Содержание
- 3. Peculiarities of the Ancient Eastern way of life and philosophy Intelligent interruption Traditionalism & conservatism; Cyclic
- 4. Traditionalism & conservatism; Cyclic attitude to the time and history; Practical orientation;
- 5. 4. Closely connected with religion; 5. Cognition = the content and the way of spiritual development;
- 6. Ancient India The oldest – 4000 years B.C. (Mohenjo-Daro & Harappa) very developed cities – 2-storied
- 7. 2. The specificity of Ancient Indian culture. Periods of Ancient Indian culture: Who were the founder
- 8. Indian religion are: polytheistic – 33 -333-3339 henotheistic animism - the soul is immortal. Samsara -the
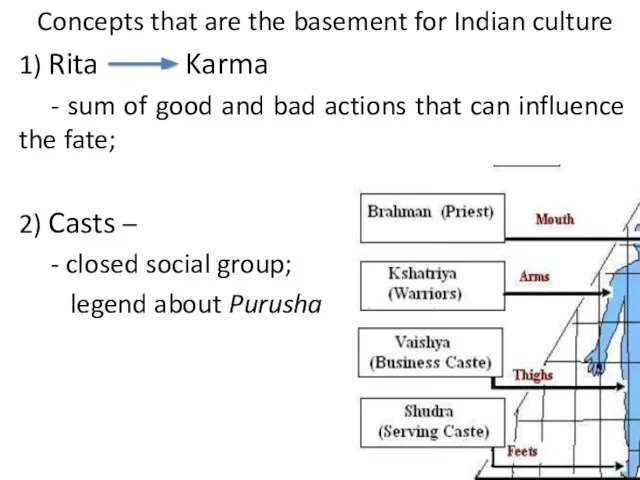
- 9. Concepts that are the basement for Indian culture 1) Rita Karma - sum of good and
- 10. 3) Ahimsa – “not to injure” – do no harm, non violence;
- 11. 4) Samsara - endless circle of life and death; 5) Nirvana - highest spiritual state that
- 12. II period – Brahmanic period (10 – 6 century B.C.) - transformation of the Karma concept:
- 13. Features of Brahmanism 1. Recognition of all the Vedic gods; 2. The main divine triad -
- 14. Philosophical schools = DARSHANA Astika Nastika Confirming Denying
- 15. The Orthodox schools. They recognize the authority of the Veda and to some degree based on
- 18. The origin and development of Buddhism. The most ancient in the world - 6-5 centuries BC.
- 19. The most non-religious religion philosophy there’s NO - God-creator; - God-judge; Teaching about mind – that
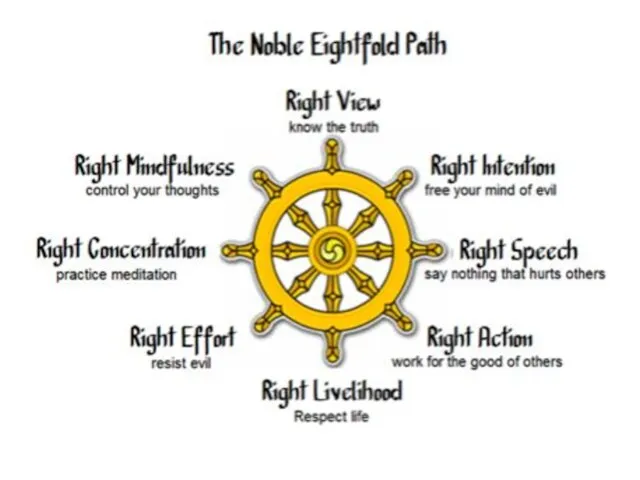
- 20. Goals are liberation from suffering, inner peace, the disclosure of the quality of the mind for
- 21. The History Of Buddhism: - Shakyamuni 5 century BC city of Kapilavastu - the only son
- 22. The first sermon - Deer Grove - the first disciples - 5 ascetics The first turning
- 23. It is the world's largest book " - pagoda Khutodo To read this "book", a man
- 24. Myanmar (Burma)
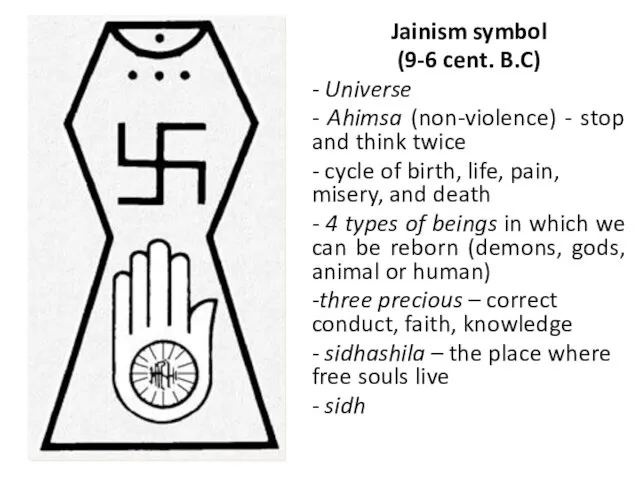
- 28. Jainism symbol (9-6 cent. B.C) - Universe - Ahimsa (non-violence) - stop and think twice -
- 30. 3. The specificity of philosophical knowledge of Ancient China. The first Ancient Chinese ideas - VII
- 31. Confucianism - concentration on the ethical and philosophical issues. The founder is Confucius, the VI -
- 32. Watch the episode and answer the questions: Specify years od birth/death of Confucius. How he formulated
- 33. Taoism. The founder Lao Tzu (the «Old wise man» or «Old child») VI - V centuries
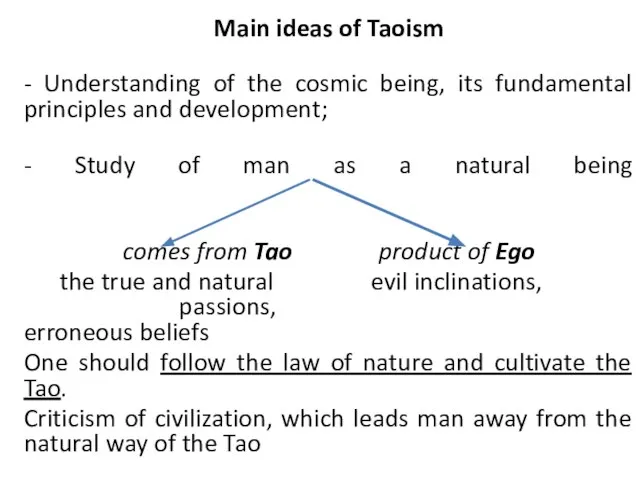
- 34. Main ideas of Taoism - Understanding of the cosmic being, its fundamental principles and development; -
- 36. Скачать презентацию




























 Город Герой - Москва!
