Содержание
- 2. Module Overview Overview of Message Transport and Routing Planning and Configuring Message Transport Managing Transport Rules
- 3. Lesson 1: Overview of Message Transport and Routing Message Transport Services Message Transport Components Message-Routing Changes
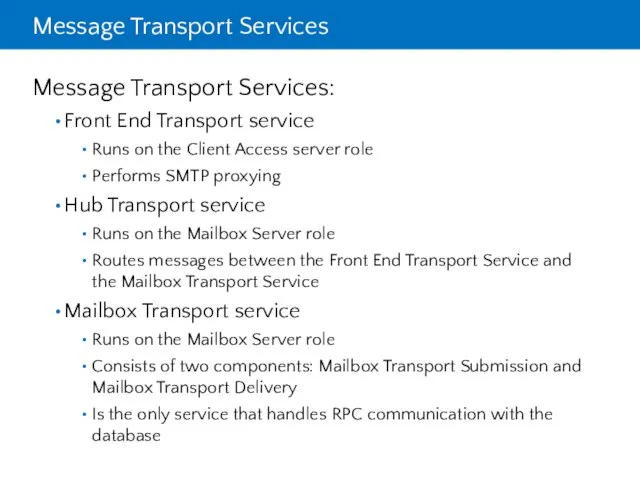
- 4. Message Transport Services Message Transport Services: Front End Transport service Runs on the Client Access server
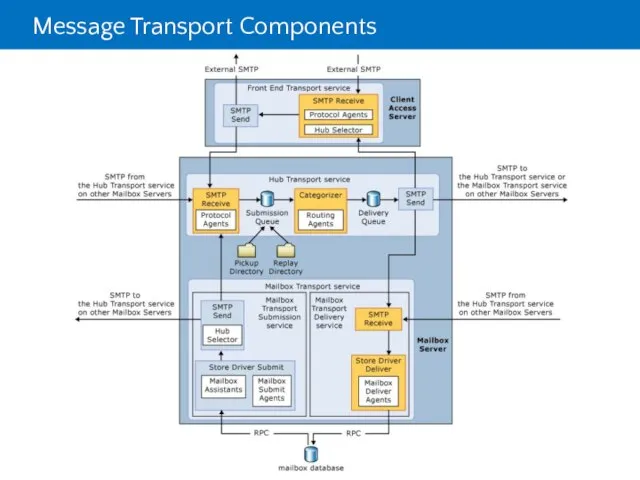
- 5. Message Transport Components
- 6. Message-Routing Changes in Exchange Server 2013 Changes in message routing in Exchange 2013 are: Routing is
- 7. Routing Destinations and Delivery Groups Routing destinations: Mailbox database Connector Distribution group expansion server Delivery Groups:
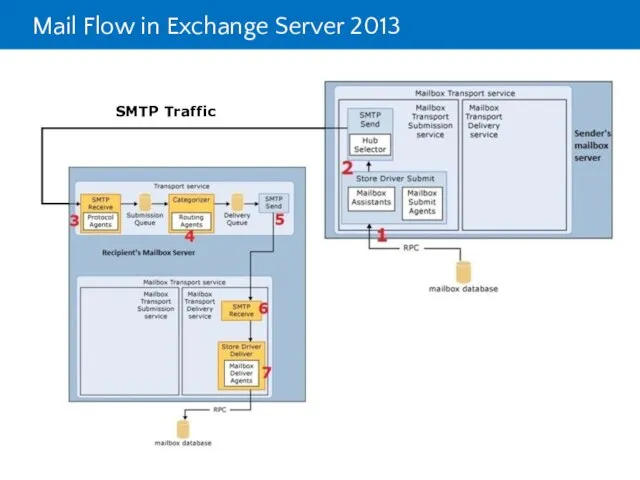
- 8. Mail Flow in Exchange Server 2013 SMTP SMTP Traffic
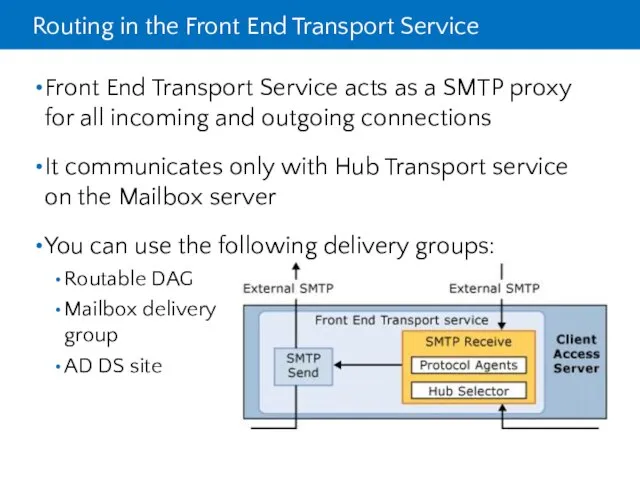
- 9. Routing in the Front End Transport Service Front End Transport Service acts as a SMTP proxy
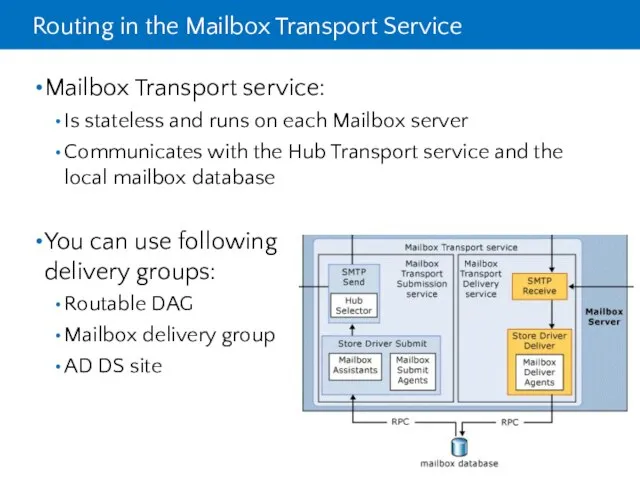
- 10. Routing in the Mailbox Transport Service Mailbox Transport service: Is stateless and runs on each Mailbox
- 11. Modifying the Default Message Flow You can modify default message flow by performing the following: Configuring
