Содержание
- 2. Agenda for Week Two
- 3. Current Events
- 4. Theoretical Approaches
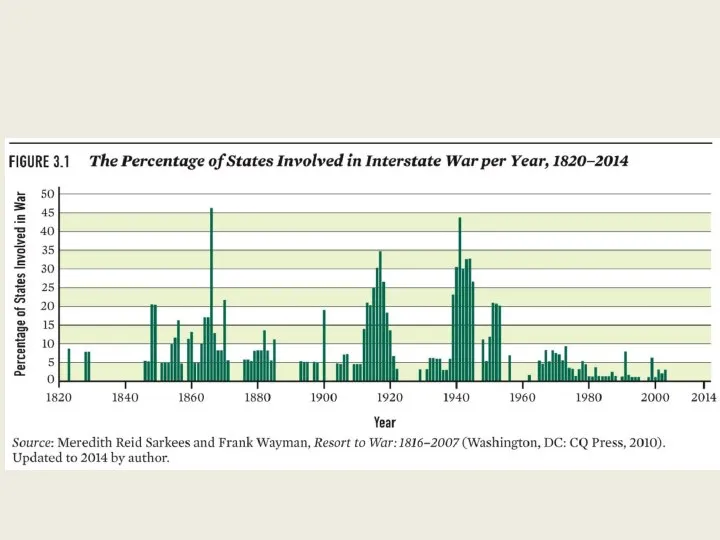
- 6. Realist IR Thucydides’ Melian Dialogue - 460 BCE Machiavelli’s The Prince – 15 century Thomas Hobbes’
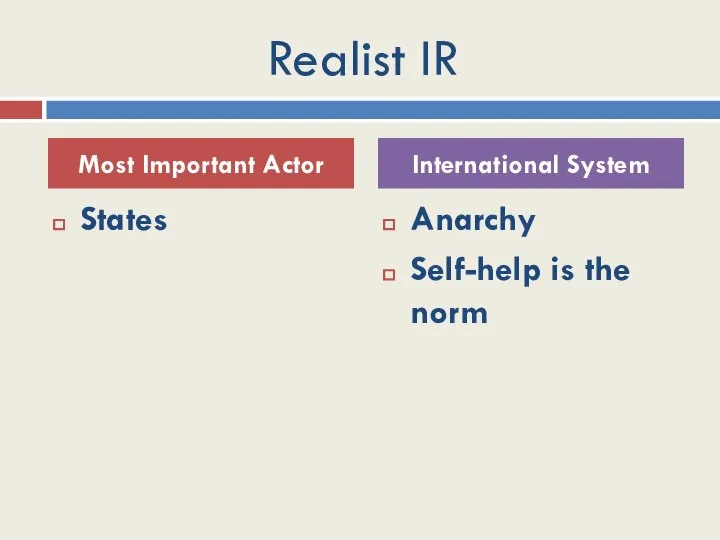
- 7. Realist IR States Anarchy Self-help is the norm Most Important Actor International System
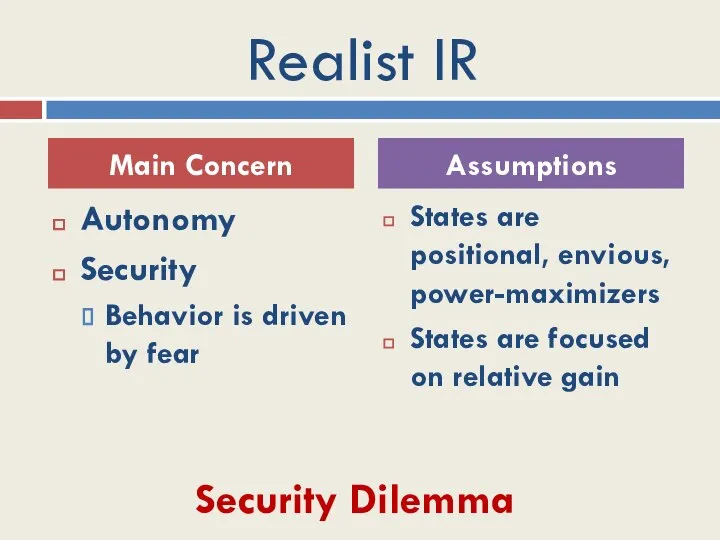
- 8. Realist IR Autonomy Security Behavior is driven by fear States are positional, envious, power-maximizers States are
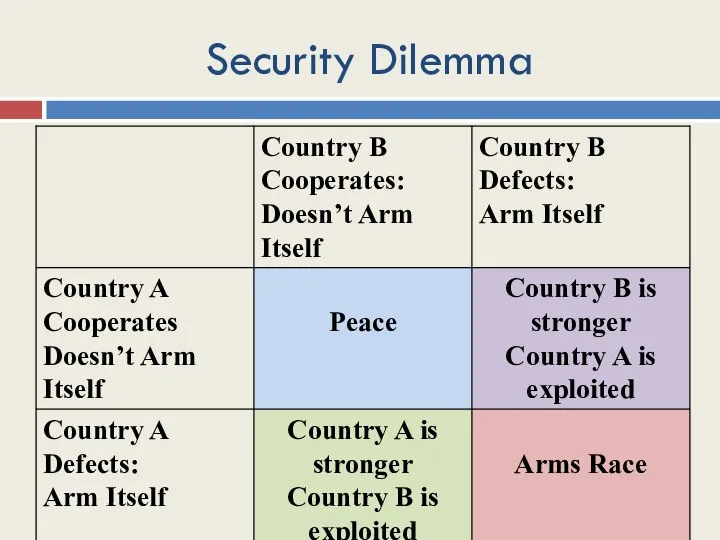
- 9. Security Dilemma
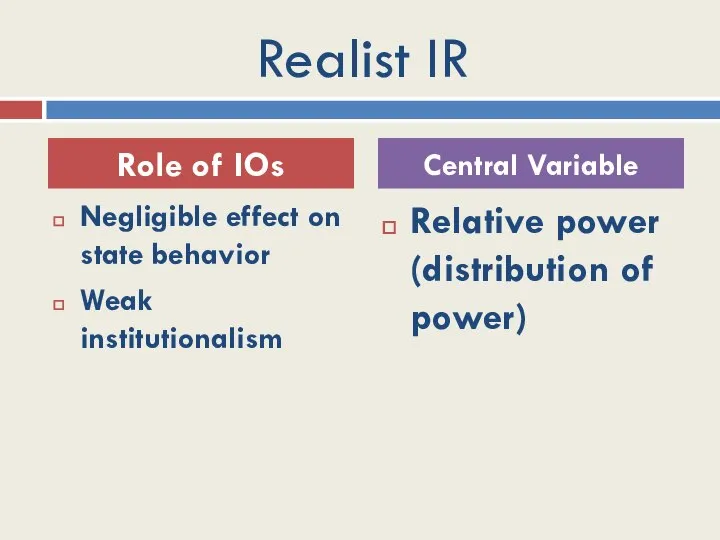
- 10. Realist IR Negligible effect on state behavior Weak institutionalism Relative power (distribution of power) Role of