Город Герой - Москва! Правление Павла I (1796-1801 гг.)
Правление Павла I (1796-1801 гг.) Эпоха застоя (1964-1986)
Эпоха застоя (1964-1986) Культура Древней Руси IX – начало XII века
Культура Древней Руси IX – начало XII века Триумфальная арка Тита в Риме
Триумфальная арка Тита в Риме Военно-политические конфликты XX-XXIвв. Украинский конфликт 2014-2017гг
Военно-политические конфликты XX-XXIвв. Украинский конфликт 2014-2017гг История метрологии от древности к современности
История метрологии от древности к современности The great inventions of India
The great inventions of India Общественно-политическое развитие России в 1894 – 1904 гг
Общественно-политическое развитие России в 1894 – 1904 гг Золотой век Афин
Золотой век Афин Формы правления и основы конституционного строя России. (Тема 4)
Формы правления и основы конституционного строя России. (Тема 4) События начала Великой Отечественной войны, которые привели к крушению плана Барбаросса
События начала Великой Отечественной войны, которые привели к крушению плана Барбаросса Презентация "Города-герои"
Презентация "Города-герои" На крыльях мира. Привлечение внимания молодого поколения к мировой безопасности и изучение истории Великой Отечественной войны
На крыльях мира. Привлечение внимания молодого поколения к мировой безопасности и изучение истории Великой Отечественной войны Греческие полисы
Греческие полисы Медальерное искусство. Немного истории
Медальерное искусство. Немного истории Город Ангелов
Город Ангелов Мир и счастье для меня - мама
Мир и счастье для меня - мама Иван III Васильевич Иван III Васильевич (известен также как Иван Великий 22 января 1440 — 27 октября 1505) — великий князь москов
Иван III Васильевич Иван III Васильевич (известен также как Иван Великий 22 января 1440 — 27 октября 1505) — великий князь москов Олимпийские игры в древности
Олимпийские игры в древности Крестьянская реформа 1861 года Д/З: § 20, читать, вопрос 3, пересказ.
Крестьянская реформа 1861 года Д/З: § 20, читать, вопрос 3, пересказ.  Презентация на тему "Внутренняя политика Александра III" - презентации по Истории скачать
Презентация на тему "Внутренняя политика Александра III" - презентации по Истории скачать  Правление Ярослава Мудрого
Правление Ярослава Мудрого Презентация на тему "Крестьянство: повседневный быт и обычаи" - презентации по Истории скачать
Презентация на тему "Крестьянство: повседневный быт и обычаи" - презентации по Истории скачать  Монгольские завоевания в XIII-XV вв. Средневековая Индия. Средневековый Китай
Монгольские завоевания в XIII-XV вв. Средневековая Индия. Средневековый Китай 22 июня. День памяти и скорби
22 июня. День памяти и скорби Сухарева башня
Сухарева башня СОБИРАНИЕ РУССКИХ ЗЕМЕЛЬ ВОКРУГ МОСКВЫ
СОБИРАНИЕ РУССКИХ ЗЕМЕЛЬ ВОКРУГ МОСКВЫ