Содержание
- 2. Instructional Objectives : Title After the completion of the lesson, students can compare generic structure, social
- 3. Simple Present Tense is the tense used to express an action or activity that takes place
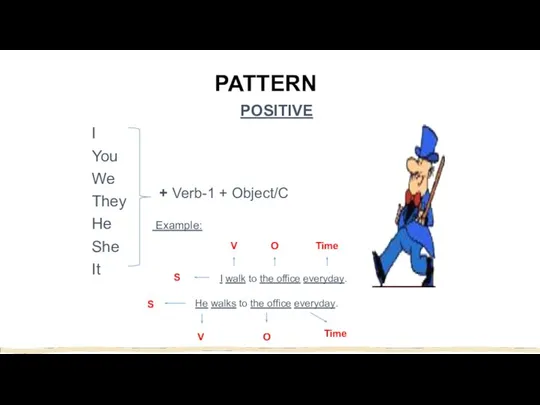
- 4. PATTERN POSITIVE I You We They He Example: She It + Verb-1 + Object/C I walk
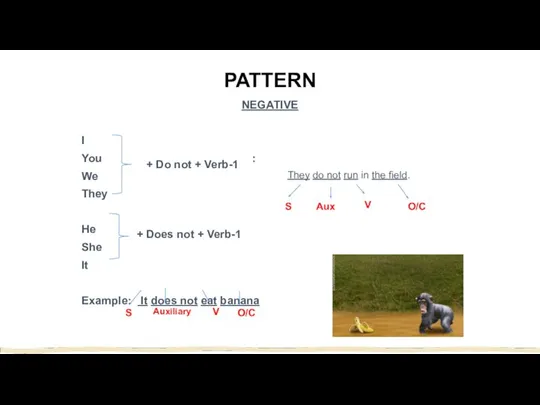
- 5. PATTERN NEGATIVE I You Example : We They He She It Example: It does not eat
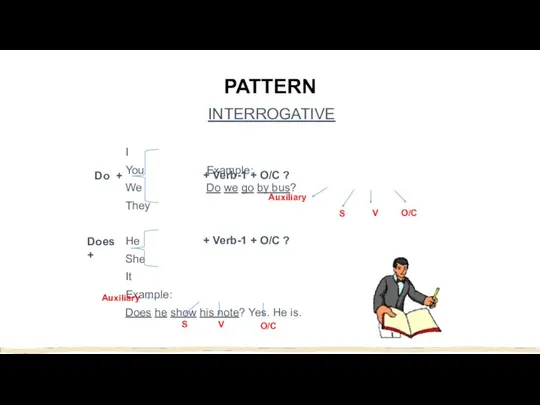
- 6. PATTERN INTERROGATIVE I You Example: We Do we go by bus? They He She It Example:
- 7. Simple Present Tense using this type of "TO BE 1" and "VERB 1" TO BE 1
- 8. Remember! Only in positive sentences, for the subject "He, She, It" , the use of the
- 9. Remember! Verb that ends in the letters " ch, o, s, sh, x " plus the
- 10. Remember! Whereas the verb ending with the letter "- y " that begins with a vowel,
- 11. Let’s Practice Change The Sentences below into Simple Past Tense Form! I talked to him yesterday.
- 12. Let’s Practice Change The Sentences below into Simple Past Tense Form! The went to the beach
- 14. Скачать презентацию







 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Соединенное королевство Великобритании" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Соединенное королевство Великобритании" - скачать  This is a cat
This is a cat Food
Food Grade 9. Lesson 101
Grade 9. Lesson 101 Читаем по-английски. Сочетания букв c,g + e, i, y. Чтение буквы у
Читаем по-английски. Сочетания букв c,g + e, i, y. Чтение буквы у Презентация к уроку английского языка "Water Pollution." - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Water Pollution." - скачать 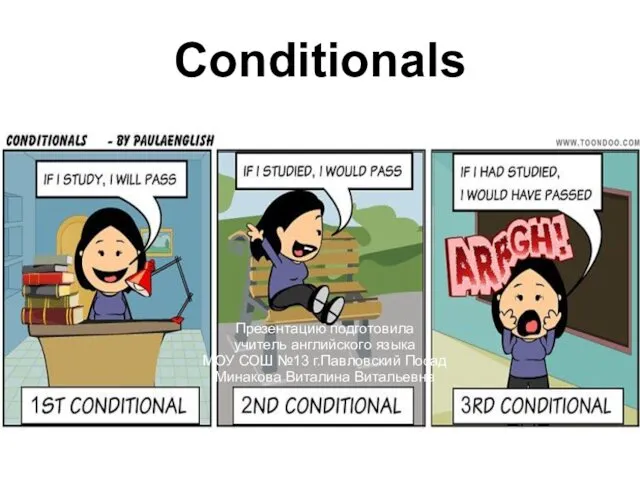 Conditionals
Conditionals Supermarket. My trip to the supermarket
Supermarket. My trip to the supermarket Project “New Zealand’s Specials: A Future Sociologist’s View”
Project “New Zealand’s Specials: A Future Sociologist’s View” Для тебя
Для тебя Презентация к уроку английского языка "Project Professions Italy" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Project Professions Italy" - скачать бесплатно Неправильные глаголы Irregular Verbs
Неправильные глаголы Irregular Verbs Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense  Презентация к уроку английского языка "Welcome to school radio" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Welcome to school radio" - скачать  Past Continuous
Past Continuous Writing Reports
Writing Reports Презентация к уроку английского языка "Лимерик как одно из проявлений английского юмора" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Лимерик как одно из проявлений английского юмора" - скачать  Prosody. General character of english intonation. (Lecture 7)
Prosody. General character of english intonation. (Lecture 7) Путешествие в страну сказок – Travelling to the fairytale country.
Путешествие в страну сказок – Travelling to the fairytale country. Урок-соревнование «Seasons»
Урок-соревнование «Seasons» Giving advice bingo game
Giving advice bingo game Обстоятельство длительности. Урок 29
Обстоятельство длительности. Урок 29 Parts of the Automobile
Parts of the Automobile Открытый урок Тема: «THE UNKNOWN ANIMAL» (НЕИЗВЕСТНОЕ ЖИВОТНОЕ) Animals are our little friends
Открытый урок Тема: «THE UNKNOWN ANIMAL» (НЕИЗВЕСТНОЕ ЖИВОТНОЕ) Animals are our little friends Аттестационная работа. Буклет Путешествуем по Великобритании
Аттестационная работа. Буклет Путешествуем по Великобритании Eating Out. Lesson 28
Eating Out. Lesson 28 Презентация к уроку английского языка "What is your medical history?" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "What is your medical history?" - скачать  Environmental protection Created by Vazheliuk Liza
Environmental protection Created by Vazheliuk Liza