Содержание
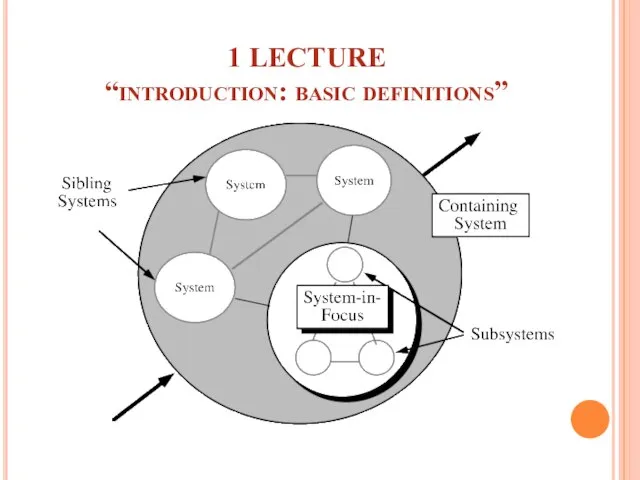
- 2. 1 LECTURE “introduction: basic definitions”
- 3. The system is an object or a process where elements are related by some connections and
- 4. Features of the "system" term such as ordering, integrity and availability of certain laws - appear
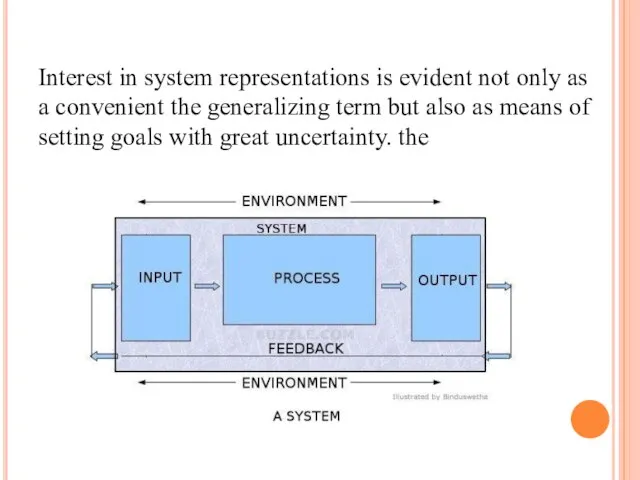
- 5. Interest in system representations is evident not only as a convenient the generalizing term but also
- 6. Four basic properties of the system can be identified: system is a set of elements that
- 7. availability of a specific organization; the existence of integrative properties, i.e., inherent in the system as
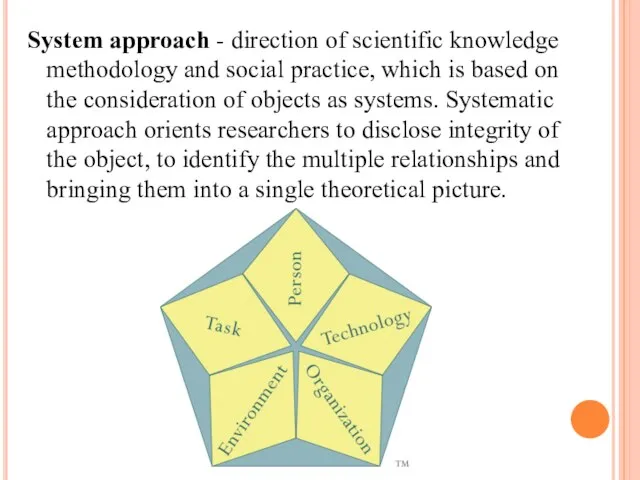
- 8. System approach - direction of scientific knowledge methodology and social practice, which is based on the
- 9. Systemic approach requires in the study of any object or phenomenon, the Systemic approach may be
- 11. definition of the basic criteria describing a targeted operation of the system, the main restrictions and
- 13. preparation of the system model functioning, taking into account all significant factors. The significance of factors
- 14. designing of optimal structures and functional activities of the system. Determination of the optimal scheme of
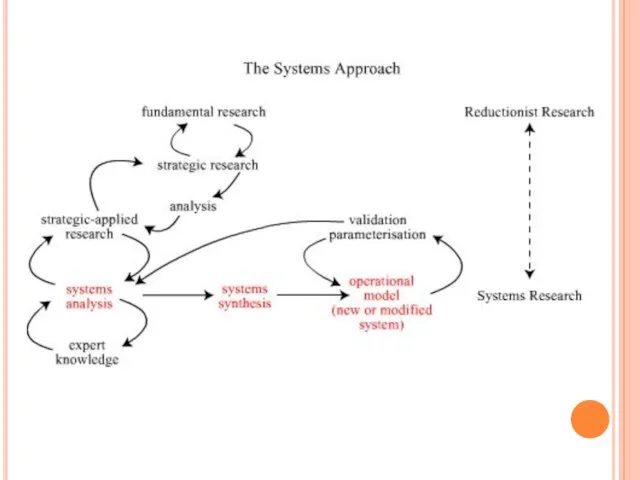
- 15. 2 LECTURE SYSTEM RESEARCH System research is set of scientific theories, concepts and methods, where the
- 16. The main methodological features of system research: System Studies characterized by special type of the studied
- 17. 3. High level of system research abstraction creates the possibility of formation a large empirical material
- 18. The systemic study identified three aspects: • development of theoretical foundations of systematic approach; • research
- 19. There are "soft systems methodology" and "hard system methodology.« The general scheme of "soft systems methodology"
- 20. Creating and testing of conceptual models aimed at identifying ways to complete or partial resolution of
