Содержание
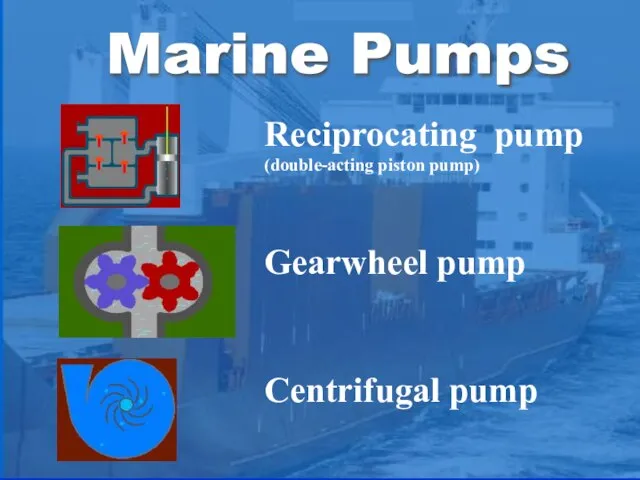
- 2. Marine Pumps Reciprocating pump (double-acting piston pump) Gearwheel pump Centrifugal pump
- 3. NON-RETURN VALVES Delivery lines and discharge lines to and from the pump are often fitted with
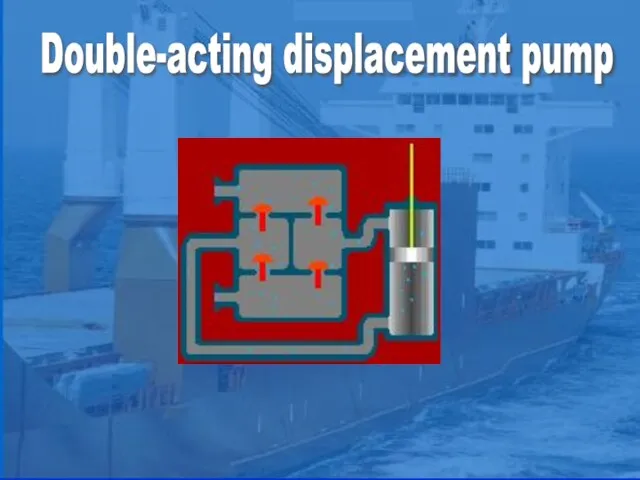
- 4. Double-acting displacement pump
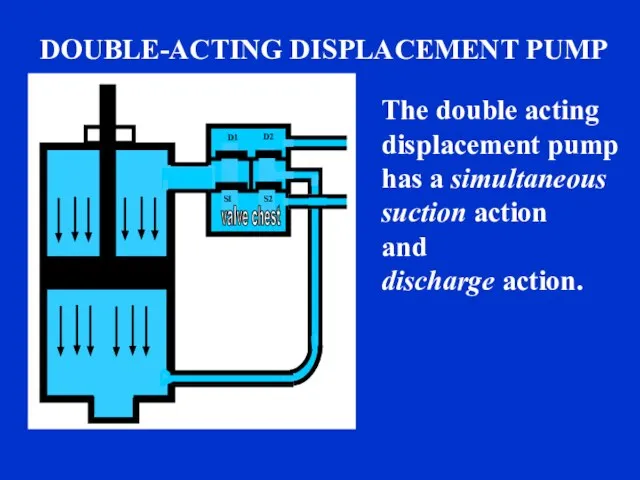
- 5. sound DOUBLE-ACTING DISPLACEMENT PUMP The double acting displacement pump has a simultaneous suction action and discharge
- 6. The volumes of the pump chambers are increased and decreased by the reciprocating motion of the
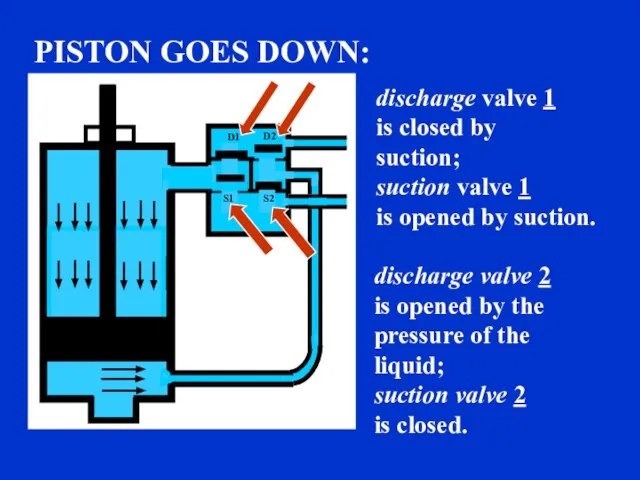
