Содержание
- 2. What to do with records? Declaring records Accessing records Accessing the field of a record What
- 3. Records Recall that elements of arrays must all be of the same type In some situations,
- 4. Records RECORDS are used to group related components of different types Components of the record are
- 5. Records C++ struct structured data type fixed number of components elements accessed by name, not by
- 6. Declaring struct Variables Given Declare : struct part_struct { char descrip [31], part_num [11]; float unit_price;
- 7. Accessing Components Use the name of the record the name of the member separated by a
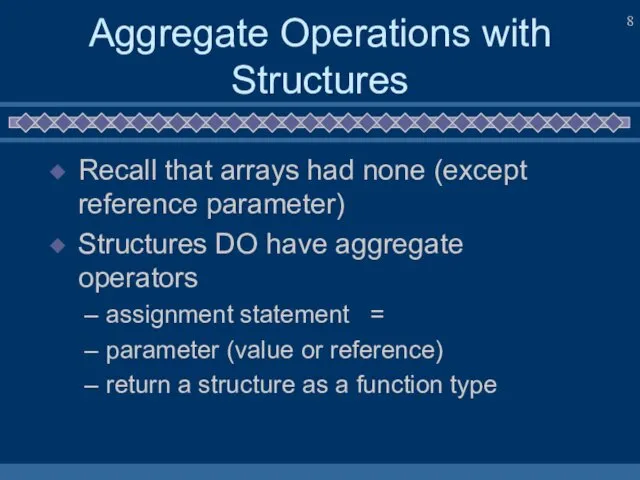
- 8. Aggregate Operations with Structures Recall that arrays had none (except reference parameter) Structures DO have aggregate
- 9. Aggregate Operations with Structures Limitations on aggregate operations no I/O no arithmetic operations no comparisons cout
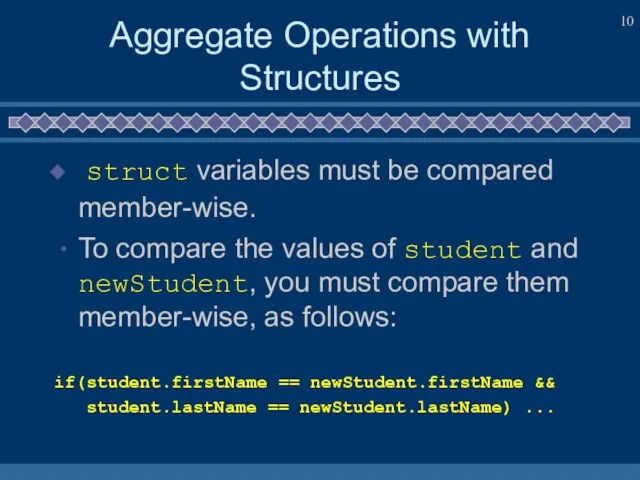
- 10. Aggregate Operations with Structures struct variables must be compared member-wise. To compare the values of student
- 11. Input/Output There are no aggregate input/output operations on struct. Data in a struct variable must be
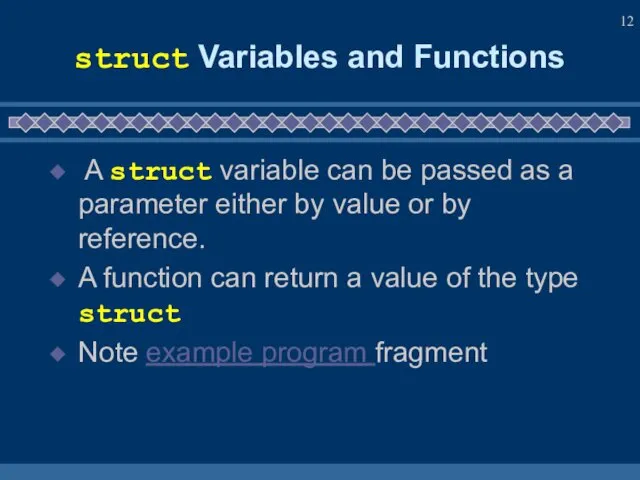
- 12. struct Variables and Functions A struct variable can be passed as a parameter either by value
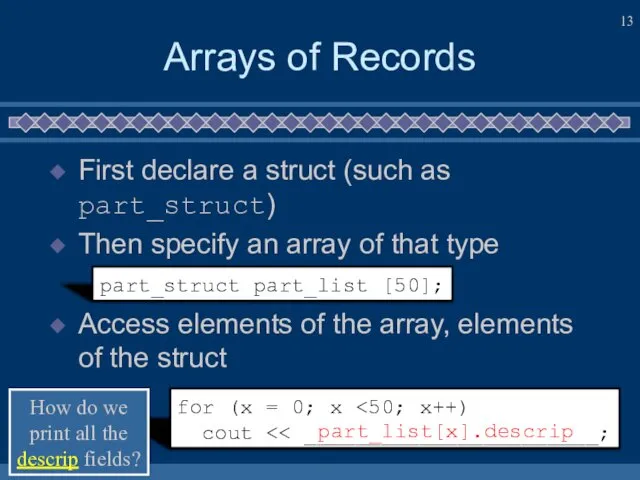
- 13. Arrays of Records First declare a struct (such as part_struct) Then specify an array of that
- 14. Records with Arrays Example const int arraySize = 1000; struct listType { int elements[arraySize]; //array containing
- 15. Hierarchical Records records where at least one of the components is, itself, a record Example: struct
- 16. Choosing Data Structures Strive to group logical elements of a structure together calls for hierarchical structures
- 17. Testing and Debugging Hints Declaration of a struct type must end with a semicolon ; Be
- 18. Testing and Debugging When using an array in a struct, the index goes at the end
- 19. Testing and Debugging Process struct members separately … the only aggregate operations will be Assignment =
- 21. Скачать презентацию














 Проектирование и администрирование компьютерной сети малого офиса
Проектирование и администрирование компьютерной сети малого офиса Нормальная форма
Нормальная форма Влияние социальных сетей на психологию подростка
