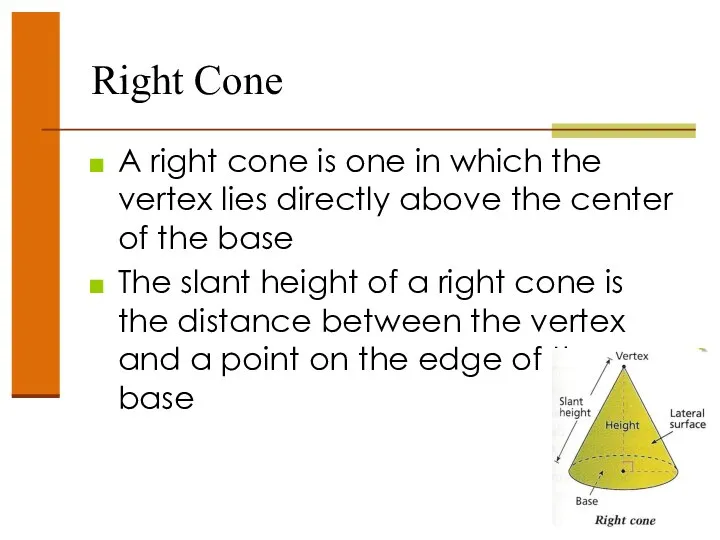
- 48. Right Cone A right cone is one in which the vertex lies directly above the center
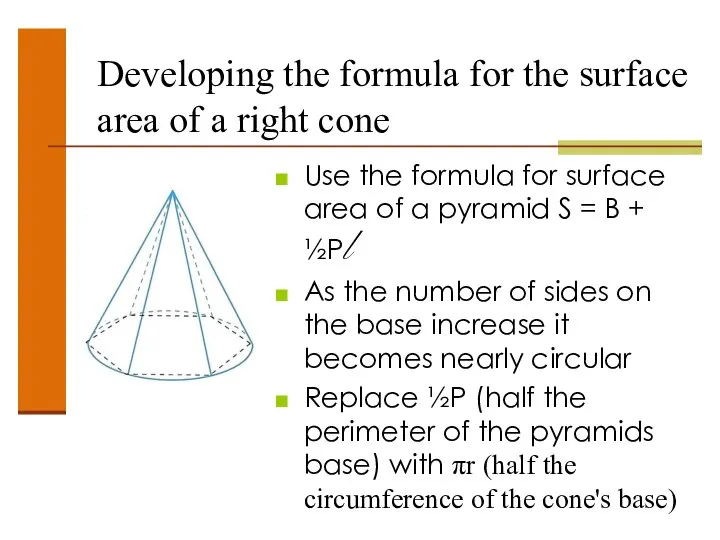
- 49. Developing the formula for the surface area of a right cone Use the formula for surface
- 50. Surface Area of a Right Cone The surface area, S, of a right cone is S
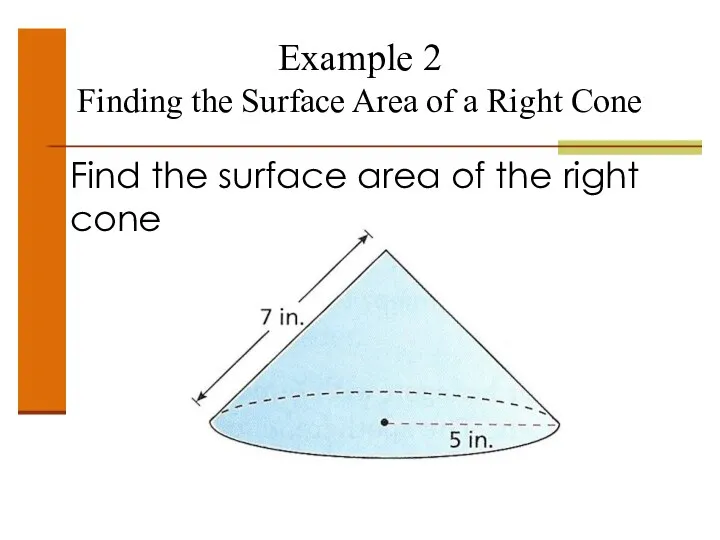
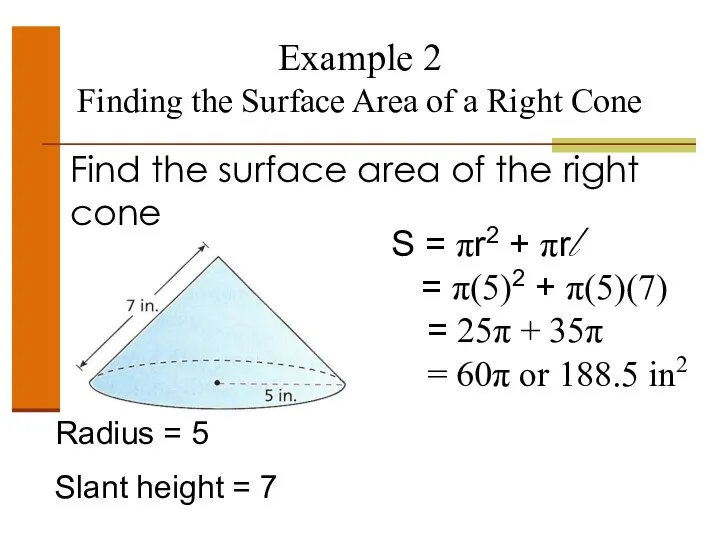
- 51. Example 2 Finding the Surface Area of a Right Cone Find the surface area of the
- 52. Example 2 Finding the Surface Area of a Right Cone Find the surface area of the
- 53. Volume formulas The Volume, V, of a prism is V = Bh The Volume, V, of
- 54. Volume The volume of a polyhedron is the number of cubic units contained in its interior
- 55. Postulates All the formulas for the volumes of polyhedrons are based on the following three postulates
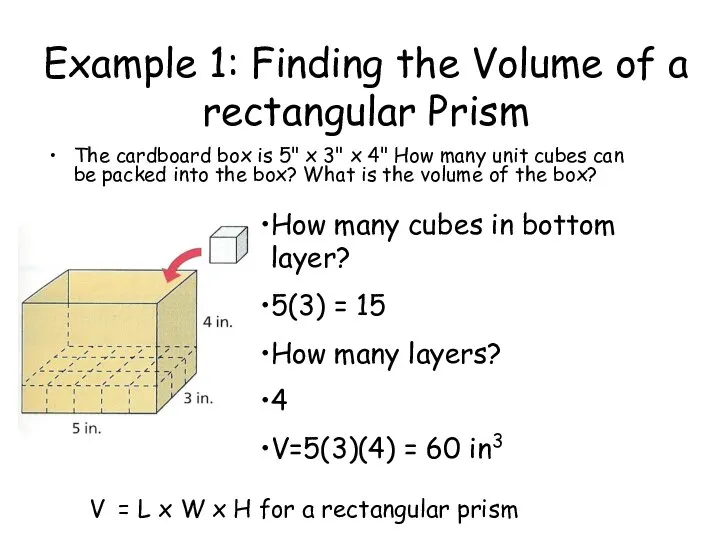
- 56. Example 1: Finding the Volume of a Rectangular Prism The cardboard box is 5" x 3"
- 57. Example 1: Finding the Volume of a rectangular Prism The cardboard box is 5" x 3"
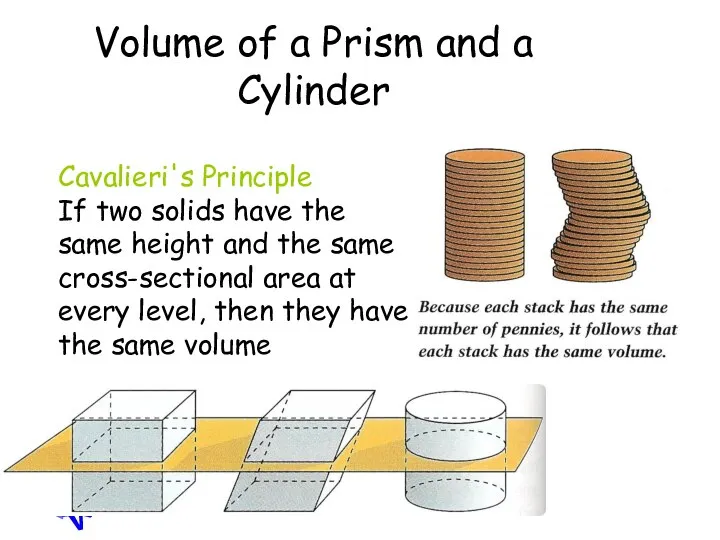