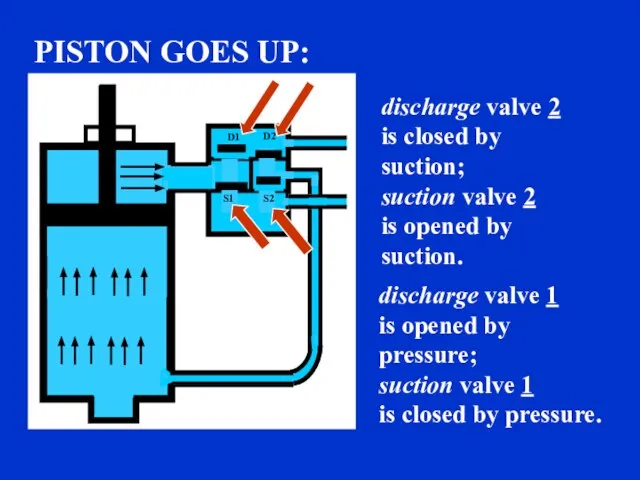
- 7. discharge valve 1 is closed by suction; suction valve 1 is opened by suction. discharge valve
- 8. discharge valve 2 is closed by suction; suction valve 2 is opened by suction. discharge valve
- 9. Gearwheel pump
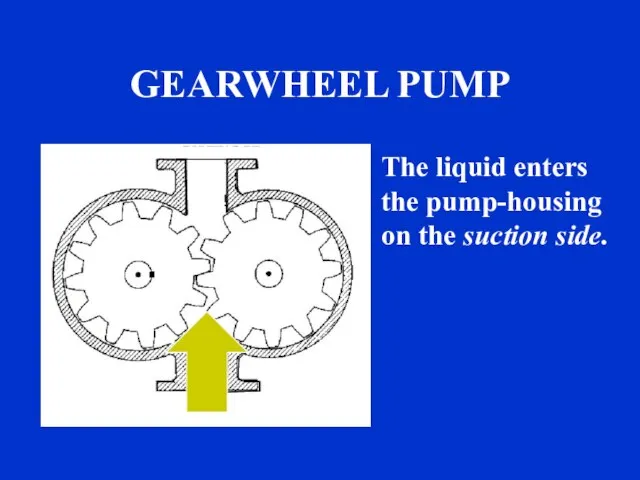
- 10. The liquid enters the pump-housing on the suction side.
- 11. GEARWHEEL PUMP s The liquid is carried around between the teeth of the gearwheels.
- 12. The liquid is discharged through the discharge line . GEARWHEEL PUMP
- 13. Centrifugal pump
- 14. CENTRIFUGAL PUMP The liquid enters the pump house through the suction intake .