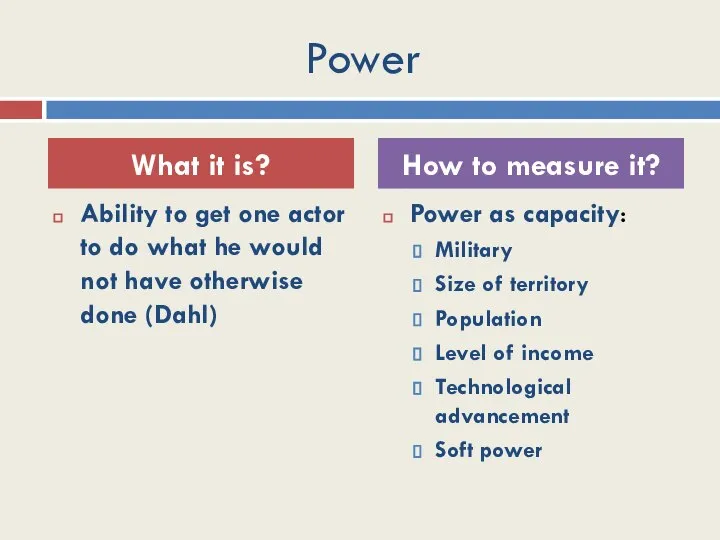
- 11. Power Ability to get one actor to do what he would not have otherwise done (Dahl)
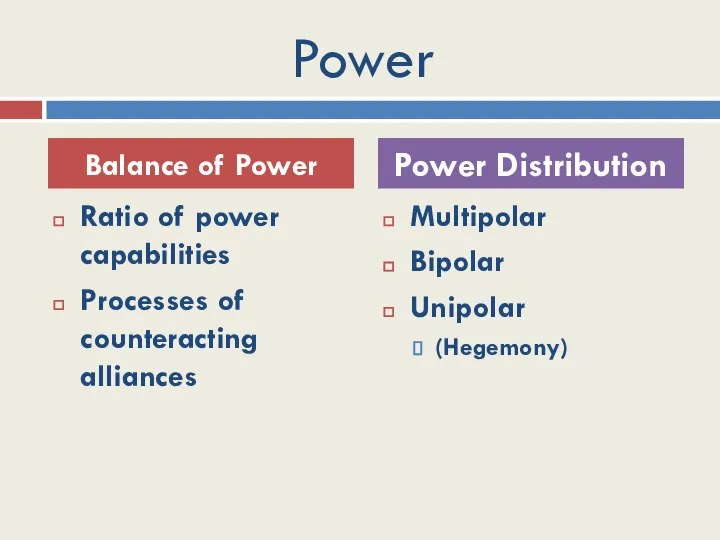
- 12. Power Ratio of power capabilities Processes of counteracting alliances Multipolar Bipolar Unipolar (Hegemony) Balance of Power
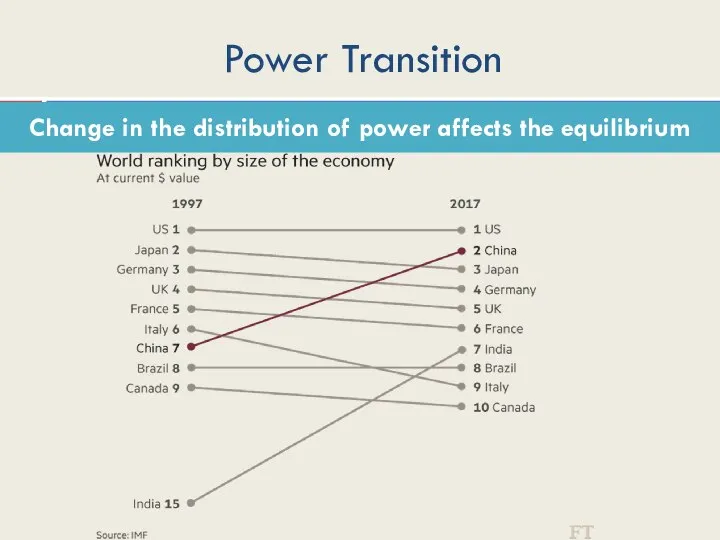
- 13. Power Transition Change in the distribution of power affects the equilibrium
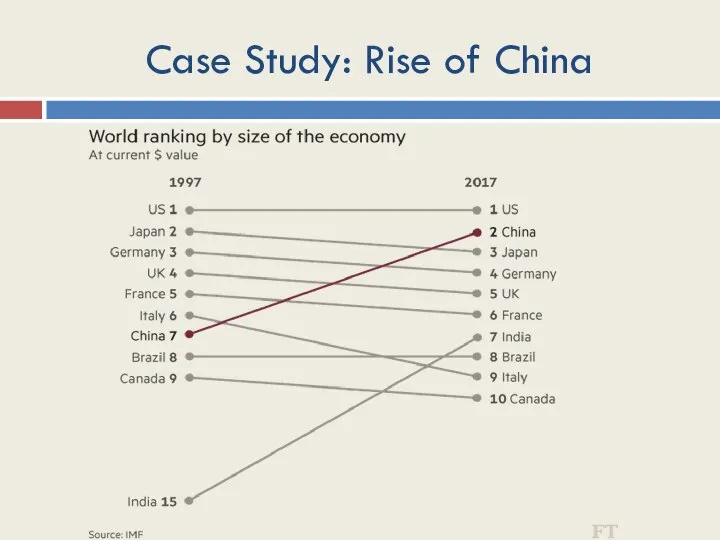
- 14. Case Study: Rise of China
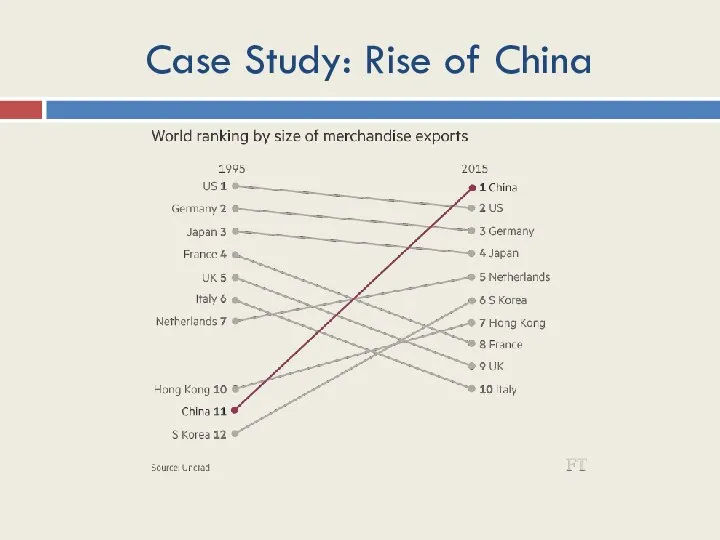
- 15. Case Study: Rise of China
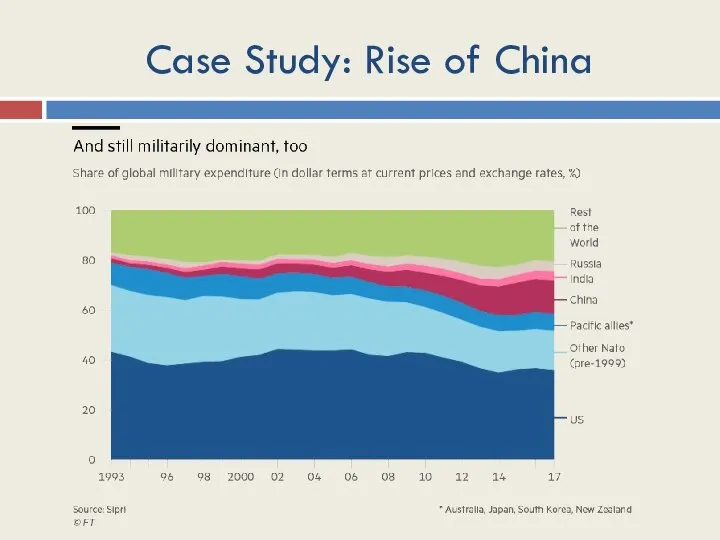
- 16. Case Study: Rise of China
- 17. Realist’s View on China Offensive realism: transition in power will not be smooth Defensive realism: China
