Содержание
- 2. Lecture objectives How does the economy operate in short-run and in long-run? What are the main
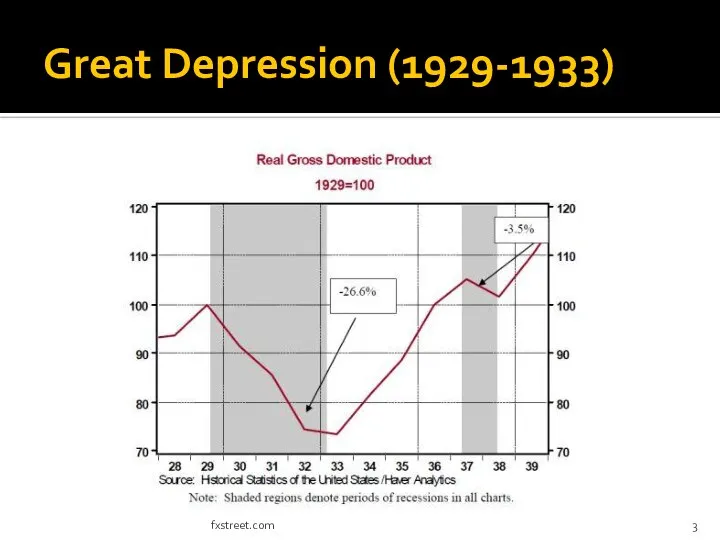
- 3. Great Depression (1929-1933) fxstreet.com
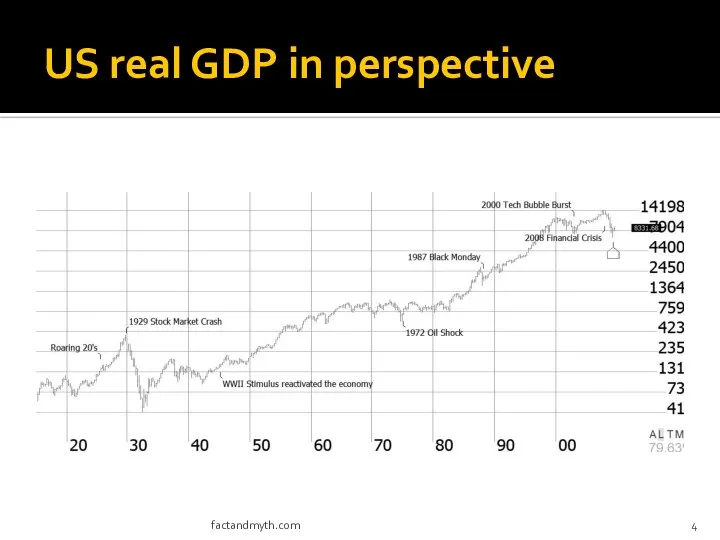
- 4. US real GDP in perspective factandmyth.com
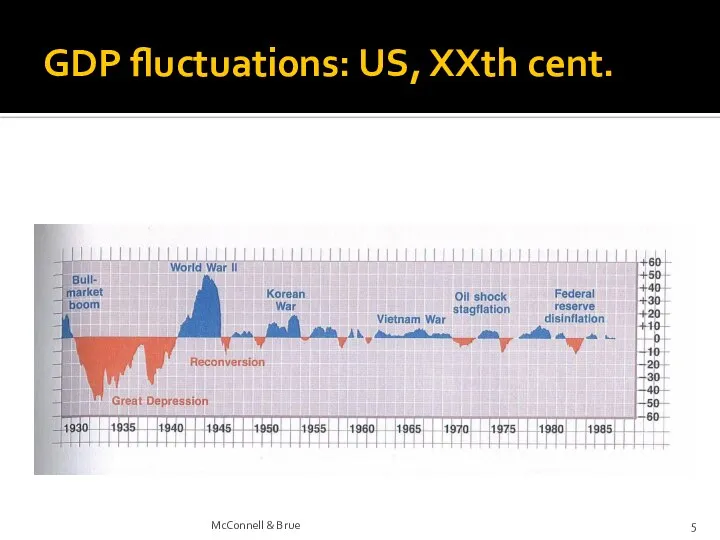
- 5. GDP fluctuations: US, XXth cent. McConnell & Brue
- 6. Business (economic) cycle Business cycle refers to the expansions and contractions in the economic activity (basically
- 7. US real GDP: key findings GDP ups and downs repeat in a cyclical way Yet, GDP
- 8. The essence of macroeconomics GDP behavior (both short-run and long-run) is at the heart of macroeconomic
- 9. Causes of economic cycles Spontaneous shifts in private spending Economic policy of government External shocks Disasters
- 10. Causes of long-run GDP increase Growing substance of production factors: labour, capital, technology.