- 12. Tools for Troubleshooting SMTP Message Delivery Queue Viewer Use to view and manage undelivered messages Tracking
- 13. Demonstration: How to Troubleshoot SMTP Message Delivery In this demonstration, you will see how to use
- 16. What Are Transport Agents? Transport agents process email messages that pass through the transport pipeline Default
- 17. Lesson 2: Planning and Configuring Message Transport Planning Exchange Messaging Transport Demonstration: Reviewing Mail-Flow Settings Planning
- 18. Planning Exchange Messaging Transport You can manage message transport on: Client Access server Mailbox server Edge
- 19. Demonstration: Reviewing Mail-Flow Settings In this demonstration, you will see available options for managing message flow
- 20. Planning Accepted Domains and Remote Domains Accepted domains define SMTP domain names for which the Exchange
- 21. Demonstration: Creating and Configuring Accepted and Remote Domains In this demonstration, you will see how to
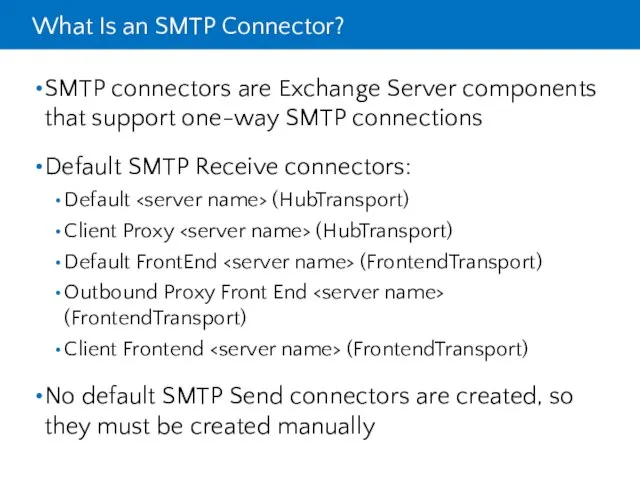
- 22. What Is an SMTP Connector? SMTP connectors are Exchange Server components that support one-way SMTP connections
- 23. Demonstration: How to Create and Configure SMTP Connectors In this demonstration, you will see how to
- 25. What Are Foreign Connectors? To send messages to non-SMTP messaging system, you can use the Foreign
