Содержание
- 2. The division of words into classes CRITERIA: Semantic (meaning) Formal (form) derivational features a set of
- 3. Traditional grammar approach Scherba: notional parts of speech (N, V, Adv, Adj, Pron, Num) Functional parts
- 4. M. Blokh (semantico-grammatical analysis): Notional (names): N,V,Adv,Adj pronominal words (substitutes of names): pronouns, numbers, words of
- 5. Modern approaches J. Sweet divided the vocabulary on the morphological properties into declinables (N, Adj, V)
- 6. Glison’s classification is based on two formal indications: morphological form and word-order (the group which has
- 7. O. Jespersen proposed a classification based on the lexical meaning and morphological function of the word
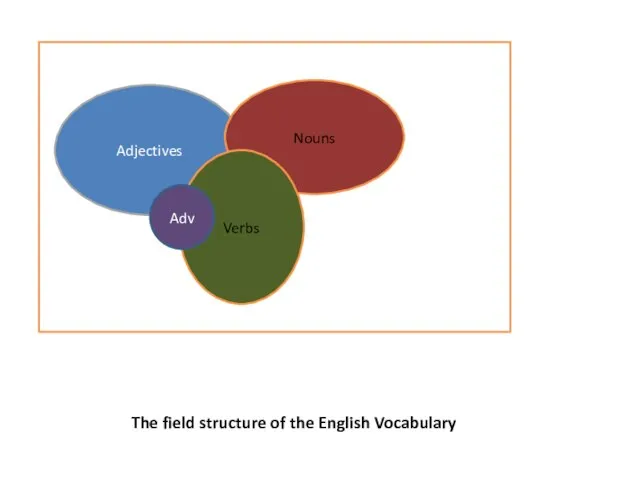
- 8. The field structure of the English Vocabulary Adjectives Nouns Verbs Adv
- 9. Notional and functional parts of speech 1 The lexical meaning is bright and distinct 2 They
- 11. Скачать презентацию







 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Kiev" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Kiev" - скачать  Collective nouns
Collective nouns Жидкова Екатерина Вадимовна МОУ лицей № 39 Город Нижний Тагил
Жидкова Екатерина Вадимовна МОУ лицей № 39 Город Нижний Тагил  London, the Capital of the UK.
London, the Capital of the UK.  Machines then and now
Machines then and now George Gordon Byron Prepared by : Galya Ovsyanikova Mary Filatova 4-B
George Gordon Byron Prepared by : Galya Ovsyanikova Mary Filatova 4-B The best way to predict the future is to cveate it
The best way to predict the future is to cveate it Презентация к уроку английского языка "Merry Christmas" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Merry Christmas" - скачать бесплатно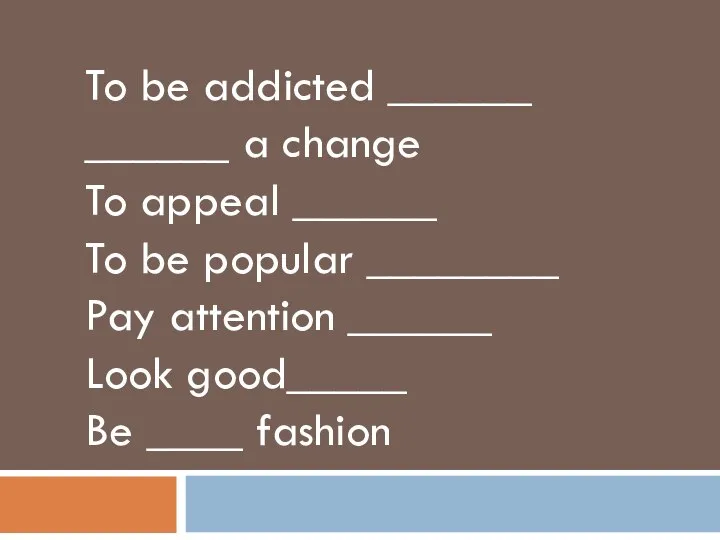 In use
In use Презентация к уроку английского языка "Steven Paul Jobs" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Steven Paul Jobs" - скачать  Welcome to the…2018 OLIMPIC GAMES
Welcome to the…2018 OLIMPIC GAMES How We Take Care of the Environment
How We Take Care of the Environment  Презентация POPULATION
Презентация POPULATION  Flora and fauna of Australia
Flora and fauna of Australia 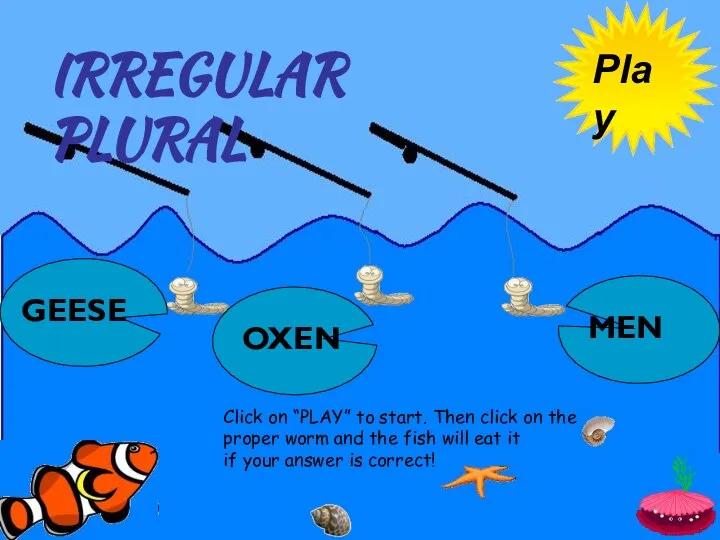 Plural forms. Game
Plural forms. Game Parts of the Body Bingo! Reading
Parts of the Body Bingo! Reading Population of Wellington 2014
Population of Wellington 2014  Picasso Memory Game (Art Vocabulary)
Picasso Memory Game (Art Vocabulary) Alarm Clock
Alarm Clock Present Simple & Present Continuous
Present Simple & Present Continuous Открытый урок ”The famous writers of Great Britain” Семенова Р.Б. учитель английского языка МБОУ « Гимназия №4 им. А. С. Пушкина» г. Йошкар-Ола
Открытый урок ”The famous writers of Great Britain” Семенова Р.Б. учитель английского языка МБОУ « Гимназия №4 им. А. С. Пушкина» г. Йошкар-Ола Bank of America
Bank of America  Идеи Гуманистической педагогики Л.Н. Толстого на уроке иностранного языка в современной школе
Идеи Гуманистической педагогики Л.Н. Толстого на уроке иностранного языка в современной школе London Taxi History
London Taxi History 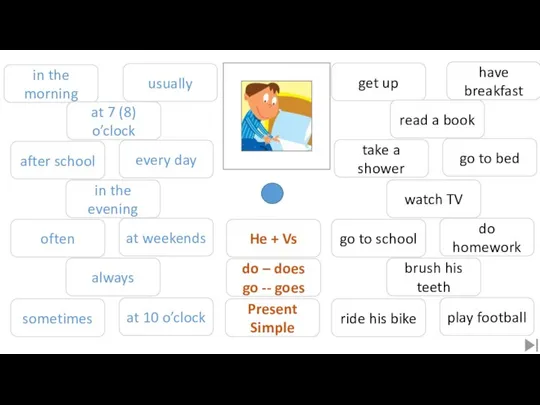 Daily routine
Daily routine What would you like - 3 лицо
What would you like - 3 лицо Was and were
Was and were Name these sounds. Read the words with these sounds
Name these sounds. Read the words with these sounds