Содержание
- 3. General Approach – Find the Cycles My primary approach is to seek out the causes of
- 4. Content We will cover: How submarine volcanoes can cause climate change – as compared to surface
- 5. Theory Statement - Definite “Submarine volcanism is significant, cyclically variable, and changes global and regional climate
- 6. It’s been suggested before.......and ignored Also: Published papers of geophysicists Michael House http://dx.doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1995.085.01.01 and: John Wahr
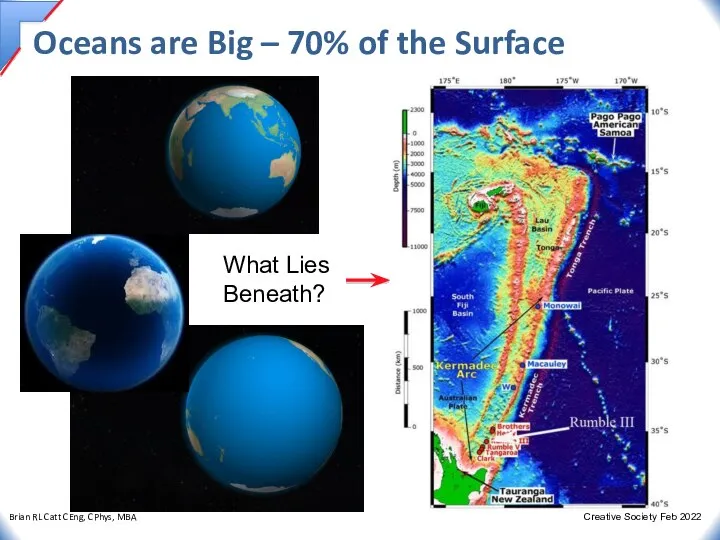
- 7. Oceans are Big – 70% of the Surface What Lies Beneath?
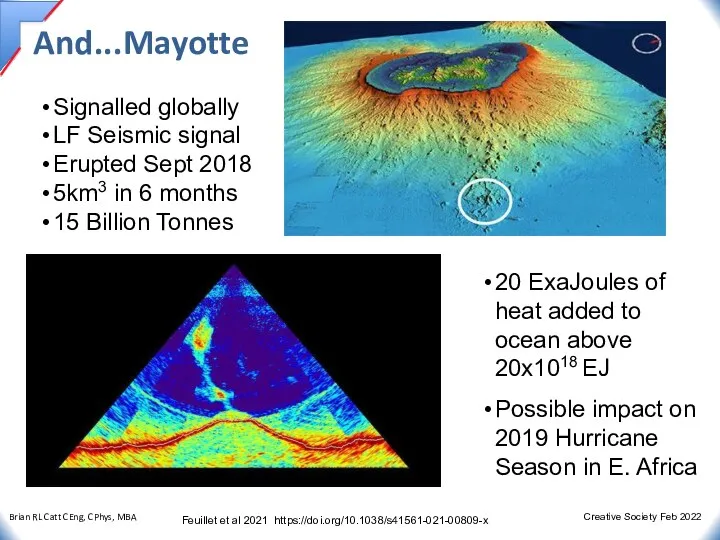
- 8. And...Mayotte Signalled globally LF Seismic signal Erupted Sept 2018 5km3 in 6 months 15 Billion Tonnes
- 9. Some Facts About the Ocean Floor The Earths tectonic plates mainly diverge in the oceans, up