- 26. Lesson 3: Managing Transport Rules What Are Transport Rules? Configuring Transport Rules Planning Transport Rules Demonstration:
- 27. What Are Transport Rules? Transport rules restrict message flow or modify message contents for messages in
- 28. Configuring Transport Rules Transport rules have the following components that you should configure: Conditions Specify which
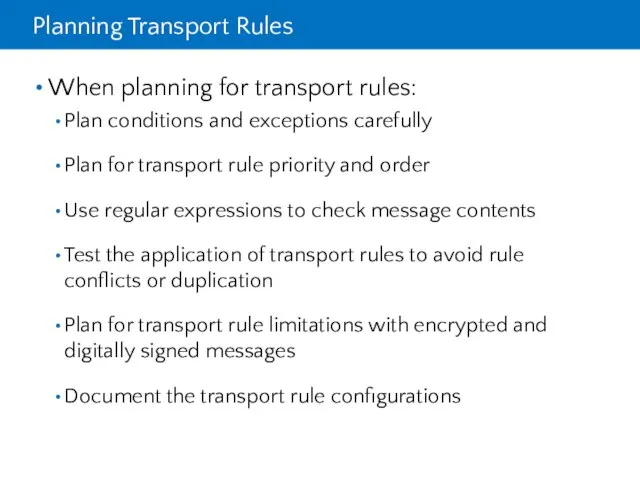
- 29. Planning Transport Rules When planning for transport rules: Plan conditions and exceptions carefully Plan for transport
- 30. Demonstration: Creating Transport Rules In this demonstration, you will see how to create a Transport rule
- 32. What Are Data-Loss Prevention Policies? Data Loss Protection policies enforce compliance requirements for business-critical data being
- 33. Demonstration: Configuring Data Loss Protection Policies In this demonstration, you will see how to create custom
- 35. Lab: Planning and Configuring Message Transport Exercise 1: Configuring Message Transport Exercise 2: Troubleshooting Message Delivery
- 36. Lab Scenario You are a messaging administrator in A. Datum Corporation, which is a large multinational
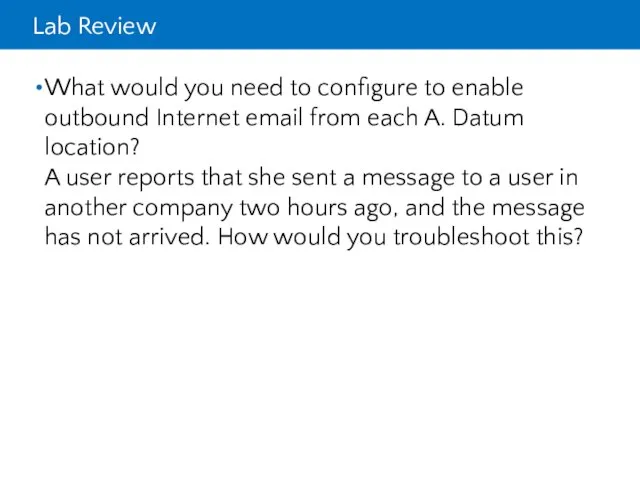
- 37. Lab Review What would you need to configure to enable outbound Internet email from each A.