- 15. The rotating impeller causes a centrifugal force. CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
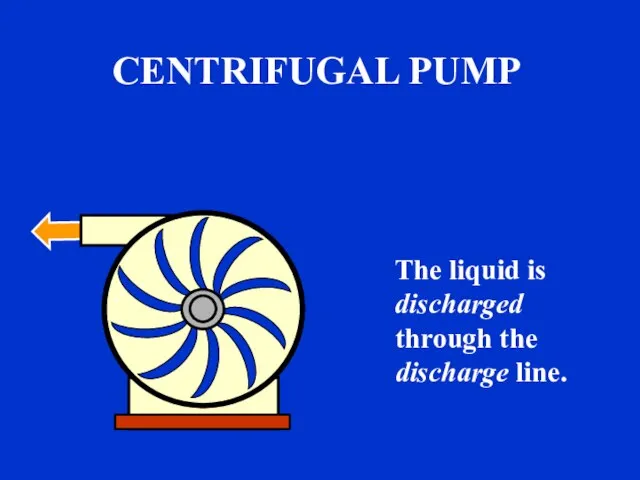
- 16. The liquid is discharged through the discharge line. CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
- 17. The Anchor Winch shafts band brakes gearwheels warping drums cable lifters dog clutches
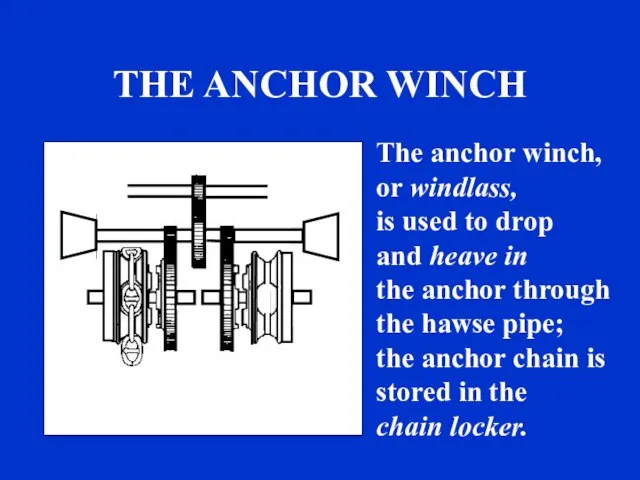
- 18. THE ANCHOR WINCH The anchor winch, or windlass, is used to drop and heave in the
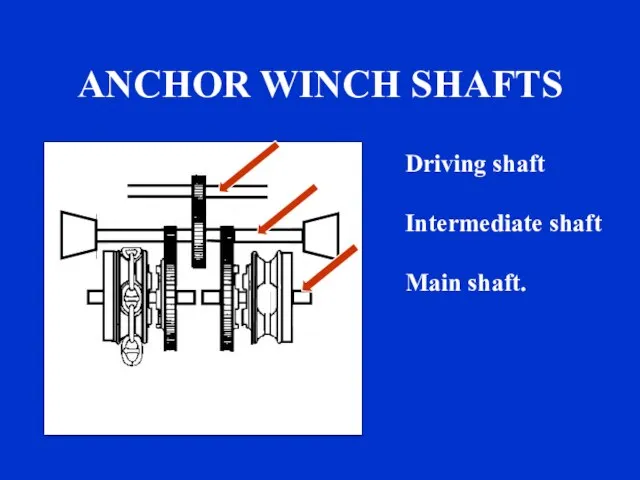
- 19. ANCHOR WINCH SHAFTS Driving shaft Intermediate shaft Main shaft. sound
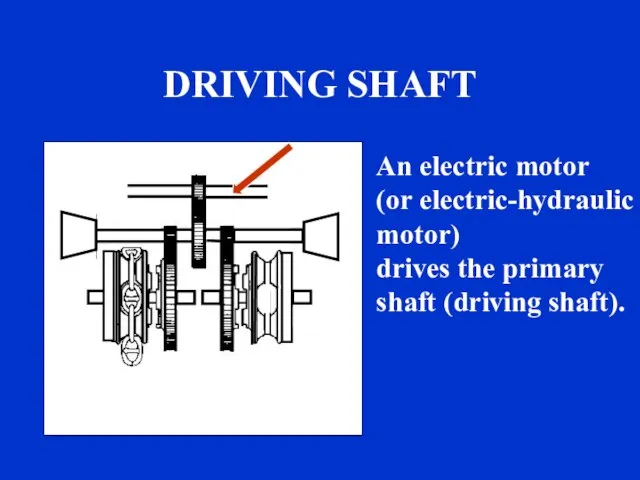
- 20. s DRIVING SHAFT An electric motor (or electric-hydraulic motor) drives the primary shaft (driving shaft).
