Содержание
- 2. What does mean transport? Transport (Latin trans - «through» and portare - «bear") - may refer
- 3. Transport weather or air water, underwater ground, underground rail and trackless Transport category
- 4. Transportation: court Means of communication: Seas and oceans, rivers, lakes and canals Signaling and Control: lighthouses,
- 5. Transport using work of animals or humans. It is the oldest known to man kind of
- 6. Cartage - view of Road Transport, which is used as a traction force of animals. People
- 7. The car - a "means trackless vehicle with its own engine." The trucks now carry virtually
- 8. The most wasteful transport compared with other modes of transport in terms of the costs involved
- 9. Rail transport was both a product and a motor of the industrial revolution. Originating in the
- 10. Vehicles: airplanes and helicopters Posts Path: air corridors Transport: Airports The main sphere of air transport
- 11. The invention ( creativity) - a new solution of the problem , the technical implementation of
- 12. Phone ( from the Greek τῆλε -. « Away " and φωνή - « voice" ,
- 13. Computer (English computer, IPA : [kəmpjuː.tə (ɹ)] - « calculator ." ) - A device or
- 14. TV ( novolat televisorium –far-seeing, from the ancient Greek τῆλε -. Far and Latin video -.
- 15. Calculator (Latin calculātor « counter " . ) - Electronic computing device to perform operations on
- 17. Скачать презентацию











![Computer (English computer, IPA : [kəmpjuː.tə (ɹ)] - « calculator ."](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/514200/slide-12.jpg)


 My country at a glance
My country at a glance Презентация к уроку английского языка "The largest citys in U.S.A" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "The largest citys in U.S.A" - скачать бесплатно Russian Federation
Russian Federation Illustration jungle. Gym tree
Illustration jungle. Gym tree Past Simple
Past Simple Present Progressive Tense What are they doing?
Present Progressive Tense What are they doing?  THANKSGIVING
THANKSGIVING  Учитель английского языка МКОУ «Правдинская ООШ» Отмашкина Олеся Анатольевна
Учитель английского языка МКОУ «Правдинская ООШ» Отмашкина Олеся Анатольевна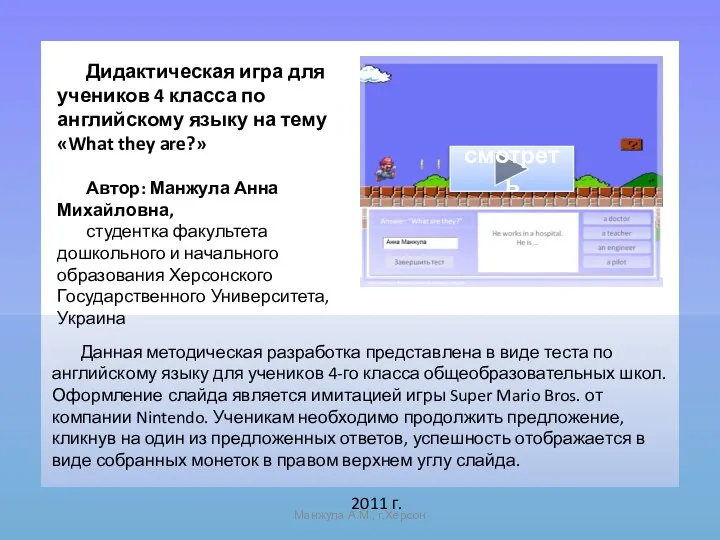 Презентация к уроку английского языка "«What they are?»" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "«What they are?»" - скачать бесплатно My favourite film V for Vendetta
My favourite film V for Vendetta  Past simple
Past simple Modal verbs must and should
Modal verbs must and should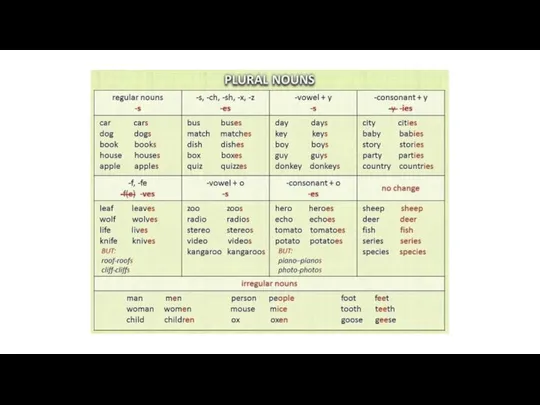 Plural nouns
Plural nouns Презентация Парадокс бережливости
Презентация Парадокс бережливости Заколдованное слово
Заколдованное слово Рифмовки на буквы алфавита УМК “Enjoy English” 2 класс
Рифмовки на буквы алфавита УМК “Enjoy English” 2 класс  Распределите слова по колонкам
Распределите слова по колонкам Family-ties teacher switcher
Family-ties teacher switcher Презентация к уроку английского языка "United States" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "United States" - скачать бесплатно Easter is a very important festival in Grait Britain
Easter is a very important festival in Grait Britain Настоящее простое время
Настоящее простое время Places in a town
Places in a town London
London Учитель английского языка ГБОУ СОШ № 797 г. Москвы Дианова Наталья Михайловна
Учитель английского языка ГБОУ СОШ № 797 г. Москвы Дианова Наталья Михайловна Урок английского языка Урок английского языка В 11 классе МОУ Камышевская ср. школа Учитель Требух С.И. 2008 г.
Урок английского языка Урок английского языка В 11 классе МОУ Камышевская ср. школа Учитель Требух С.И. 2008 г. Основные нефтедобывающие районы, особенности технологии, уровень добычи углеводородов в странах Азии Выполнил : Аванесян Ю.П. Гру
Основные нефтедобывающие районы, особенности технологии, уровень добычи углеводородов в странах Азии Выполнил : Аванесян Ю.П. Гру Magic world of fairy tales Lesson for junior pupils English teacher: G.N.Gavrilevich
Magic world of fairy tales Lesson for junior pupils English teacher: G.N.Gavrilevich Global Warming – Climate Change What do I need to know? What do I need to do?
Global Warming – Climate Change What do I need to know? What do I need to do?