- 21. The basis of "hard system methodology" is definition of the alternative ways to achieve set objectives
- 22. The system research specifics are determined by extension of new approach principles of the study subject.
- 23. the same material acts in a system research as possessing at the same time different characteristics,
- 24. 3 LECTURE “SYSTEM ANALYSIS” System analysis - a set of concepts, methods, procedures and techniques for
- 25. System analysis provides for use in a variety of sciences, the following system methods and system
- 26. 2) Analysis and synthesis, induction and deduction. Analysis is mental separation of an object or phenomenon
- 27. 3) Formalizing. Formalizing is the method of objects investigating by presenting their elements in the form
- 28. 5) Linearization and selection of non-linear components. Linearization - one of the most common methods for
- 29. 7) Prototyping. Prototyping is a form of research project modeling, simulation in volumetric images. The model
- 30. 9) Algorithmization. Algorithmization - stage of problem solution, consisting of finding the algorithm on the problem
- 31. 11) Clustering and classification. Classification - systemic distribution of studied objects, phenomena, processes, by type, stile,
- 32. 12) Program control and regulation 13) Recognition and Identification 14) The expert evaluation and testing 15)
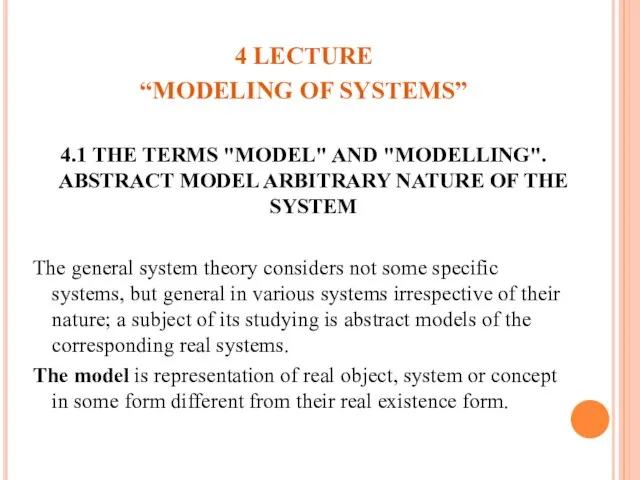
- 33. 4 LECTURE “MODELING OF SYSTEMS” 4.1 THE TERMS "MODEL" AND "MODELLING". ABSTRACT MODEL ARBITRARY NATURE OF
- 34. Every model is a certain analogy: for one system, there has to be other system which
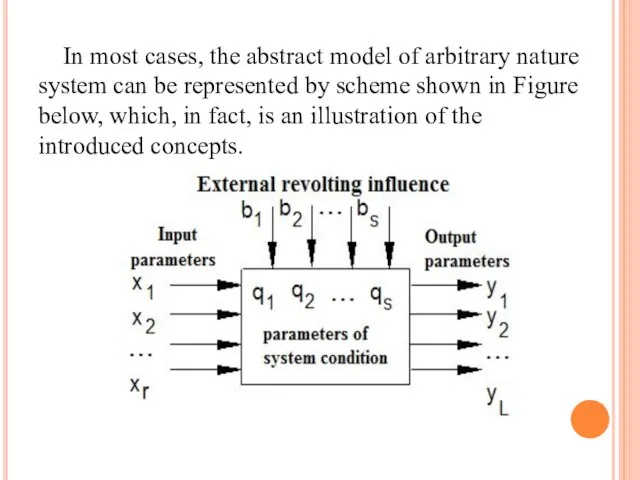
- 35. In most cases, the abstract model of arbitrary nature system can be represented by scheme shown
- 36. The system does not exist by itself, but it stands out from the surrounding environment at
- 37. Output parameters - a set of system parameters that have a direct impact on the external