- 10. Why the World is Smooth and Round-ish It isn’t rigid, its an spinning oblate spheroid contained
- 11. It’s Mostly Rock By Scale of weight: Rock is 4,000 x Water Rock is 1 Million
- 12. Summary: What this means for Submarine Volcanoes The ocean floor that oceanic volcanoes must penetrate is
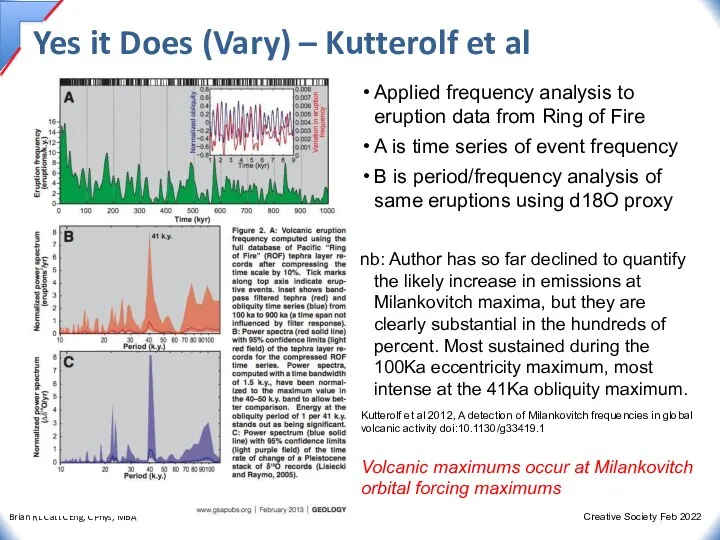
- 13. Yes it Does (Vary) – Kutterolf et al Kutterolf et al 2012, A detection of Milankovitch
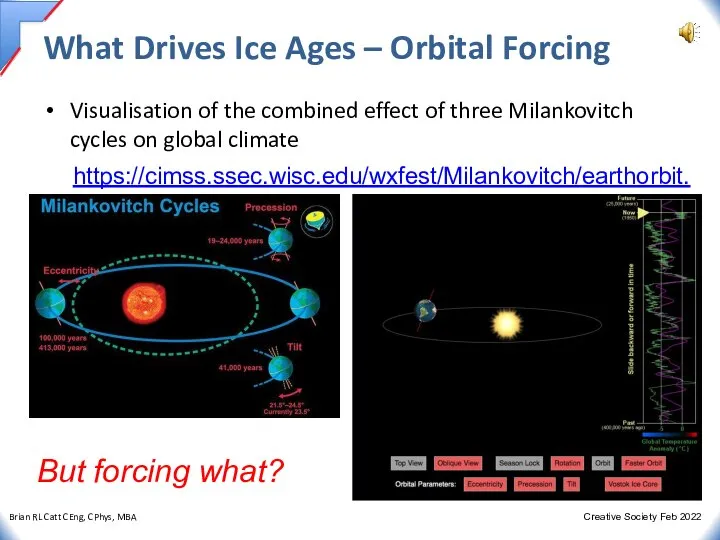
- 14. What Drives Ice Ages – Orbital Forcing Visualisation of the combined effect of three Milankovitch cycles
- 15. How Much Warming is That? (Numbers at last!) 28x106m3/pa per volcano x 5,000 volcanoes = 140Km3
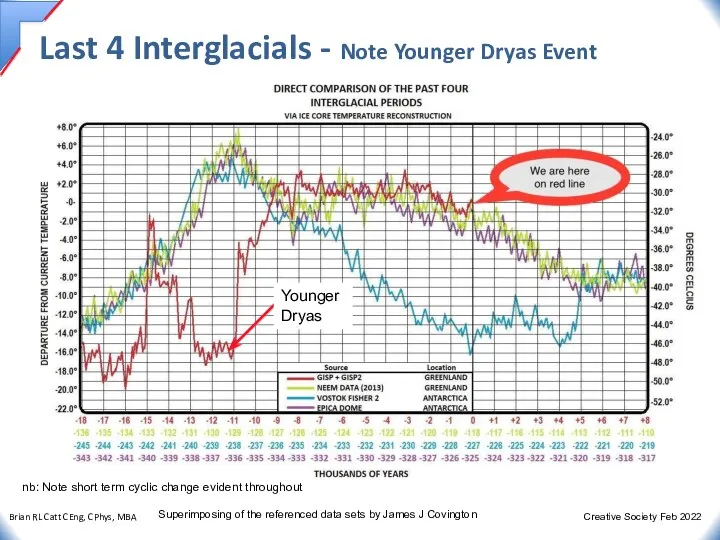
- 16. Last 4 Interglacials - Note Younger Dryas Event Younger Dryas Superimposing of the referenced data sets
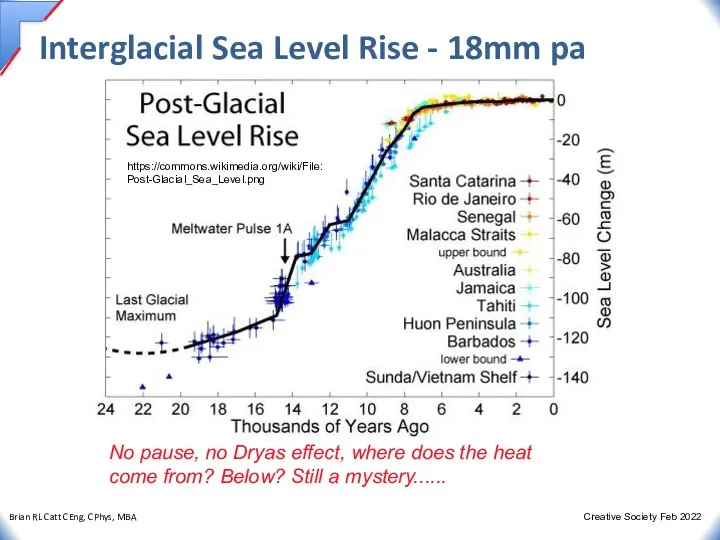
