Содержание
- 2. Presentation Outline The Standard Audit Report Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act Conditions Requiring an Explanatory
- 3. I. The Standard Audit Report The Seven Parts of the Auditor’s Standard Report Five Conditions for
- 4. A. The Seven Parts of the Auditor’s Standard Report Report title – Must include the word
- 5. B. Five Conditions for the Standard Report All 4 of the basic financial statements are included.
- 6. II. Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act PCAOB Auditing Standard 2 The Time Period Covered The
- 7. A. PCAOB Auditing Standard 2 Section 404 requires the auditor of a public company to attest
- 8. B. The Time Period Covered Although the audit opinion on the financial statements addresses multiple reporting
- 9. C. The Audit Report The auditor may choose to issue separate reports or a combined report,
- 10. III. Conditions Requiring an Explanatory Paragraph or Modified Report Wording Lack of Consistency Going Concern Problem
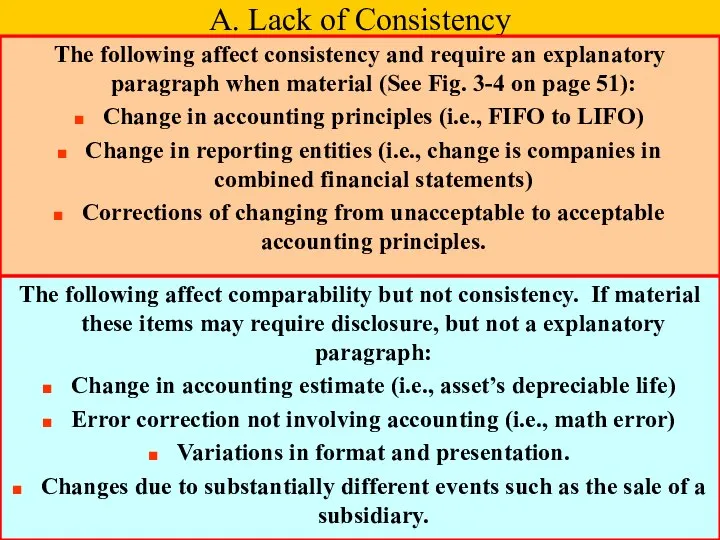
- 11. A. Lack of Consistency The following affect consistency and require an explanatory paragraph when material (See
- 12. B. Going Concern Problem SAS No. 59 requires auditor to evaluate going concern for a reasonable
- 13. C. Auditor Agrees with a Departure from GAAP An auditor may issue an unqualified opinion when
- 14. D. Emphasis of A Matter The auditor may add an explanatory paragraph to emphasize items such
- 15. E. Reports Involving Other Auditors Assume Responsibility If you accept responsibility for the other auditor’s work
- 16. IV. Other Opinion Possibilities Qualified Opinion Adverse Opinion Disclaimer of Opinion
- 17. A. Qualified Opinion Use the term “except for” in the opinion paragraph to exclude a specific
- 18. B. Adverse Opinion Financials as a whole are not fairly presented. Used when auditor feels that
- 19. C. Disclaimer of Opinion Auditor can not express an opinion. Disclaimer of opinion is appropriate when:
- 20. V. Scope Limitation Scope Limitation Defined Effect of Scope Limitation on Audit Report – Qualified Opinion
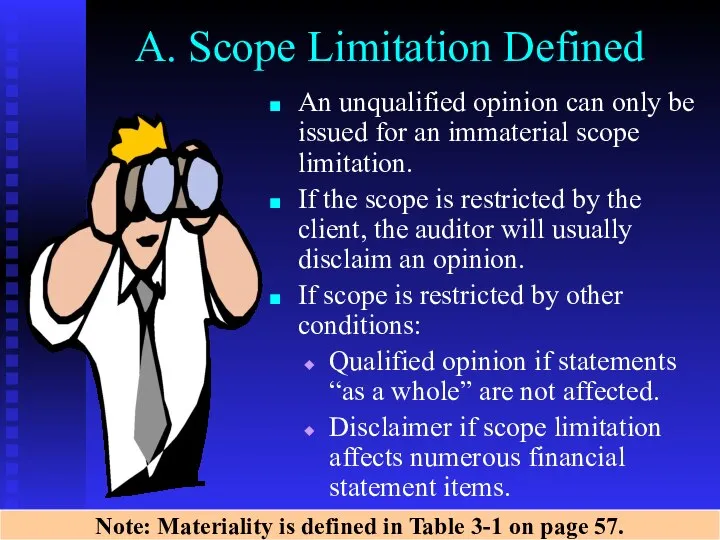
- 21. A. Scope Limitation Defined An unqualified opinion can only be issued for an immaterial scope limitation.