- 38. Perhaps, parameters of the external environment which are directly influencing behavior of system (that is parameters
- 39. Impact on system of similar unaccounted factors is compensated by introduction to additional communications model -
- 40. Thus, the system is characterized by three groups of variables: 1. Input variables which are generated
- 41. 4.2 Physical and mathematical modeling As the concept "modelling" is rather general and universal, so various
- 42. Physical modelling is carried out by reproduction of the researched process on the model having generally
- 43. The mathematical model is a set of mathematical objects (numbers, symbols, sets, etc.) reflecting the properties
- 44. Macroapproach - a way of carrying out the external description of system. At a stage of
- 45. At the same time degree of a variety of entrance influences essentially is connected with a
- 46. So, the method of "black box" consists in revealing structure of system and principles of its
- 47. Microapproach - a way of carrying out the internal description of system, i.e. the description of
- 48. The problem of realization consists in transition from the external description of system to internal description.
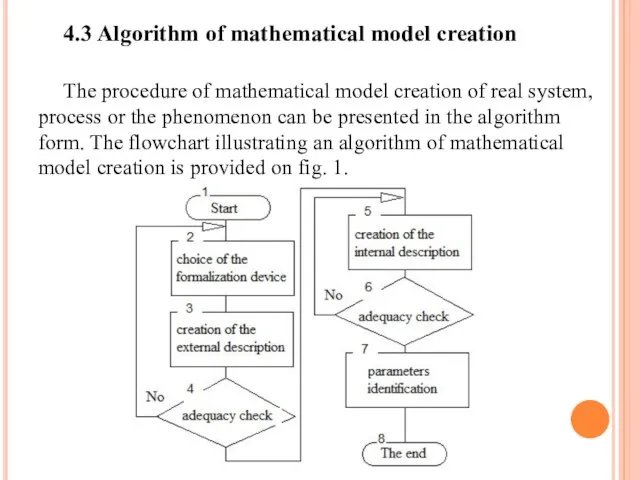
- 49. 4.3 Algorithm of mathematical model creation The procedure of mathematical model creation of real system, process
- 50. Main stages of mathematical model creation. 1. Allocation of system from the external environment. Allocation of
- 51. 3. Creation of the external description comes down to search of definition range (in space of
- 52. 5. In case of the successful created external description, transition to the internal description is carried
- 53. The problem of parametrical identification comes down to values search of parameters providing minimization of some
- 54. 5 LECTURE ASSESSMENT OF COMPLEX SYSTEMS MAIN TYPES OF MEASUREMENT SCALES 5.1. Assessment of complex systems
- 55. Generally the efficiency evaluation of complex systems can be carried out for the different purposes. Firstly,