- 21. INTERMEDIATE SHAFT At the extremities of the intermediate shaft are the warping drums. Warping drums are
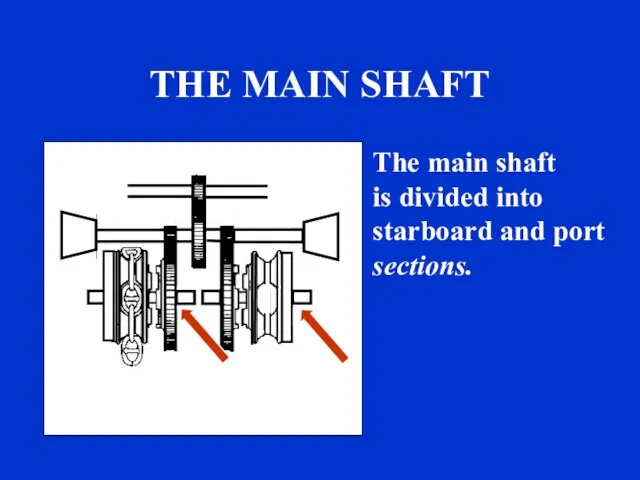
- 22. THE MAIN SHAFT The main shaft is divided into starboard and port sections. sound
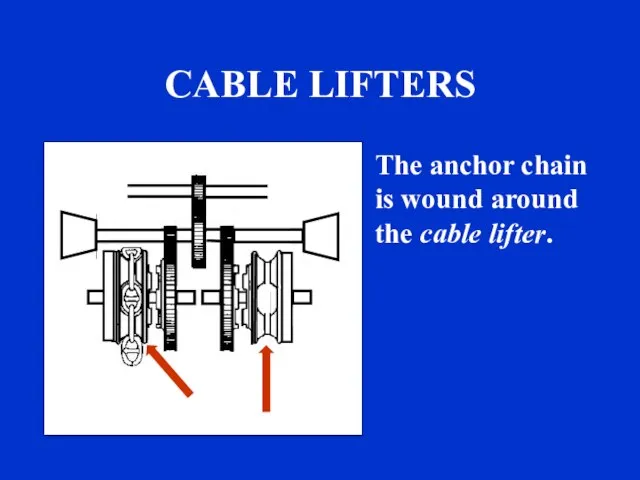
- 23. CABLE LIFTERS The anchor chain is wound around the cable lifter. sound
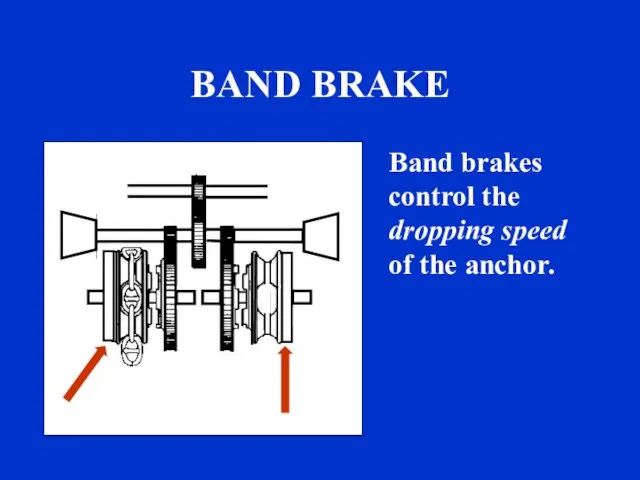
- 24. BAND BRAKE Band brakes control the dropping speed of the anchor. sound
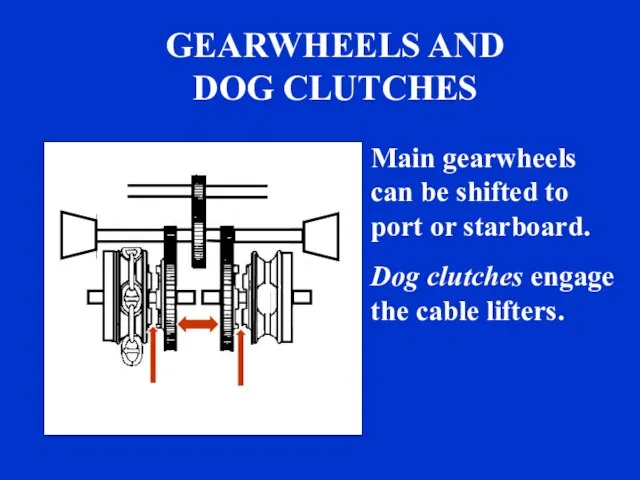
- 25. GEARWHEELS AND DOG CLUTCHES Main gearwheels can be shifted to port or starboard. sound Dog clutches
- 26. s the steering engine
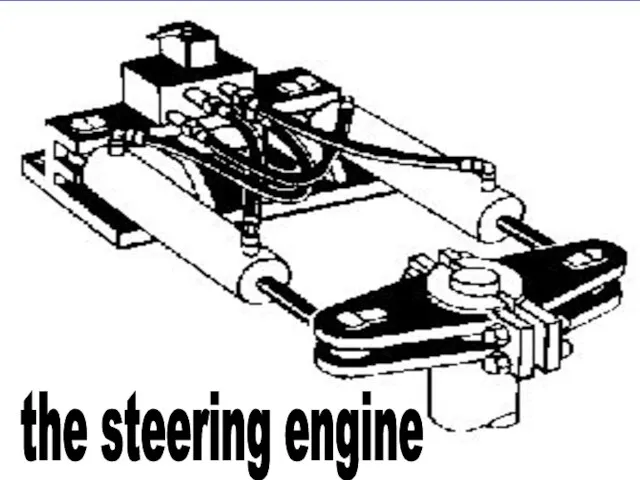
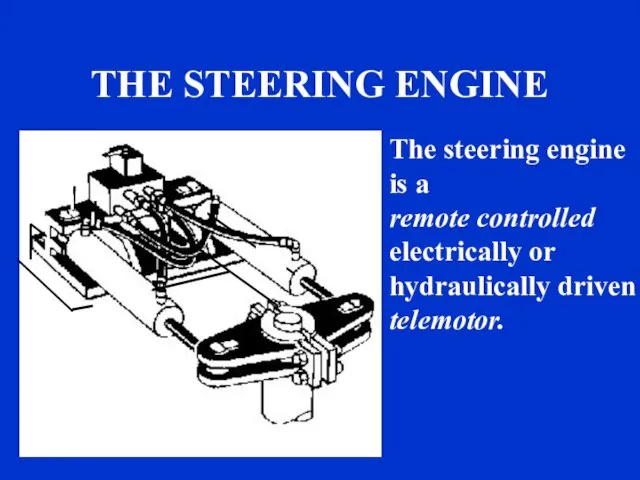
- 27. THE STEERING ENGINE The steering engine is a remote controlled electrically or hydraulically driven telemotor. sound
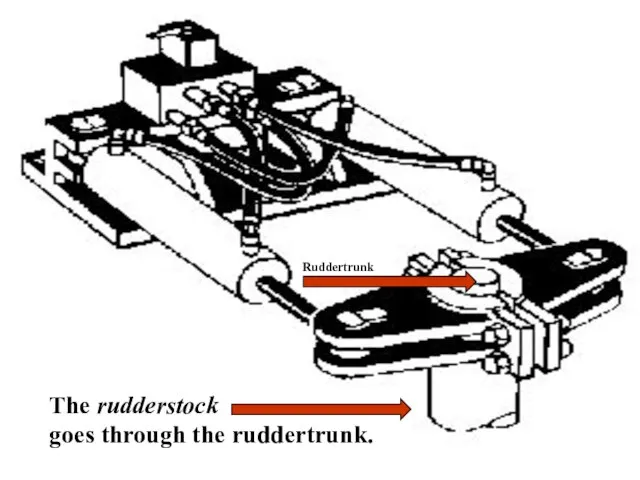
- 28. sound The rudderstock goes through the ruddertrunk. Ruddertrunk
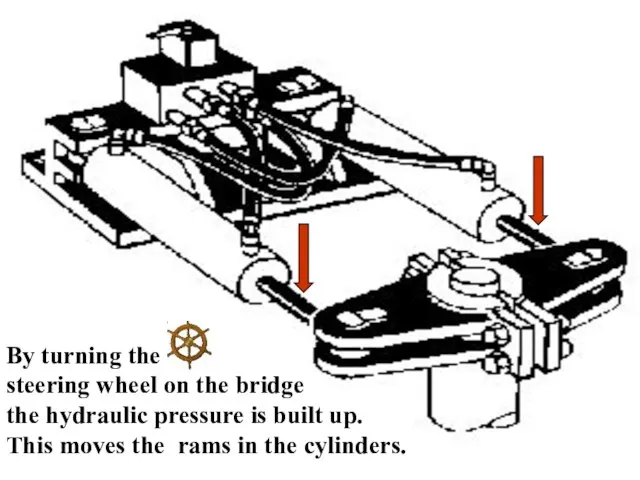
- 29. By turning the steering wheel on the bridge the hydraulic pressure is built up. This moves
- 30. Exhaust gas boilers s