- 58. Volume of a Prism and a Cylinder Cavalieri's Principle If two solids have the same height
- 59. Volume of a Prism The Volume, V, of a prism is V = Bh where B
- 60. Volume of a Cylinder The volume, V, of a cylinder is V=Bh or V = πr2h
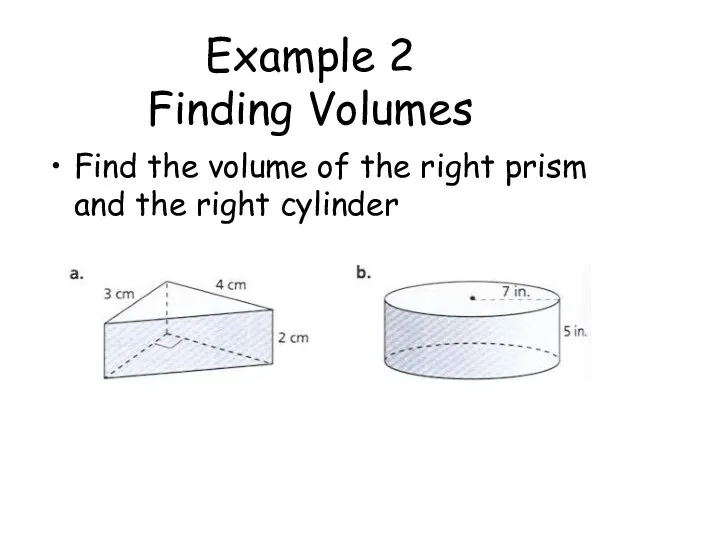
- 61. Example 2 Finding Volumes Find the volume of the right prism and the right cylinder
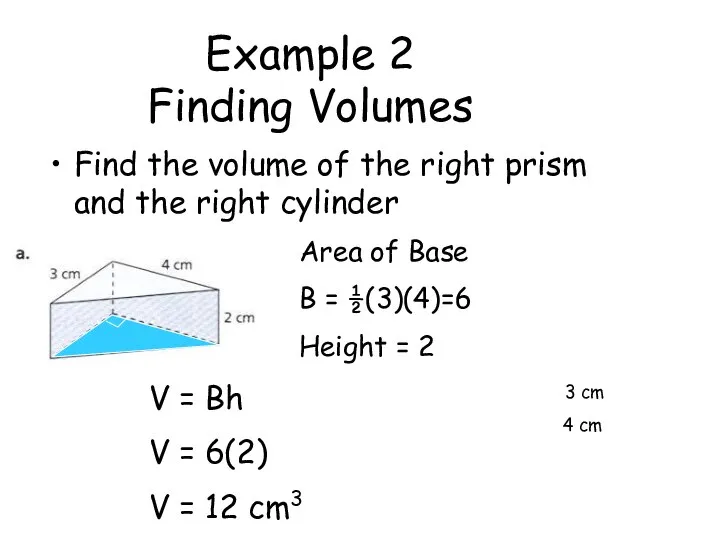
- 62. Example 2 Finding Volumes Find the volume of the right prism and the right cylinder 3
- 63. Example 2 Finding Volumes Find the volume of the right prism and the right cylinder Area
- 64. Example 3 Estimating the Cost of Moving You are moving from Newark, New Jersey, to Golden,
- 66. Скачать презентацию




















 Інтер'єрі в стилі Бароко
Інтер'єрі в стилі Бароко Презентация "Экономические школы" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Экономические школы" - скачать презентации по Экономике Подготовка Чтение ЗАНЯТИЕ 3
Подготовка Чтение ЗАНЯТИЕ 3 Дорожная безопасность Материалы к занятиям по ПДД для учащихся 3 класса
Дорожная безопасность Материалы к занятиям по ПДД для учащихся 3 класса Устройства ввода информации. Сканеры