- 17. Interglacial Sea Level Rise - 18mm pa No pause, no Dryas effect, where does the heat
- 18. Can El Nino be Driven by Cyclic Volcanicity? I additionally propose this is the case, that
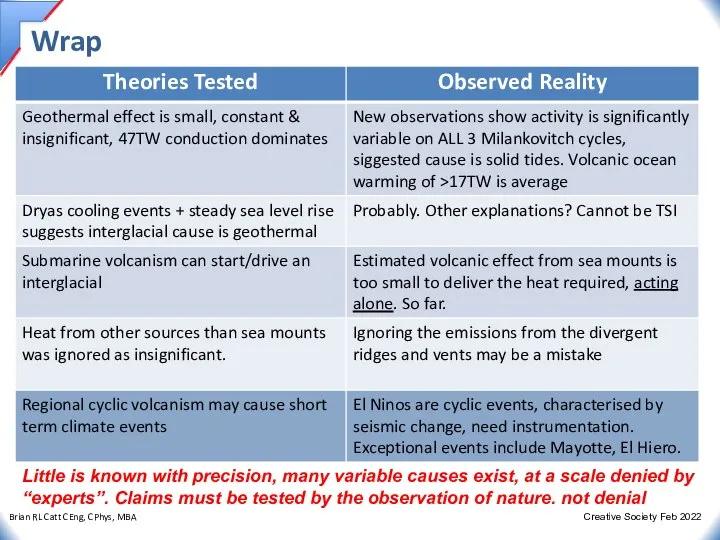
- 19. Wrap Little is known with precision, many variable causes exist, at a scale denied by “experts”.
- 20. What Controls the Planetary Climate? The atmosphere is primarily an effect of dominant solar radiation, gravitational
- 21. THE END Thank you for your attention! Questions? Please send questions regarding the facts and the
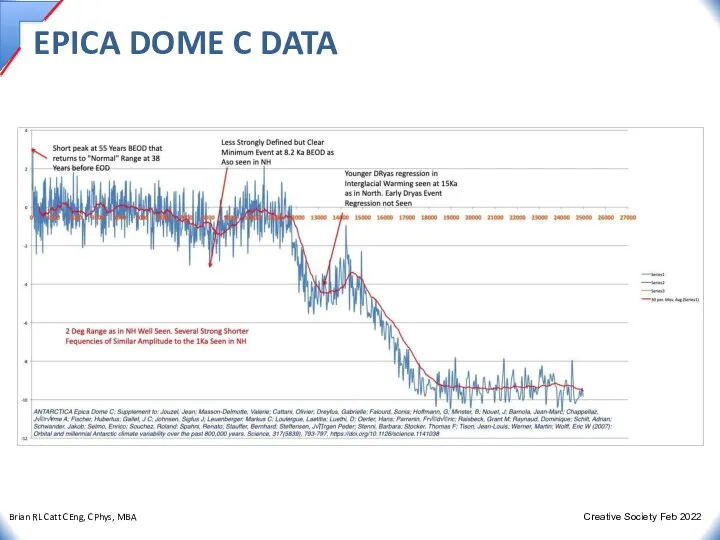
- 22. EPICA DOME C DATA
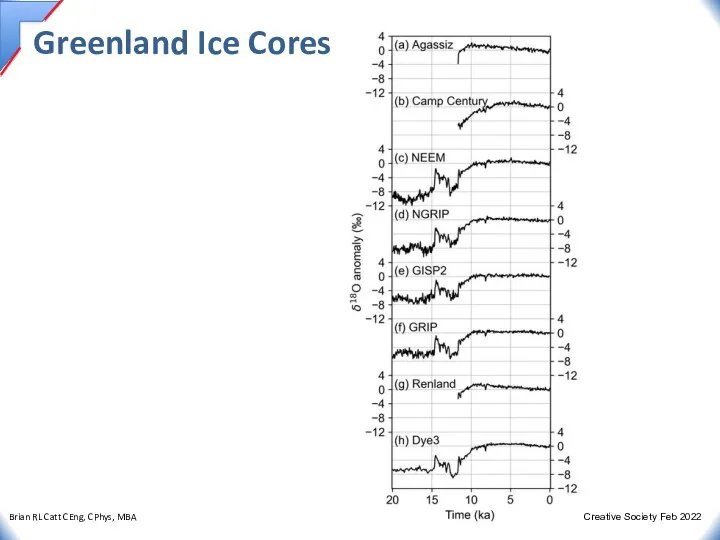
- 23. Greenland Ice Cores
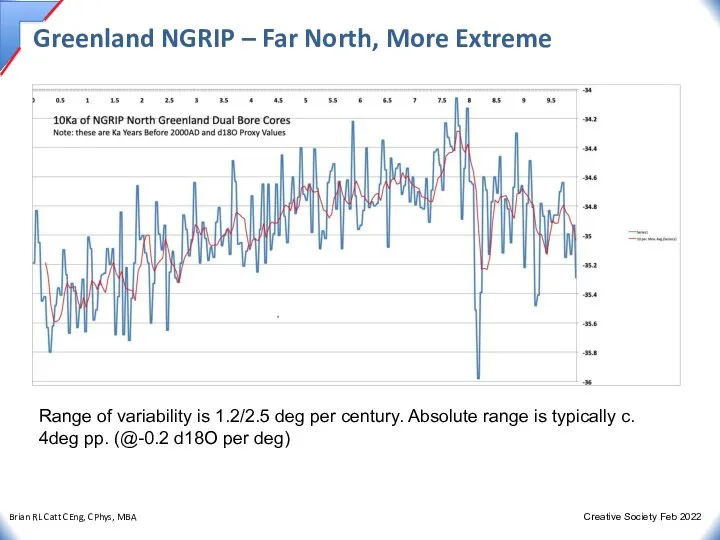
- 24. Greenland NGRIP – Far North, More Extreme Range of variability is 1.2/2.5 deg per century. Absolute
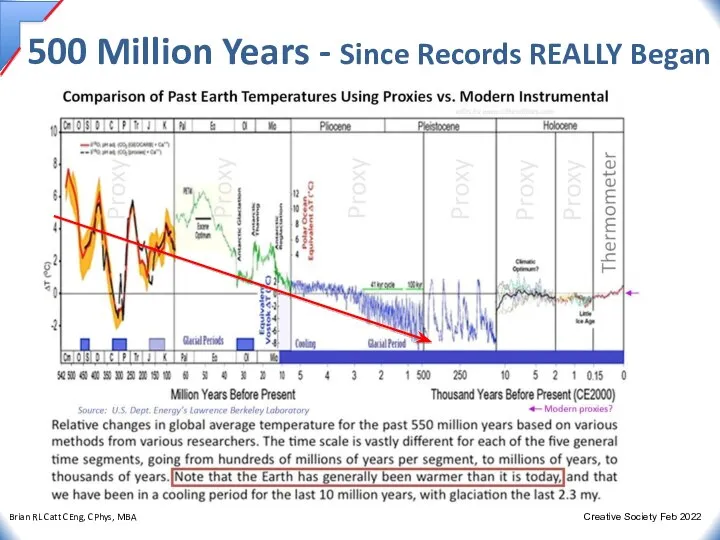
- 25. 500 Million Years - Since Records REALLY Began
