Содержание
- 2. Geographical Isolation Geographic isolation is a term that refers to a population of animals, plants, or
- 3. Since the two groups are in their own unique ecosystems and each experience unique pressures, they
- 4. Geographic isolation can be caused by many factors such as: Isolation by Barriers Isolation by Distance
- 5. Isolation by Barriers The people of Finland, who are secluded to some degree from the rest
- 7. Isolation by Distance Cheetahs separated from a larger group mate with each other, resulting in a
- 9. Isolation after an Event An earthquake causes two populations to become separate from each other. Over
- 11. Isolation by Separation An isolated group of beetles on a hill only work, eat and mate
- 12. Examples Geographic isolation occurs when two populations of the same species are divided by some type
- 13. Population A happens to have more green fish than Population B. However, both groups are still
- 14. THANK YOU
- 15. How nervous system can be damaged ? The nervous system is vulnerable to various disorders. It
- 16. Signs and symptoms of nervous system disorders Persistent or sudden onset of a headache A headache
- 17. These are some branch of medicine that deals with such disorders Neurology Neurological surgery Neuroradiologists and
- 18. Neurology The branch of medicine that manages nervous system disorders is called neurology. The medical healthcare
- 19. Rehabilitation for neurological disorders The branch of medicine that provides rehabilitative care for patients with nervous
- 21. Скачать презентацию





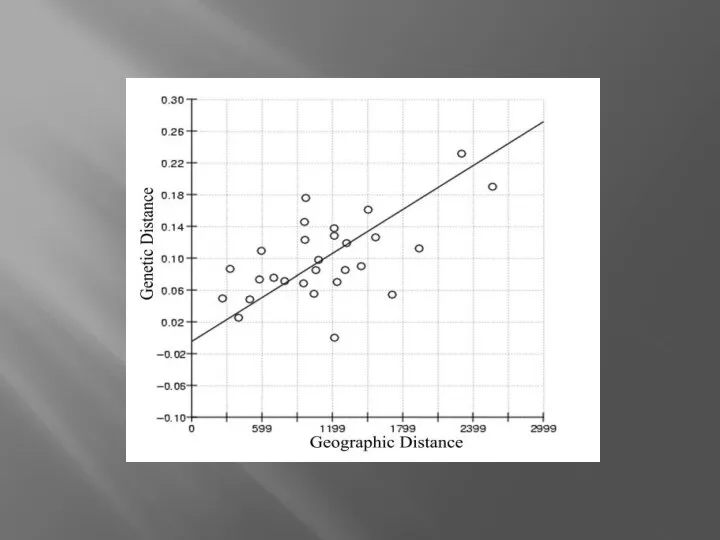










 Презентация Красная Книга
Презентация Красная Книга  Характеристика учеников 9 класса “а” школы 91 в соответствии с особенностями территорий, на которых они проживают
Характеристика учеников 9 класса “а” школы 91 в соответствии с особенностями территорий, на которых они проживают Загрязнение воды и последствия
Загрязнение воды и последствия окр. мир 2.03
окр. мир 2.03 Презентация на тему Что такое снег?
Презентация на тему Что такое снег?  Истоки и интонационное своеобразие фольклора. Этническая музыка
Истоки и интонационное своеобразие фольклора. Этническая музыка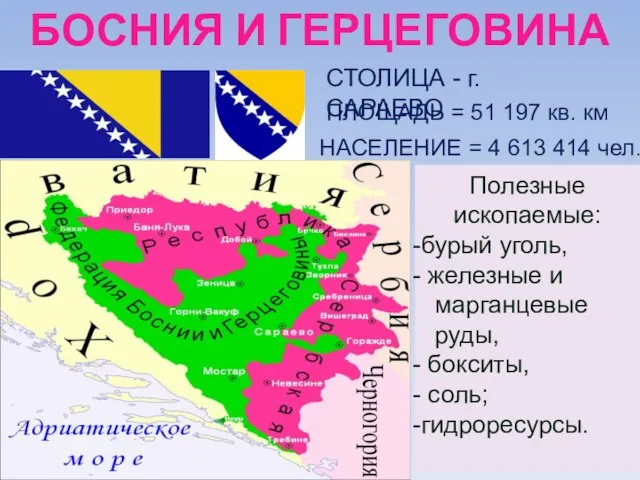 Босния и Герцеговина - презентация к уроку Географии
Босния и Герцеговина - презентация к уроку Географии Страна Польша
Страна Польша Животный мир Евразии
Животный мир Евразии Вермикулит
Вермикулит Система образования в мире и группе стран Подготовила: Крочак Виолетта Группа 1302
Система образования в мире и группе стран Подготовила: Крочак Виолетта Группа 1302 ИНДИЯ Презентация выполнена учеником 11 «В» класса Зверевым Вениамином
ИНДИЯ Презентация выполнена учеником 11 «В» класса Зверевым Вениамином  Имена русских путешественников на карте Мира
Имена русских путешественников на карте Мира Экономия воды-условие выживания человечества
Экономия воды-условие выживания человечества Республика Северная Осетия-Алания
Республика Северная Осетия-Алания Внутренние воды северной Америки 7 класс - презентация к уроку Географии_
Внутренние воды северной Америки 7 класс - презентация к уроку Географии_ Језера Србије
Језера Србије Пол и половая структура населения
Пол и половая структура населения Горные породы и минералы. Автор: Бурова Таня
Горные породы и минералы. Автор: Бурова Таня Острова и полуострова Евразии
Острова и полуострова Евразии Мегалополисы мира
Мегалополисы мира  Расы и народы земли
Расы и народы земли Приспособляемость живых организмов к суровым условиям Антарктиды
Приспособляемость живых организмов к суровым условиям Антарктиды Тахеометрическая съемка
Тахеометрическая съемка Работу выполнили ученики 10 класса
Работу выполнили ученики 10 класса Презентация на тему Благовещенск
Презентация на тему Благовещенск  Дания
Дания «Красная Поляна» курорт мирового уровня
«Красная Поляна» курорт мирового уровня