Влияние социальных сетей на психологию подростка Операционная Система Microsoft Windows
Операционная Система Microsoft Windows Презентация "Исполнители вокруг нас" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Исполнители вокруг нас" - скачать презентации по Информатике Компьютерная графика 08/17/15
Компьютерная графика 08/17/15  Создание презентации в Microsoft Power Point
Создание презентации в Microsoft Power Point Носители информации
Носители информации Сервис онлайн голосования собственников МКД №С1-53417
Сервис онлайн голосования собственников МКД №С1-53417 Тренинг курьеров
Тренинг курьеров Информационные ресурсы интернета
Информационные ресурсы интернета Информационные ресурсы. Этические и правовые нормы информационной деятельности
Информационные ресурсы. Этические и правовые нормы информационной деятельности Итерационные циклы. Сходимость итерационного процесса
Итерационные циклы. Сходимость итерационного процесса Алгоритм и его свойства. Виды алгоритмов
Алгоритм и его свойства. Виды алгоритмов  Nissan G13 USB Reflash procedure
Nissan G13 USB Reflash procedure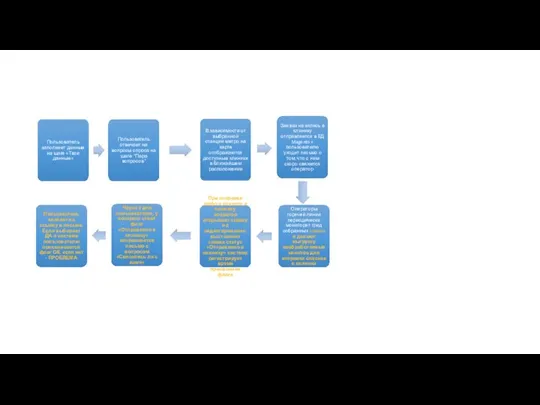 Заявка пользователя
Заявка пользователя JavaScript головного мозга. История одного фреймворка
JavaScript головного мозга. История одного фреймворка История развития вычислительной техники
История развития вычислительной техники Software Quality Assurance. Graphic User Interface Testing
Software Quality Assurance. Graphic User Interface Testing Базы данных. Процедуры и функции
Базы данных. Процедуры и функции PHP - Урок 1 (1)
PHP - Урок 1 (1) Википедия. Как она устроена и почему она работает? Станислав Козловский Wikimedia Russia
Википедия. Как она устроена и почему она работает? Станислав Козловский Wikimedia Russia Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Раскрашивание компьютерного рисунка
Раскрашивание компьютерного рисунка Ролик Мои правила безопасного поведения в сети
Ролик Мои правила безопасного поведения в сети Урок информатики и ИКТ
Урок информатики и ИКТ Лекция №7. Языки программирования для описания задач в АСУП 7.1. Классификация языков программирования для АСУП 7.2. Характери
Лекция №7. Языки программирования для описания задач в АСУП 7.1. Классификация языков программирования для АСУП 7.2. Характери Безопасность школьников в сети интернет
Безопасность школьников в сети интернет