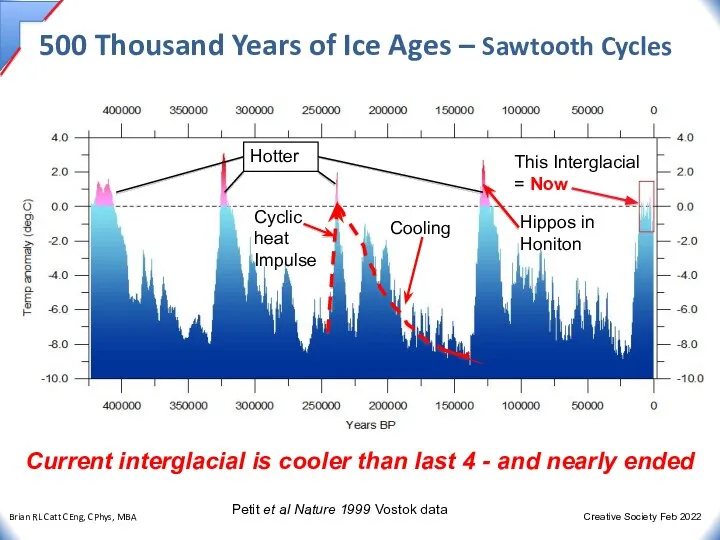
- 26. 500 Thousand Years of Ice Ages – Sawtooth Cycles Current interglacial is cooler than last 4
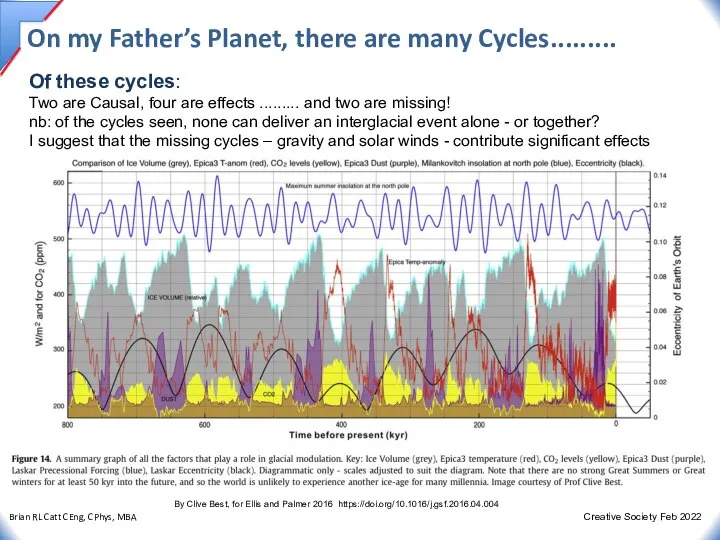
- 27. On my Father’s Planet, there are many Cycles......... Of these cycles: Two are Causal, four are
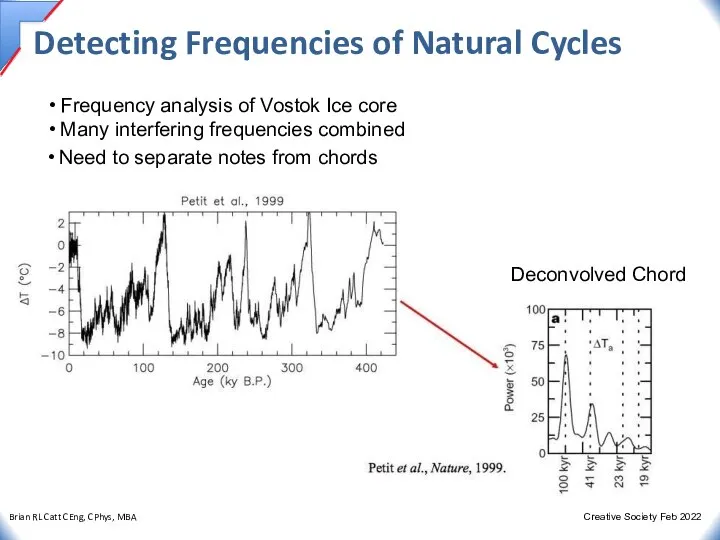
- 28. Detecting Frequencies of Natural Cycles Frequency analysis of Vostok Ice core Many interfering frequencies combined Need
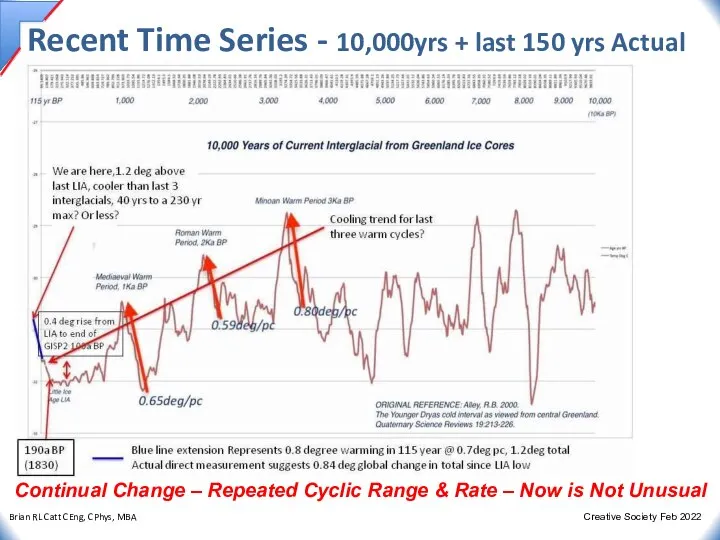
- 29. Recent Time Series - 10,000yrs + last 150 yrs Actual Continual Change – Repeated Cyclic Range
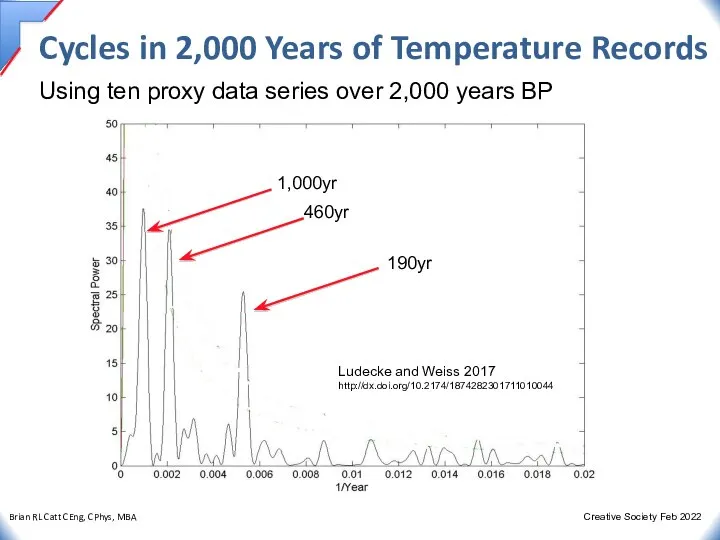
- 30. Cycles in 2,000 Years of Temperature Records Using ten proxy data series over 2,000 years BP
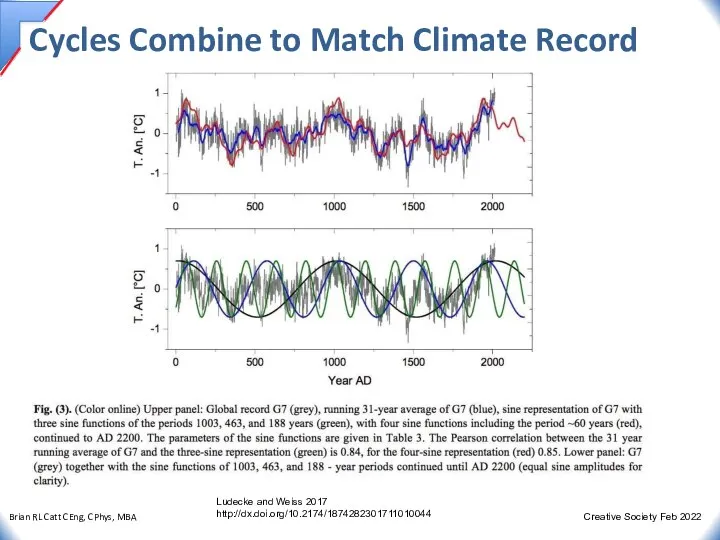
- 31. Cycles Combine to Match Climate Record Ludecke and Weiss 2017 http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1874282301711010044