- 39. Скачать презентацию

























 Prezentatsia_4 (1)
Prezentatsia_4 (1) Алгоритм с ветвлением. Исполнитель робот
Алгоритм с ветвлением. Исполнитель робот Презентация "Блок-схемы алгоритмов" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Блок-схемы алгоритмов" - скачать презентации по Информатике Презентация "Кодирование информации" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Кодирование информации" - скачать презентации по Информатике Создание БД и таблиц в СУБД. Понятие ключевого поля и индекса. Типы данных. Свойства полей
Создание БД и таблиц в СУБД. Понятие ключевого поля и индекса. Типы данных. Свойства полей Последовательный порт. Архитектура персональных компьютеров
Последовательный порт. Архитектура персональных компьютеров Алгоритмическая конструкция. Ветвление
Алгоритмическая конструкция. Ветвление Информационное обеспечение прогнозирования
Информационное обеспечение прогнозирования Разработка web-представительства агентства недвижимости
Разработка web-представительства агентства недвижимости Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа внеурочной деятельности по информатике Занимательная компьютерная графика
Аттестационная работа. Образовательная программа внеурочной деятельности по информатике Занимательная компьютерная графика Проектировка и разработка игры в жанре RPG
Проектировка и разработка игры в жанре RPG Что умеет компьютер
Что умеет компьютер Международная электронная платёжная система Wallet One (единый кошелёк)
Международная электронная платёжная система Wallet One (единый кошелёк)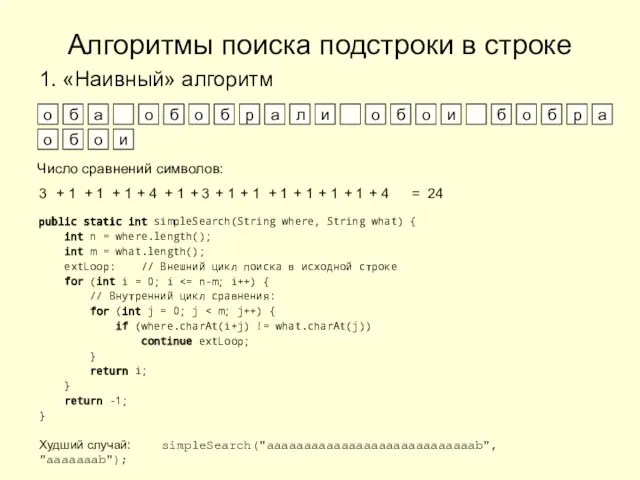 Алгоритмы поиска подстроки в строке
Алгоритмы поиска подстроки в строке Бесплатные аналоги коммерческих программ для Windows Подготовила учитель информатики МОУ «ООШ №10» Нестеренко Е.С.
Бесплатные аналоги коммерческих программ для Windows Подготовила учитель информатики МОУ «ООШ №10» Нестеренко Е.С. Типы данных
Типы данных Оформление презентаций
Оформление презентаций Основы работы MS Excel
Основы работы MS Excel Создание документов средствами on-line сервисов
Создание документов средствами on-line сервисов Контент для социальных сетей
Контент для социальных сетей Технологии 3D печати и тенденции их развития
Технологии 3D печати и тенденции их развития Базы данных и СУБД. Модели данных. Реляционная модель данных
Базы данных и СУБД. Модели данных. Реляционная модель данных Радиопрограмма Адреса милосердия союз НКО и социального СМИ
Радиопрограмма Адреса милосердия союз НКО и социального СМИ Кодирование информации ( шифровка информации ) Подготовила: Беломестнова Марина Вадимовна учитель начальных классов МОУ ООШ № 1
Кодирование информации ( шифровка информации ) Подготовила: Беломестнова Марина Вадимовна учитель начальных классов МОУ ООШ № 1 Классификация информационных систем
Классификация информационных систем CSS Properties. The position property
CSS Properties. The position property Презентация на тему: Графология как инструмент кадрового менеджмента.
Презентация на тему: Графология как инструмент кадрового менеджмента. База данных. Прикладная среда-система управления базой данных Аccess.
База данных. Прикладная среда-система управления базой данных Аccess.