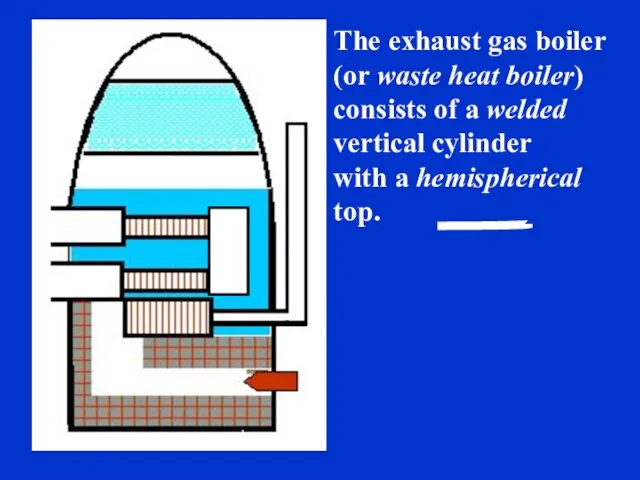
- 31. The exhaust gas boiler (or waste heat boiler) consists of a welded vertical cylinder with a
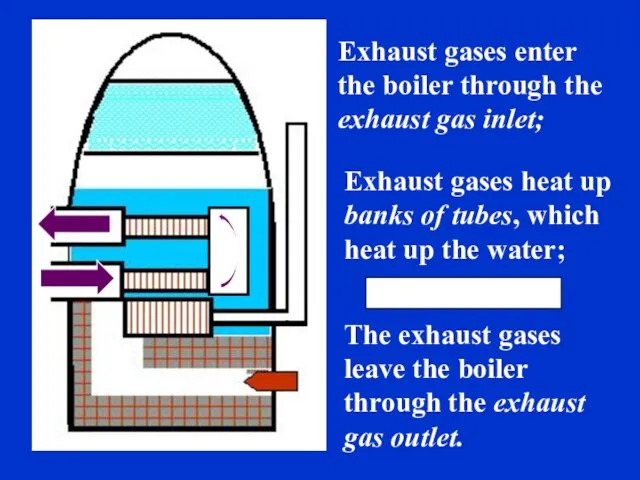
- 32. Exhaust gases enter the boiler through the exhaust gas inlet; Exhaust gases heat up banks of
- 33. Water turns to steam, which is used to produce energy for heating purposes, or even for
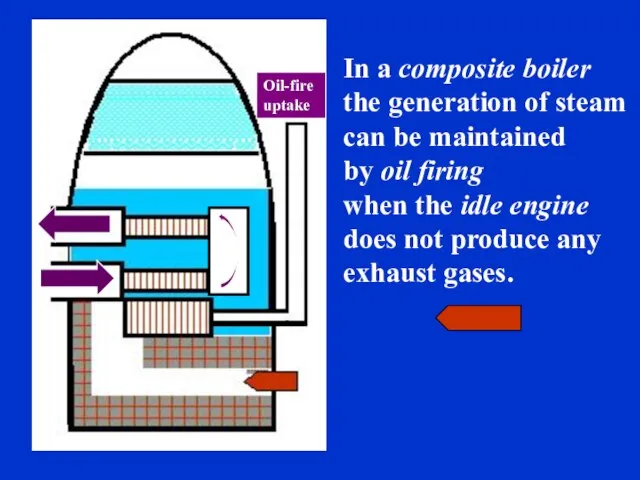
- 34. In a composite boiler the generation of steam can be maintained by oil firing when the
- 35. s Generators and Electric motors
- 36. sound A generator produces either alternating current (A/C) or direct current (D/C). THE GENERATOR
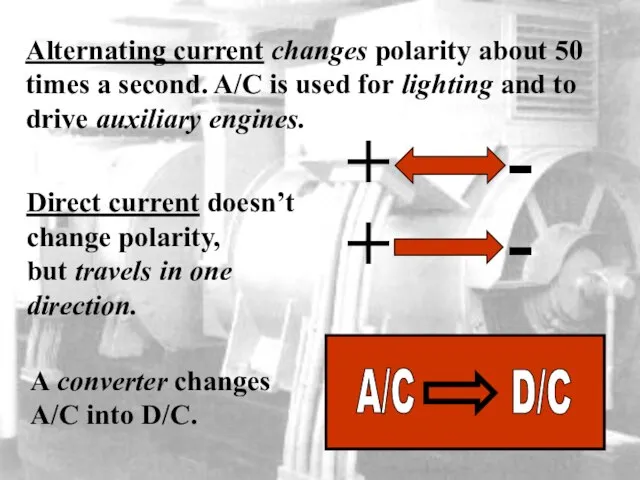
- 37. Alternating current changes polarity about 50 times a second. A/C is used for lighting and to
- 38. sound A transformer increases the voltage (step-up) or reduces the voltage (step-down) THE TRANSFORMER
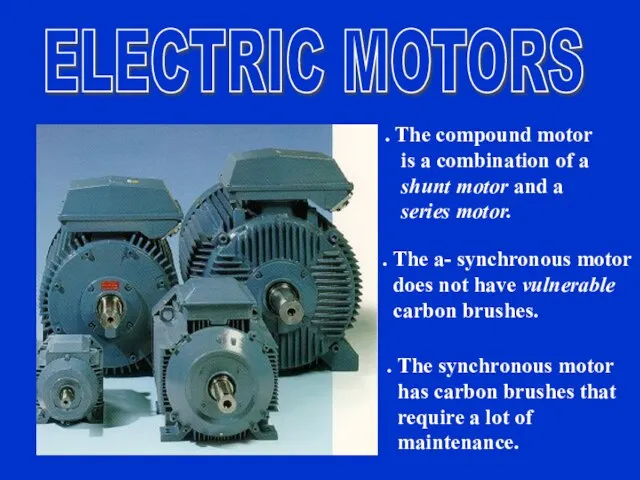
- 39. . The compound motor is a combination of a shunt motor and a series motor. .
- 40. sound The compound motor combines the advantages of the shunt motor and series motor: it has