Устройства ввода информации. Сканеры Методология системного анализа
Методология системного анализа Противодействие необоснованным требованиям, подтвержденным судебным актом. Дела о банкротстве
Противодействие необоснованным требованиям, подтвержденным судебным актом. Дела о банкротстве Автоматическая коробка передач
Автоматическая коробка передач Алгоритм RSA
Алгоритм RSA Выполнила: Жулей А (3рсш-ф) Проверила : Ахметова Ш.Ф Риба
Выполнила: Жулей А (3рсш-ф) Проверила : Ахметова Ш.Ф Риба General information. Service bulletint LG
General information. Service bulletint LG Реализация и толкование права
Реализация и толкование права Контроль качества строительной продукции. (Лекция 13)
Контроль качества строительной продукции. (Лекция 13) Синтез зубчатых передач
Синтез зубчатых передач Строительство межшкольного стадиона в г. Нытва, Пермский край
Строительство межшкольного стадиона в г. Нытва, Пермский край Масиви. Створення консольних проектів у C#. (10 клас)
Масиви. Створення консольних проектів у C#. (10 клас) ekzamenatsionnye_bilety
ekzamenatsionnye_bilety Государственная (итоговая) аттестация в 9 классе Обучающиеся, завершающие освоение основных общеобразовательных программ осно
Государственная (итоговая) аттестация в 9 классе Обучающиеся, завершающие освоение основных общеобразовательных программ осно Презентация Реформы Александра 1
Презентация Реформы Александра 1 Рекомендации Arber Women 05.09.2019 (1)
Рекомендации Arber Women 05.09.2019 (1)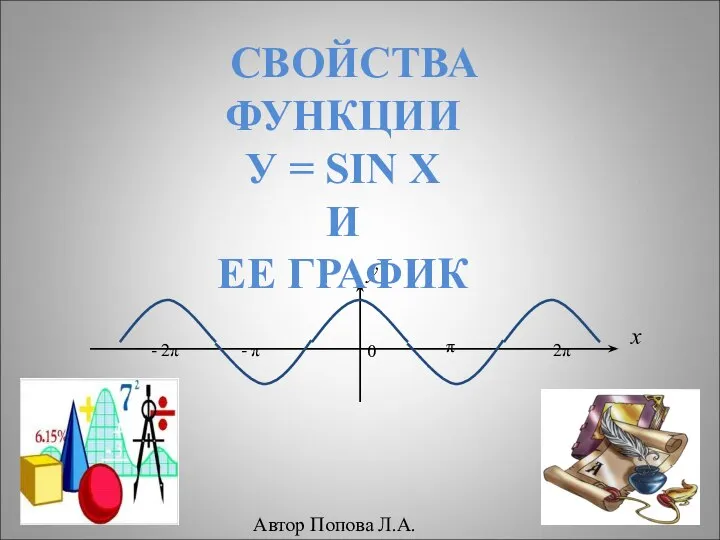 Свойства функции У = sin x и ее график - презентация по Алгебре_
Свойства функции У = sin x и ее график - презентация по Алгебре_ Разработка функционального контроля восьмиразрядных микроконтроллеров
Разработка функционального контроля восьмиразрядных микроконтроллеров Гигиеническое нормирование химических веществ
Гигиеническое нормирование химических веществ Продвижение с помощью событий Киселев Артем
Продвижение с помощью событий Киселев Артем Готические соборы
Готические соборы Социальный центр Святителя Тихона
Социальный центр Святителя Тихона Обыкновенное чудо – люди России
Обыкновенное чудо – люди России Системные характеристики, функции, структура в СМИ. (Тема 3)
Системные характеристики, функции, структура в СМИ. (Тема 3)