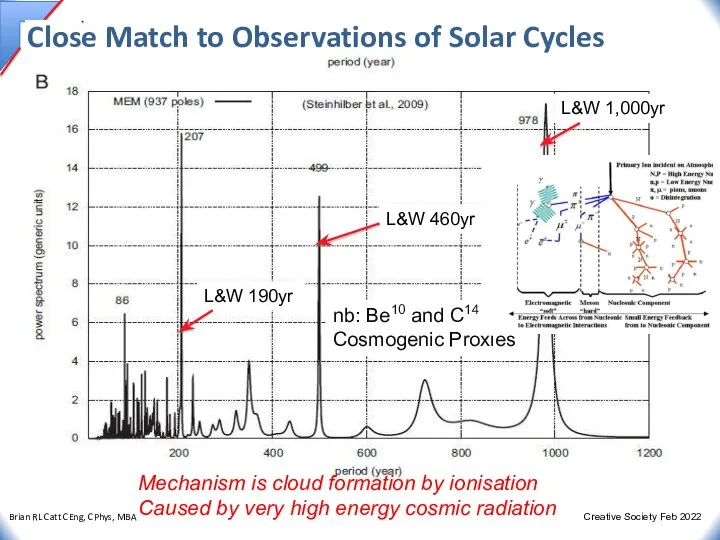
- 32. Close Match to Observations of Solar Cycles nb: Be10 and C14 Cosmogenic Proxies Mechanism is cloud
- 33. Summary: Climate is Continuously Changing Naturally, cyclically, on Multiple Frequencies, from multiple causes Primarily short term
- 35. Скачать презентацию














 Методы изучения космического пространства
Методы изучения космического пространства Солнце, Луна
Солнце, Луна Звезды и созвездия. Небесные координаты. Звездные карты
Звезды и созвездия. Небесные координаты. Звездные карты «Вселенная» 5 класс
«Вселенная» 5 класс Небесные тела Выполнила ученица МБОУ СОШ № 8 г. Каменск-Шахтинского Кадыкова Олеся
Небесные тела Выполнила ученица МБОУ СОШ № 8 г. Каменск-Шахтинского Кадыкова Олеся  Фізичні характеристики зір
Фізичні характеристики зір Занятия по развитию речи Космос
Занятия по развитию речи Космос Галактики - презентация по Астрономии скачать бесплатно