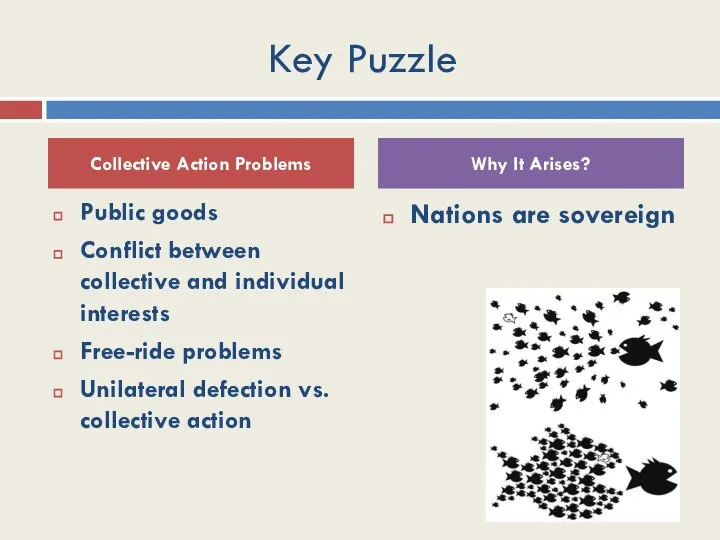
- 18. Key Puzzle Public goods Conflict between collective and individual interests Free-ride problems Unilateral defection vs. collective
- 19. Agenda for Week Two
- 20. Current Events
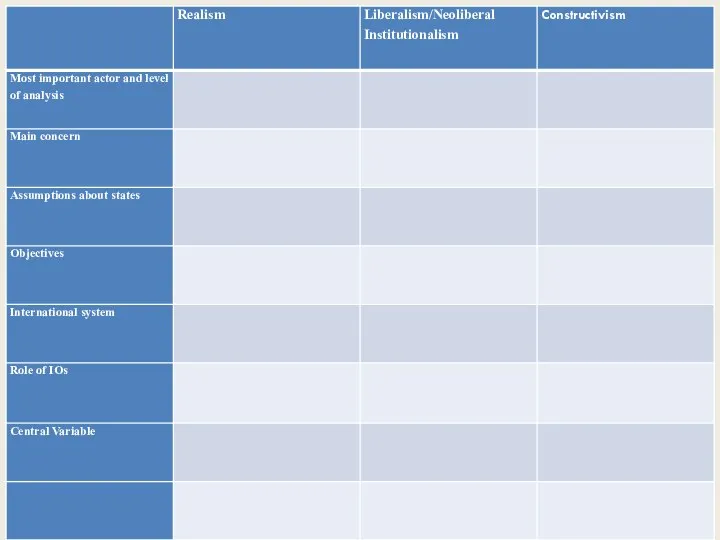
- 21. Theoretical Approaches
- 23. Conceptual Distinction US politics Neo-liberal institutionalism Liberals in political sense Liberalism in IR
- 24. Neo-Liberal Institutionalism John Lock’s idea of limited government Immanuel Kant’s Perpetual Peace Adam Smith’s critique of
- 25. Neo-Liberal Institutionalism State is important unitary actor But other actors matter as well such as International
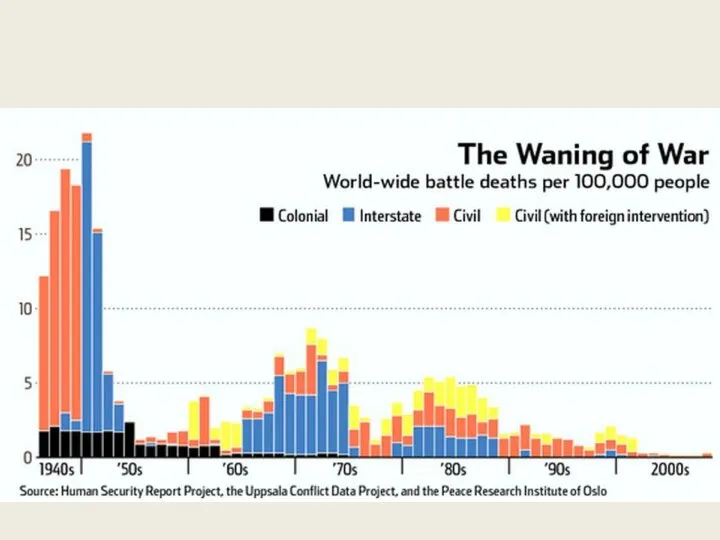