- 11. Basic macroeconomic indicators GDP change (economic growth) Unemployment Inflation
- 12. Gross domestic product (GDP) GDP is the market value of the final goods and services produced
- 13. Economic growth rate Economic growth rate is the annual percentage change of real GDP.
- 14. Expanssion and recession Periods of positive real GDP growth are called expansions. Periods of negative real
- 15. Peak and through Periodic maximum of real GDP is called peak. Periodic minimum of real GDP
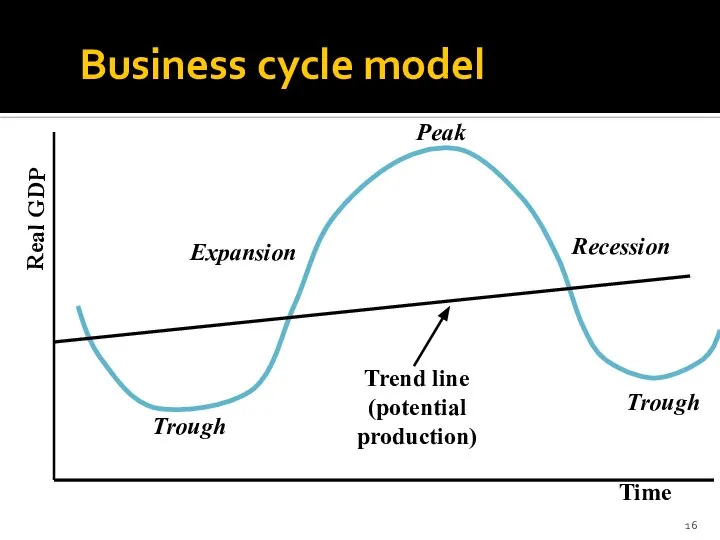
- 16. Business cycle model Time Real GDP Trough Expansion Peak Recession Trough Trend line (potential production)
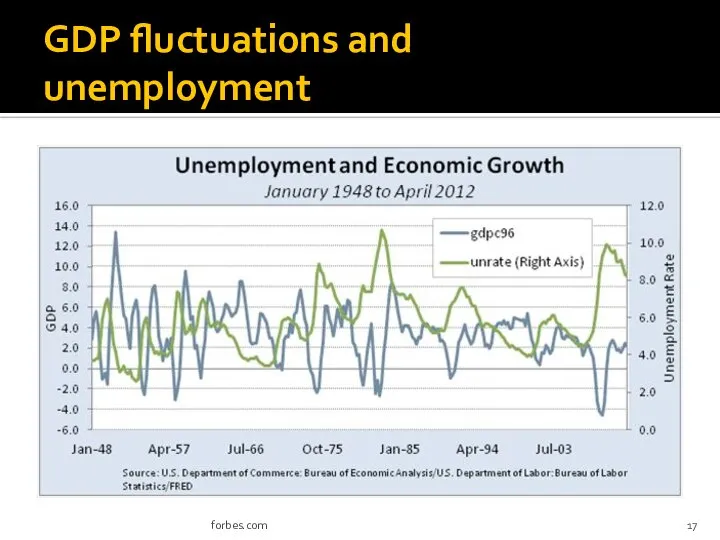
- 17. GDP fluctuations and unemployment forbes.com
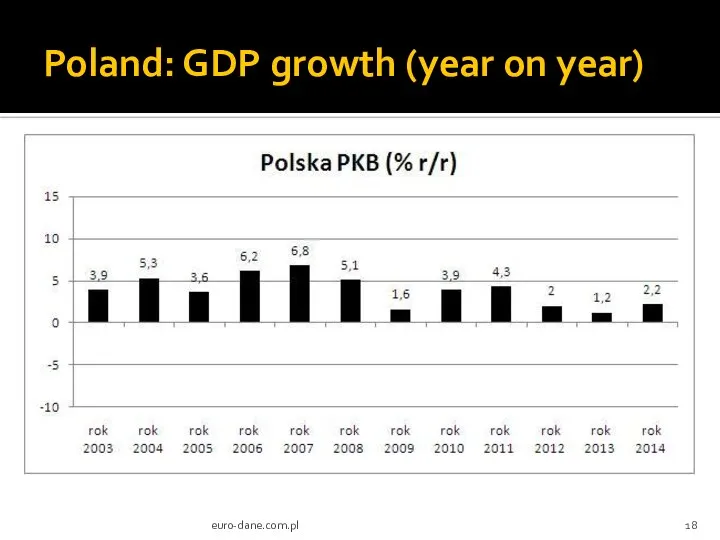
- 18. Poland: GDP growth (year on year) euro-dane.com.pl