- 41. sound sound The advantage of the a-synchronous motor is, that it doesn’t have carbon brushes and
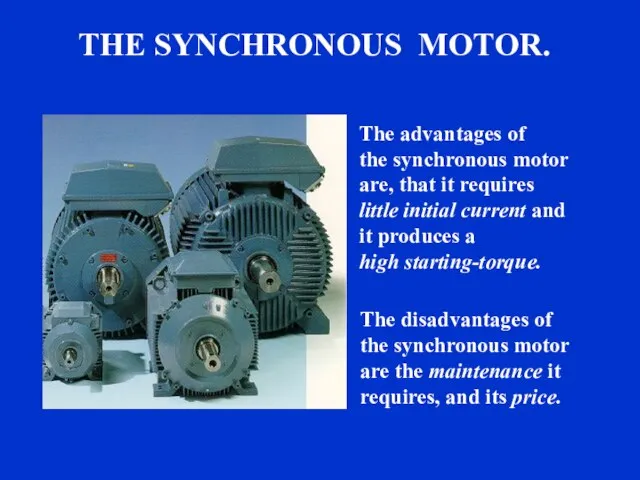
- 42. sound sound THE SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR. The advantages of the synchronous motor are, that it requires little
- 44. Скачать презентацию














 Валы и оси
Валы и оси Ближнепольная оптическая спектроскопия
Ближнепольная оптическая спектроскопия История создания пылесоса. «От швабры до пылесоса-робота»
История создания пылесоса. «От швабры до пылесоса-робота» Аттестационная работа. Бурение нефтяных и газовых скважин. Методика расчета утяжеленных бурильных труб
Аттестационная работа. Бурение нефтяных и газовых скважин. Методика расчета утяжеленных бурильных труб влажность воздуха
влажность воздуха Рентгеновское излучение
Рентгеновское излучение Петрофизика. Физико-механические свойства горных пород
Петрофизика. Физико-механические свойства горных пород МОУ «Котельниковская средняя общеобразовательная школа №1 имени Героя Советского Союза Л. Д. Чурилова. МОУ «Котельниковская сред
МОУ «Котельниковская средняя общеобразовательная школа №1 имени Героя Советского Союза Л. Д. Чурилова. МОУ «Котельниковская сред Устройство подвески Лада Веста
