Содержание
- 2. EXPANDING SIMPLE SENTENCES WITH VERBAL PHRASES Verbal phrase consists of a verbal and any objects or
- 3. GERUND PHRASES A gerund phrase consists of a gerund and any objects and/or modifiers. A gerund
- 4. GERUND PHRASES Example: Riding my bike is enjoyable in the evening. Gerund: riding Direct object: my
- 5. GERUND PHRASES I welcomed beginning a new life. Gerund is: Beginning I began opening the window.
- 6. INFINITIVE PHRASES An infinitive phrase starts with an infinitive (to), which is followed by any objects,
- 7. INFINITIVE PHRASES Examples: To tour Australia slowly is my dream. Infinitive is to tour (subject). Object:
- 8. INFINITIVE PHRASES Object is my exams (the direct object of the infinitive). Modifier is with good
- 9. PARTICIPIAL PHRASES A participial phrase consists of either a past or a present participle and any
- 10. PARTICIPIAL PHRASES Object: the ducks (direct object of the participle) Modifier: keenly (an adverb modifying the
- 11. EXPANDING SIMPLE SENTENCES WITH APPOSITIVES Appositives rename noun phrases and are usually placed beside what they
- 12. APPOSITIVES A noun phrase that adds more information about a noun or pronoun. Use a comma
- 13. USING MODIFIERS A misplaced modifier appears to describe the wrong word or phrase, or it is
- 14. MISPLACED MODIFIERS Misplaced modifier: A word or phrase placed too far from the word or phrase
- 15. A DANGLING MODIFIER Rule: Avoid dangling modifiers. Method 1: Fix a dangling modifier by making it
- 16. EXAMPLES Dangling: Paddling down the river, the canoe overturned. Correction # 1: As we paddled down
- 17. APPOSITIVES Appositives can also rename nouns phrases that are not the subject. We waited in our
- 18. EXPANDING SIMPLE SENTENCES WITH COMPOUND CONSTRUCTIONS Compounds may be joined in three ways: with commas, with
- 19. COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS Examples: Do you want to study math or English? The coordinating conjunction “or” is
- 20. COORDINATING CONJUNCTIONS I got up and left the room. The conjunction “and” is connecting the words.
- 22. Скачать презентацию



















 Halloween lesson plan Form 3-4
Halloween lesson plan Form 3-4 Plurals
Plurals How did the fall in love with each other
How did the fall in love with each other My visit to Turkey The project is made by Alisa Oleksyuk Surgut, Russia. School №13 Form 5-A Coordinator: LUDMILA ARNOLDOVNA LAPINA
My visit to Turkey The project is made by Alisa Oleksyuk Surgut, Russia. School №13 Form 5-A Coordinator: LUDMILA ARNOLDOVNA LAPINA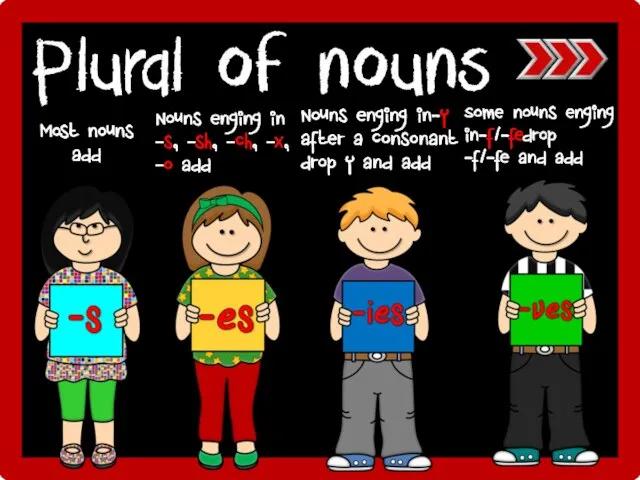 Plurals of nouns
Plurals of nouns Презентация к уроку английского языка "30 Seconds to Mars" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "30 Seconds to Mars" - скачать  урок для 2–го класу підготувала вчитель Городнянської школи І-ІІІ ст. №2 Бойко Надія Павлівна
урок для 2–го класу підготувала вчитель Городнянської школи І-ІІІ ст. №2 Бойко Надія Павлівна  Goldilocks. Philip
Goldilocks. Philip ЖИЗНЬ М.В. ЛОМОНОСОВА В ГЕРМАНИИ
ЖИЗНЬ М.В. ЛОМОНОСОВА В ГЕРМАНИИ  Тема «Пассивный залог» Форма проведения урока: викторина
Тема «Пассивный залог» Форма проведения урока: викторина The magic cat
The magic cat Englishnessing: a freedom vehicle of consciousness development
Englishnessing: a freedom vehicle of consciousness development Презентация к уроку английского языка "7 wonders of the world" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "7 wonders of the world" - скачать  Module 6
Module 6 Прослушай диалог и прочитай его
Прослушай диалог и прочитай его Презентация к уроку английского языка "Tyumen is the first Russian settlement in Siberia." - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Tyumen is the first Russian settlement in Siberia." - скачать бесплатно Letters and sounds
Letters and sounds Презентация к уроку английского языка "Pablo Picasso" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Pablo Picasso" - скачать бесплатно Презентация дополнительных платных услуг МБДОУ д/с №15 «Маячок» на 2013-2014 год
Презентация дополнительных платных услуг МБДОУ д/с №15 «Маячок» на 2013-2014 год What do we do with?
What do we do with? Стихотворение Р.Киплинга If Если
Стихотворение Р.Киплинга If Если Презентация Symbols of the USA
Презентация Symbols of the USA Can
Can Подготовка к контрольной работе по английскому языку
Подготовка к контрольной работе по английскому языку Презентация к уроку английского языка "Месяца и времена года" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Месяца и времена года" - скачать  Keep calm and use correct grammar
Keep calm and use correct grammar Extinct animals
Extinct animals Презентация к уроку английского языка "Russia’s state emblem is a double headed eagle" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Russia’s state emblem is a double headed eagle" - скачать