- 56. Four stages of complex systems evaluation: Step 1. Definition of the estimation purpose. In the system
- 57. Step3. Reasons for quality criteria preferences and criteria of systems functioning efficiency on the basis of
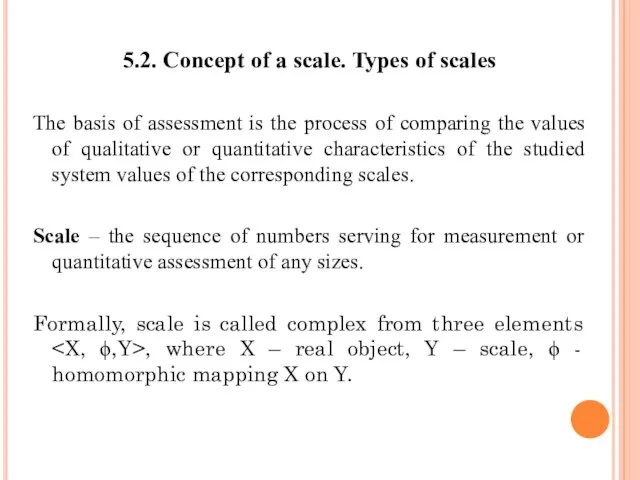
- 58. 5.2. Concept of a scale. Types of scales The basis of assessment is the process of
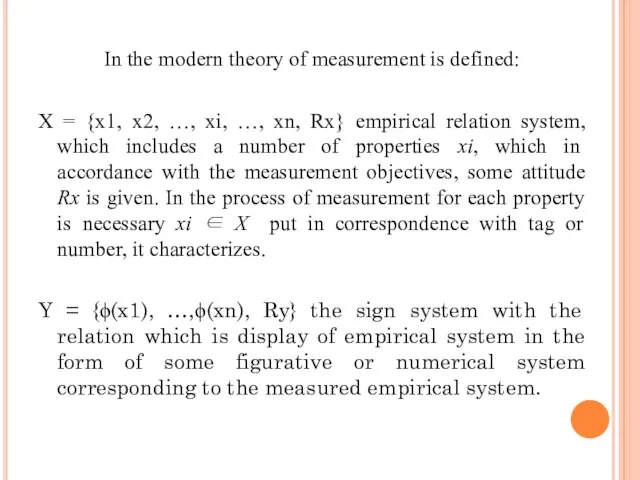
- 59. In the modern theory of measurement is defined: X = {x1, x2, …, xi, …, xn,
- 60. 5.2.1. The scales of the nominal type The weakest quality scale is nominal scale (scale items,
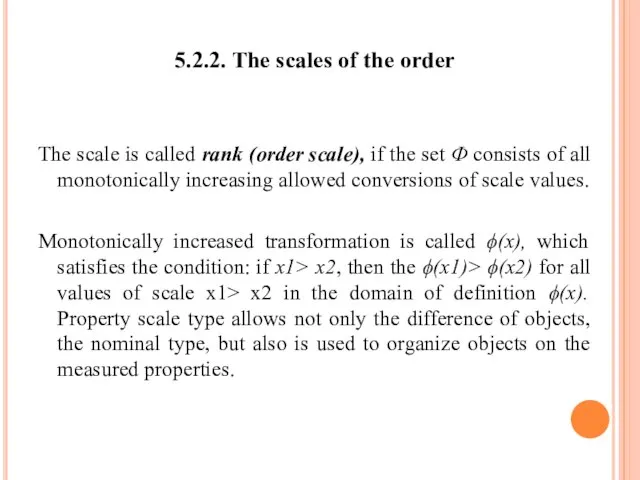
- 61. 5.2.2. The scales of the order The scale is called rank (order scale), if the set
- 62. Measuring in order scale may be used in the following situations: • It is necessary to
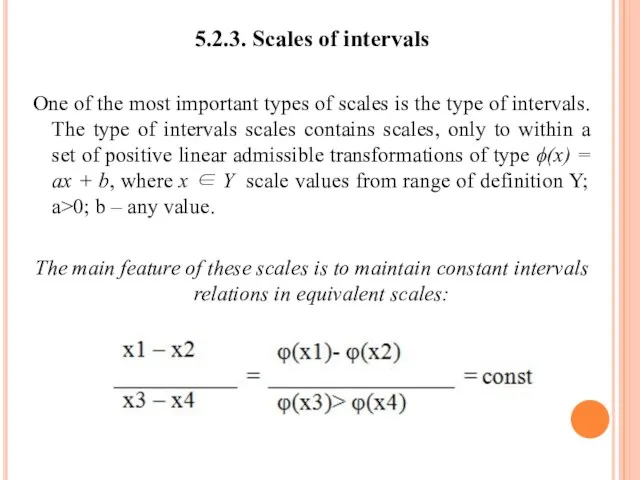
- 63. 5.2.3. Scales of intervals One of the most important types of scales is the type of
- 64. Thus, upon transition to equivalent scales by means of linear transformations in scales of intervals there
- 66. Скачать презентацию







































 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Eddie Murphy" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Eddie Murphy" - скачать бесплатно My project «Traditional Russian kitchen»
My project «Traditional Russian kitchen»  Dance as the lifestyle
Dance as the lifestyle  Вежливость открывает все двери Формирование социальных компетенций на уроках английского языка Подготовила: Камнева Инна Ан
Вежливость открывает все двери Формирование социальных компетенций на уроках английского языка Подготовила: Камнева Инна Ан Summer holidays
Summer holidays How to give an opinion
How to give an opinion Whose hat is it (professions)
Whose hat is it (professions) Drag and drop house
Drag and drop house Презентация к уроку английского языка "Письмо на английском языке" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Письмо на английском языке" - скачать бесплатно Emphatic Constractions. Inversion. Elliptical Constructions