Устройство подвески Лада Веста Какая сила движет электрическими приборами
Какая сила движет электрическими приборами Введение в магнитостатику. Сила Лоренца
Введение в магнитостатику. Сила Лоренца Простые механизмы. Рычаг
Простые механизмы. Рычаг Аттестация 1-2012. Вопросы теста
Аттестация 1-2012. Вопросы теста Презентация по физике "Законы сохранения" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по физике "Законы сохранения" - скачать бесплатно Тепловое излучение и люминесценция
Тепловое излучение и люминесценция Инвариантность модуля скорости света в вакууме. Постулаты Эйнштейна. Пространство и время специальной теории. Занятие №77
Инвариантность модуля скорости света в вакууме. Постулаты Эйнштейна. Пространство и время специальной теории. Занятие №77 Проблемное обучение на уроках физики
Проблемное обучение на уроках физики Входной контроль 1. Одно и то же вещество может находиться только А) в твёрдом состоянии К) в жидком состоянии С) в газообразном со
Входной контроль 1. Одно и то же вещество может находиться только А) в твёрдом состоянии К) в жидком состоянии С) в газообразном со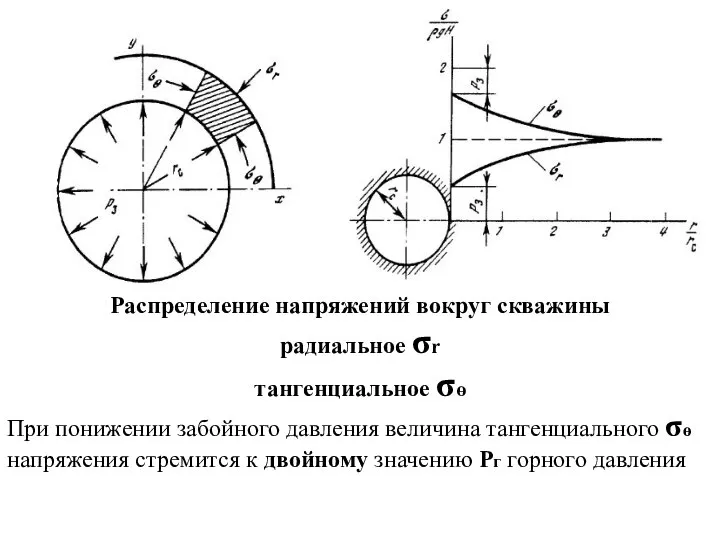 Распределение напряжений вокруг скважины
Распределение напряжений вокруг скважины Решение задачи изгиба многослойной упругопластической пластины
Решение задачи изгиба многослойной упругопластической пластины Дыбыс күшейту аппараттуралары
Дыбыс күшейту аппараттуралары Методы моментов. Метод сферических гармоник. Уравнение переноса в Р1-приближении. Диффузионное приближение
Методы моментов. Метод сферических гармоник. Уравнение переноса в Р1-приближении. Диффузионное приближение Презентация Применение конденсаторов
Презентация Применение конденсаторов  Двойной электрон-ядерный резонанс. Введение в теорию кристаллического поля
Двойной электрон-ядерный резонанс. Введение в теорию кристаллического поля Электроемкость и конденсаторы
Электроемкость и конденсаторы Модель сечения выведения для быстрых нейтронов. Сечение выведения гетерогенных сред. Основные предположения
Модель сечения выведения для быстрых нейтронов. Сечение выведения гетерогенных сред. Основные предположения Кипение. Температура кипения
Кипение. Температура кипения Основные уравнения движения жидкостей
Основные уравнения движения жидкостей