Галактики - презентация по Астрономии скачать бесплатно Особенность астрономии и ее методов
Особенность астрономии и ее методов Звездные умники и умницы
Звездные умники и умницы Астрономія Робота учня 11-А класу Демченка Ігоря
Астрономія Робота учня 11-А класу Демченка Ігоря  Башкирский экономико-юридический колледж Экзопланеты
Башкирский экономико-юридический колледж Экзопланеты Європа – супутник Юпітера
Європа – супутник Юпітера  Арудхи
Арудхи Добро пожаловать в космос
Добро пожаловать в космос Моё большое космическое путешествие
Моё большое космическое путешествие Дослідження Венери
Дослідження Венери  Муниципальное общеобразовательное бюджетное учреждение основная общеобразовательная школа № 24 х. Северокавказский Вандин
Муниципальное общеобразовательное бюджетное учреждение основная общеобразовательная школа № 24 х. Северокавказский Вандин  Астероиды - презентация по Астрономии скачать бесплатно
Астероиды - презентация по Астрономии скачать бесплатно Планеты-Гиганты, Общая характеристика
Планеты-Гиганты, Общая характеристика Вся Солнечная система
Вся Солнечная система XXVI Всероссийская олимпиада школьников по астрономии. Практический тур
XXVI Всероссийская олимпиада школьников по астрономии. Практический тур Космонавтика как объект философского анализа
Космонавтика как объект философского анализа Способы исследования космического пространства
Способы исследования космического пространства Сын Земли. Юрий Алексеевич Гагарин (9 марта 1934 - 27 марта 1968)
Сын Земли. Юрий Алексеевич Гагарин (9 марта 1934 - 27 марта 1968) Склад атмосфери та значення атмосферного тиску на планетах Сонячної системи
Склад атмосфери та значення атмосферного тиску на планетах Сонячної системи Звездное небо
Звездное небо  Лунная база
Лунная база