- 28. Countries are at peace most of the time American deaths from: 9/11: 2,996 Terrorism: a few
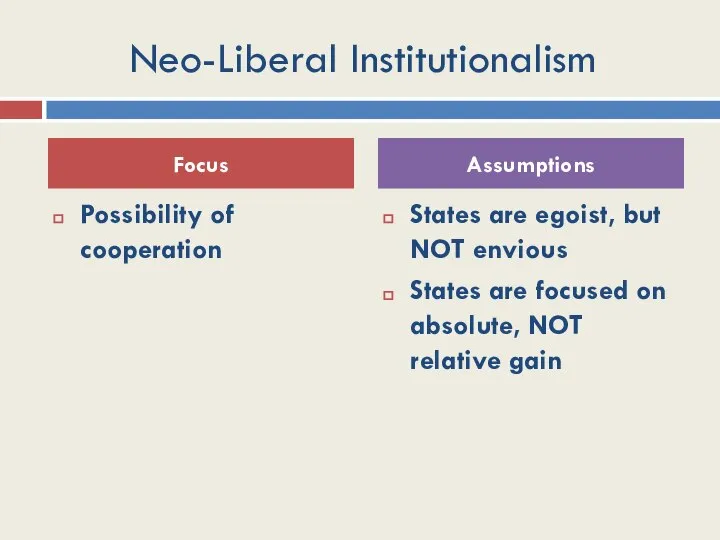
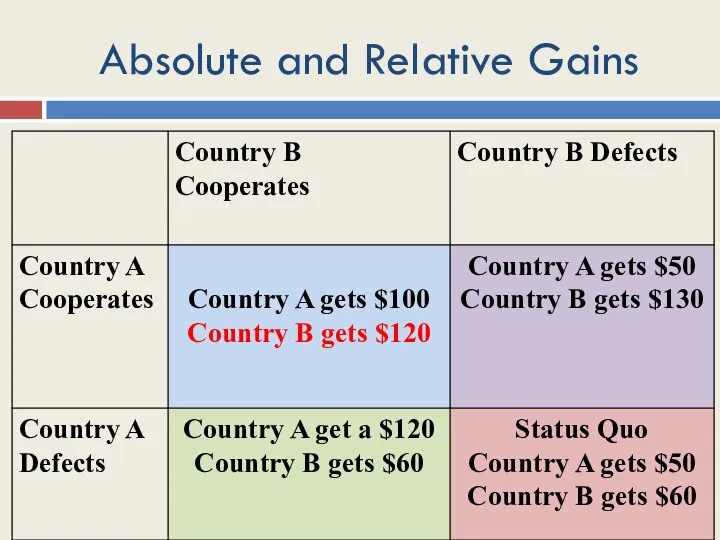
- 29. Neo-Liberal Institutionalism Possibility of cooperation States are egoist, but NOT envious States are focused on absolute,
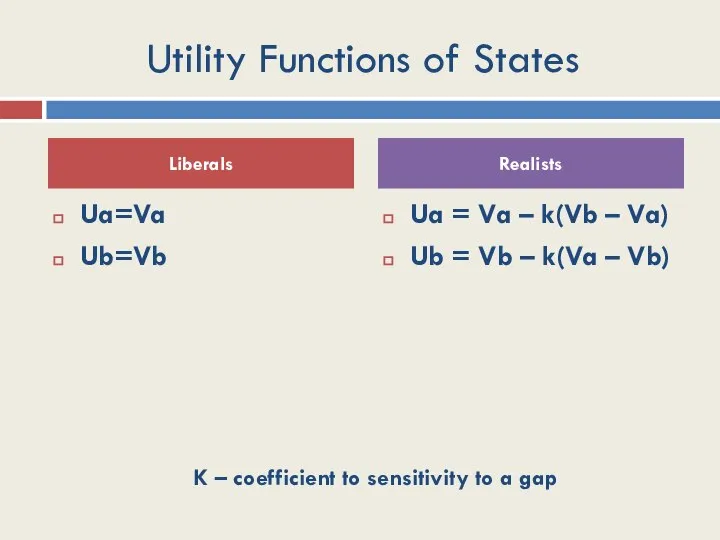
- 30. Utility Functions of States Ua=Va Ub=Vb Ua = Va – k(Vb – Va) Ub = Vb
- 31. Absolute and Relative Gains
- 32. Agenda for Week Two
- 33. Kahoot
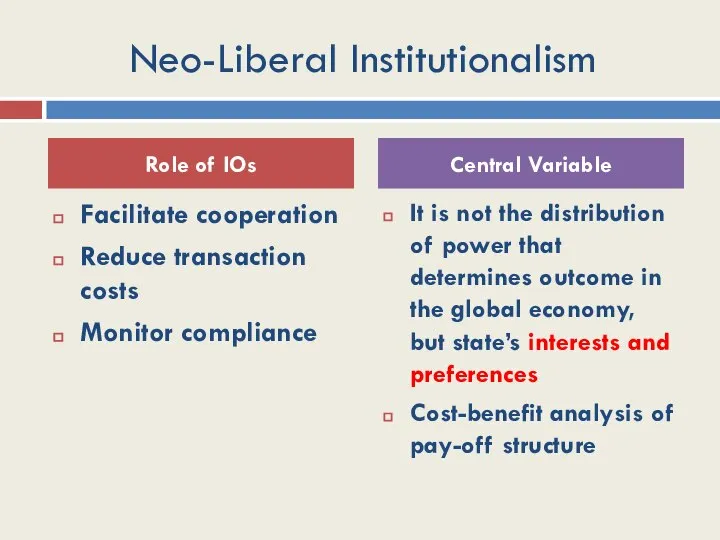
- 34. Neo-Liberal Institutionalism Facilitate cooperation Reduce transaction costs Monitor compliance It is not the distribution of power
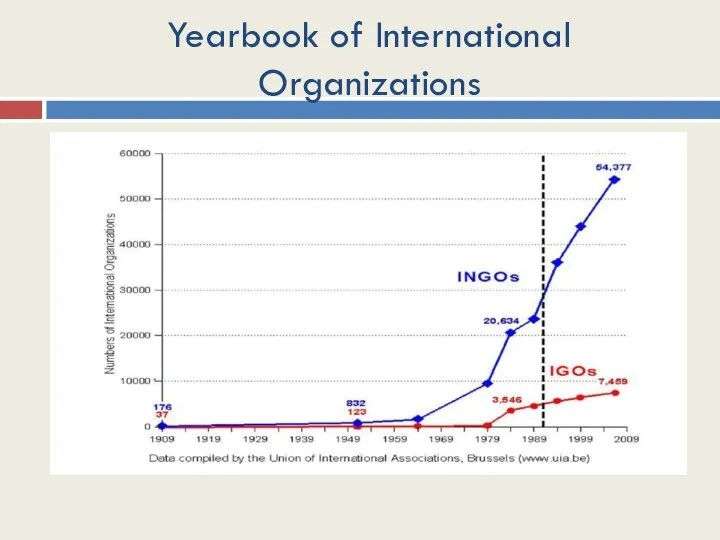