Emphatic Constractions. Inversion. Elliptical Constructions Презентация к уроку английского языка "The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" - скачать  Презентация My animals
Презентация My animals What is Hot with the Young Generation? Subculture
What is Hot with the Young Generation? Subculture  Present Simple vs Present Continuous
Present Simple vs Present Continuous Story about Chicken Licken
Story about Chicken Licken Презентация к уроку английского языка "BD_GW2600" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "BD_GW2600" - скачать  Would Like. Урок 5
Would Like. Урок 5 Аттестационная работа. Творческий проект “Our Magic Island”. Мотивация учащихся при изучении английского языка
Аттестационная работа. Творческий проект “Our Magic Island”. Мотивация учащихся при изучении английского языка Презентация к уроку английского языка "Учим английский" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Учим английский" - скачать бесплатно Shopping. Answer the questions
Shopping. Answer the questions Writing Tasks. ОГЭ. Письмо
Writing Tasks. ОГЭ. Письмо Презентация Как написать свое имя и фамилию на английском языке? Подготовила учитель английского языка МБОУ ЦСОШ № 9 Ковальч
Презентация Как написать свое имя и фамилию на английском языке? Подготовила учитель английского языка МБОУ ЦСОШ № 9 Ковальч Test. Option 1
Test. Option 1 Prepositions of Place. Worksheet House Furniture. There is are
Prepositions of Place. Worksheet House Furniture. There is are There Is Are House. Furniture Worksheet Game
There Is Are House. Furniture Worksheet Game Reported speech. Part 3
Reported speech. Part 3 Притяжательные местоимения в английском языке (3 класс)
Притяжательные местоимения в английском языке (3 класс) Презентация к уроку английского языка "«Изобразительное искусство - немецкий язык»" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "«Изобразительное искусство - немецкий язык»" - скачать