Содержание
- 2. The reactions accompanied by a change of atom oxidation number of elements are called oxidation-reduction reactions.
- 3. The particles which accept electrons are called oxidizers. The particles which donate electrons are called reducers.
- 4. Fе2+ + Се4+ ↔ Fе3+ + Се3+ Oxidized and reduced forms of one substance involved in
- 5. Electrode or redox potential (E) is the quantitative measure of redox power of different redox reactions.
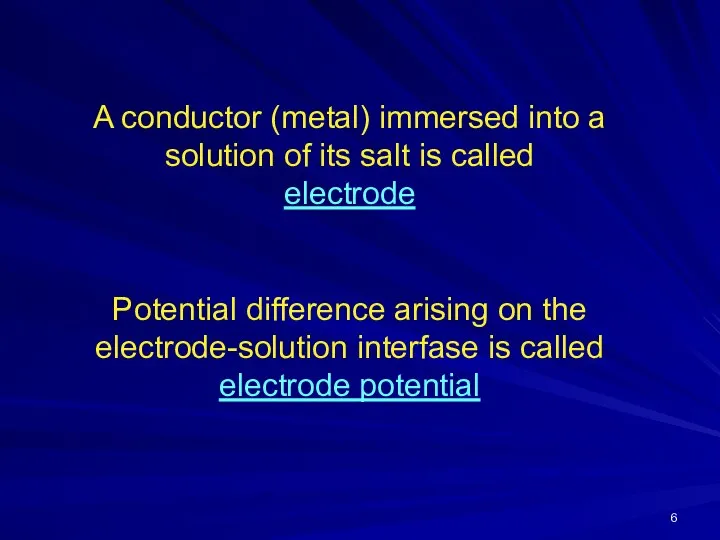
- 6. A conductor (metal) immersed into a solution of its salt is called electrode Potential difference arising
- 7. Potential difference between electrodes is known as electromotive force (EMF) EMF = Ecathode - Eanode
- 8. EMF of a chemical reaction is equal to difference between redox potentials of a redox couple
- 9. The potentials difference that occurs in the tissues of living organisms is called bioelectric potential.
- 11. Скачать презентацию







 Технические изобретения 17,18,19 и начало 20 века
Технические изобретения 17,18,19 и начало 20 века Задачи на движение
Задачи на движение Ядерная физика
Ядерная физика Излучение и спектры
Излучение и спектры Интегрированный урок по физике и математике
Интегрированный урок по физике и математике Презентация по физике "усилители" - скачать
Презентация по физике "усилители" - скачать  روشنایی فنی
روشنایی فنی Презентация Гравитационные силы решение задач
Презентация Гравитационные силы решение задач Громкость звука. 9 класс
Громкость звука. 9 класс Электростатика
Электростатика Кинематика. Нүкте кинематикасы. Қатты дене кинематикасы
Кинематика. Нүкте кинематикасы. Қатты дене кинематикасы Взаимодействие заряженных тел. Закон Кулона. Закон сохранения электрического заряда. Электрическое поле
Взаимодействие заряженных тел. Закон Кулона. Закон сохранения электрического заряда. Электрическое поле Тема: «Свинец глазами физика и химика». Выполнил ученик 11б класса МОУ «СОШ №27 с углублённым изучением отдельных предметов» Тар
Тема: «Свинец глазами физика и химика». Выполнил ученик 11б класса МОУ «СОШ №27 с углублённым изучением отдельных предметов» Тар Змінний струм. Генератор змінного струму
Змінний струм. Генератор змінного струму Кинетика ядерных реакторов
Кинетика ядерных реакторов Силы инерции
Силы инерции Электрические заряды. Способы получения зарядов. Закон сохранения электрического заряда
Электрические заряды. Способы получения зарядов. Закон сохранения электрического заряда Презентация по физике "Инструменты и приборы. Термометр" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Инструменты и приборы. Термометр" - скачать  Физика в быту
Физика в быту Расчет общего сопротивления цепи при смешанном соединении элементов (решение задач)
Расчет общего сопротивления цепи при смешанном соединении элементов (решение задач) Решение задач на тему «Движение под углом к горизонту» Авторы работы: Ершова А. Талдыкина А.
Решение задач на тему «Движение под углом к горизонту» Авторы работы: Ершова А. Талдыкина А. Проводниковые материалы. Классификация и применение. (Лекция 3.3)
Проводниковые материалы. Классификация и применение. (Лекция 3.3) Оптика. Корпускулярно-волновой дуализм
Оптика. Корпускулярно-волновой дуализм Основные методы анализа линейных электрических цепей постоянного тока
Основные методы анализа линейных электрических цепей постоянного тока Графическое изображение прямолинейного равноускоренного движения
Графическое изображение прямолинейного равноускоренного движения Организация текущего ремонта. Используемая документация. Тема 21
Организация текущего ремонта. Используемая документация. Тема 21 Физические повреждающие факторы внешней среды
Физические повреждающие факторы внешней среды Электромагнитная индукция
Электромагнитная индукция