- 35. Yearbook of International Organizations
- 36. Collective Actions Problems Dominance/Coercion Strategy: Hegemon provides collective goods Realists Solutions
- 37. Collective Actions Problems Reciprocity and linkages: Exchanges of privileges Institutions and IOs: Set standards Monitoring mechanism
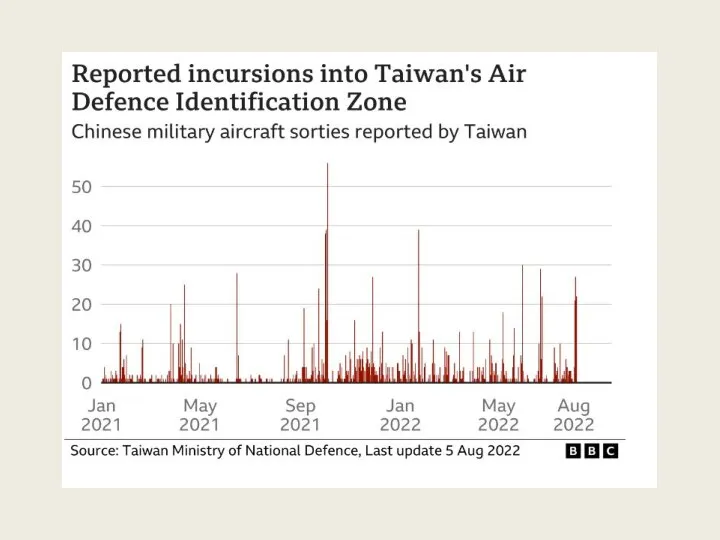
- 38. In-Class Exercise I – Taiwan Conflict Work in Pairs What are the possible implications of the
- 44. Скачать презентацию
















 Теоретические основы процессов спекания, плавления и вспучивания строительных материалов
Теоретические основы процессов спекания, плавления и вспучивания строительных материалов Управление конфликтами в организации
Управление конфликтами в организации Эскиз № 1,2,3,4,5,6,7