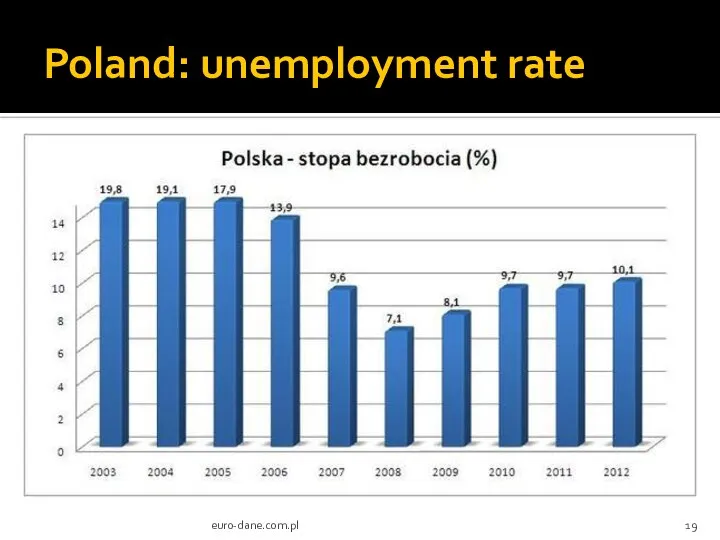
- 19. Poland: unemployment rate euro-dane.com.pl
- 20. GDP fluctuations and unemployment (short-run model) GDP change and unemployment are inversely related: as GDP increases,
- 21. GDP fluctuations and inflation (short-run model) Decrease in GDP usually leads to lower inflation (long-lasting GDP
- 22. Economic growth and inflation: the case of Latvia 2005 and Japan 2001 LATVIA: Real GDP growth
- 23. Unemployment-inflation trade-off in short-run Recession is normally accompanied by rising unemployment, yet inflation decelerates. Expanssion is
- 24. Potential production vs. actual production: additional perspective Potential GDP is the value of real GDP that
- 25. „Economic overheating”: US economy during Vietnam War In the mid-1960s US economy was at full employment.