- 22. B. Effect of Scope Limitation on Audit Report – Qualified Opinion Introductory paragraph is same as
- 23. C. Effect of Scope Limitation on Audit Report – Disclaimer of Opinion Introductory paragraph modified to
- 24. VI. GAAP Departure GAAP Departure Defined Effect of GAAP Departure on Audit Report – Qualified Opinion
- 25. A. GAAP Departure Defined An unqualified opinion can only be issued if GAAP departure is immaterial.
- 26. B. Effect of GAAP Departure on Audit Report – Qualified Opinion Introductory paragraph is same as
- 27. C. Effect of GAAP Departure on Audit Report – Adverse Opinion Introductory paragraph is same as
- 28. VII. Lack of Independence An accountant who is not independent is required to issue a special
- 29. VIII. Other Information In regard to other information included with the audited financial statements in the
- 31. Скачать презентацию


























 Презентация по английскому языку Автор: Буркатская В.А. Материал скачан с сайта: www.pedsovet.su
Презентация по английскому языку Автор: Буркатская В.А. Материал скачан с сайта: www.pedsovet.su Speaking about films
Speaking about films Презентация к уроку английского языка "Nokia" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Nokia" - скачать  Stonehenge: World Heritage In The United Kingdom.
Stonehenge: World Heritage In The United Kingdom. Александр Исаевич Солженицын Маркович Николай Представляет
Александр Исаевич Солженицын Маркович Николай Представляет Презентация к уроку английского языка "London underground" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "London underground" - скачать  cities of the world Дублин. Ирландия
cities of the world Дублин. Ирландия  Describing People 3
Describing People 3 England | Англия (44 слайдов)_
England | Англия (44 слайдов)_ Great Britain
Great Britain Простое прошедшее время
Простое прошедшее время What to prepare before the lesson!!!
What to prepare before the lesson!!! Classroom Objects
Classroom Objects What time is it?
What time is it? Millennium Bridge
Millennium Bridge Работу выполнила: ученица 8 б класса МБОУСОШ№59 Чеботникова Екатерина
Работу выполнила: ученица 8 б класса МБОУСОШ№59 Чеботникова Екатерина  Презентация основные положения кейнсианской теории
Презентация основные положения кейнсианской теории Cute Monsters
Cute Monsters Presentation National Culture of Ukraine XTL-11a By Denis Danilenko
Presentation National Culture of Ukraine XTL-11a By Denis Danilenko  History of Halloween
History of Halloween Презентация к уроку английского языка "Guy Fawkes and the gunpowder plot" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Guy Fawkes and the gunpowder plot" - скачать  Презентация дополнительных платных услуг МБДОУ д/с №15 «Маячок» на 2013-2014 год
Презентация дополнительных платных услуг МБДОУ д/с №15 «Маячок» на 2013-2014 год ГРАВИТАЦИЯ Сейчас я расскажу вам о гравитации на Земле и остальных планетах Солнечной системы
ГРАВИТАЦИЯ Сейчас я расскажу вам о гравитации на Земле и остальных планетах Солнечной системы  Present Simple Tense
Present Simple Tense Places of Interest in Russia
Places of Interest in Russia Teens’ Problems and Moral Values
Teens’ Problems and Moral Values Animals and their habitats
Animals and their habitats The doctor more than a thousand years
The doctor more than a thousand years