- 26. Summary: macroeconomic goals GDP growth Full employment Stable prices
- 27. Check point: true / false test The period of time during which real GDP increases in
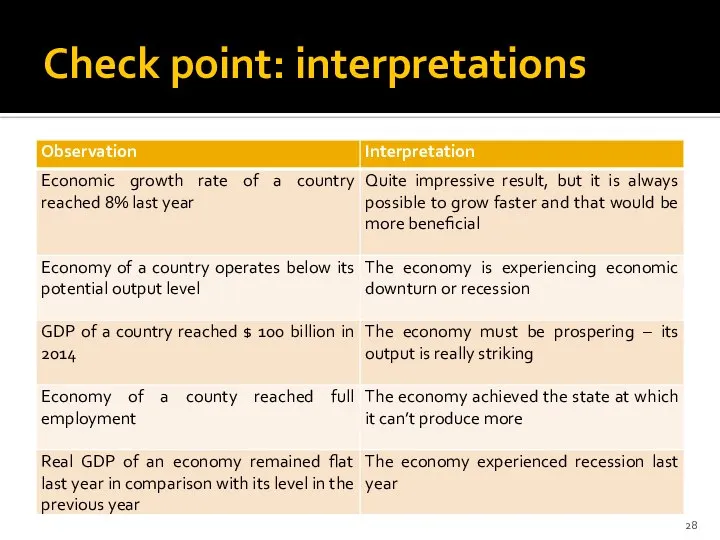
- 28. Check point: interpretations
- 29. Lecture objectives How does economy operate in short-run and in long-run? What are the main indicators
- 31. Скачать презентацию




















 Североамериканская интеграция (НАФТА)
Североамериканская интеграция (НАФТА) Место России в мировой экономике
Место России в мировой экономике Положение Грузии на туристическом рынке
Положение Грузии на туристическом рынке Продовольственная проблема
Продовольственная проблема Предмет и метод экономической теории
Предмет и метод экономической теории Сравнительный анализ эффективности макроэкономической политики в закрытой экономике. Лекция 14
Сравнительный анализ эффективности макроэкономической политики в закрытой экономике. Лекция 14 Применение БПЛА для анализа состояния и контроля использования земельных ресурсов
Применение БПЛА для анализа состояния и контроля использования земельных ресурсов Проблемы занятости и безработицы
Проблемы занятости и безработицы Риск и неопределенность
Риск и неопределенность Демографическая ситуация в современной России
Демографическая ситуация в современной России Зарубежные методы и инструменты стратегического государственного управления на примере Сингапура
Зарубежные методы и инструменты стратегического государственного управления на примере Сингапура Фирмы в экономике
Фирмы в экономике Статистическое изучение взаимосвязей. Корреляционный и регрессионный анализ
Статистическое изучение взаимосвязей. Корреляционный и регрессионный анализ Конкурентоспособность предприятия и пути ее повышения (на примере ООО «Тополёк»)
Конкурентоспособность предприятия и пути ее повышения (на примере ООО «Тополёк») Импорт и экспорт Южной Кореи и стран лидеров (1970-2013 г.г.)
Импорт и экспорт Южной Кореи и стран лидеров (1970-2013 г.г.) Экономический рост
Экономический рост Four types of econmic systems
Four types of econmic systems Презентация Психологические особенности Группового мнения
Презентация Психологические особенности Группового мнения Глобализация. Основные направления глобализации
Глобализация. Основные направления глобализации Домашнее задание на 20 декабря. Курс микроэкономики
Домашнее задание на 20 декабря. Курс микроэкономики Роль государства в экономике
Роль государства в экономике Об итогах развития потребительского рынка муниципального образования
Об итогах развития потребительского рынка муниципального образования Optimálna veľkosť objednávky
Optimálna veľkosť objednávky Теория потребительского выбора
Теория потребительского выбора Сельское хозяйство Великобритании
Сельское хозяйство Великобритании Социальные проекты поддержки моногородов России
Социальные проекты поддержки моногородов России Американская рыночная экономика
Американская рыночная экономика Влияние социально-экономического кризиса на здоровье населения как условия трудового потенциала Южно-Казахстанской области
Влияние социально-экономического кризиса на здоровье населения как условия трудового потенциала Южно-Казахстанской области