Эскиз № 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 Технология обработки наружных фасонных поверхностей деталей из древесины
Технология обработки наружных фасонных поверхностей деталей из древесины Дендрологический план
Дендрологический план Мал шаруашылығы, егін, және оның басым бөлігі мал азығын дайындау
Мал шаруашылығы, егін, және оның басым бөлігі мал азығын дайындау Кабельные линии подземной прокладки на напряжение до 500кВ. Опыт строительства и тенденции развития
Кабельные линии подземной прокладки на напряжение до 500кВ. Опыт строительства и тенденции развития Совещание с руководителями управляющих организаций и ТСЖ
Совещание с руководителями управляющих организаций и ТСЖ Техническое обслуживание и ремонт троллейбуса
Техническое обслуживание и ремонт троллейбуса Дагестан
Дагестан Устройство крыши
Устройство крыши Упаковка для мелочей
Упаковка для мелочей Металлический конструктор
Металлический конструктор 20120203_master-klass
20120203_master-klass Влияние качества элетроэнергии на элементы СЭС
Влияние качества элетроэнергии на элементы СЭС Технологический этап выполнения задания
Технологический этап выполнения задания Конструктивные элементы зданий и сооружений. Перегородки: назначение, виды и требования к ним - 2 часа
Конструктивные элементы зданий и сооружений. Перегородки: назначение, виды и требования к ним - 2 часа Серия игр про Марио
Серия игр про Марио Зависть
Зависть 20141229_tvorchestvo_nikolaya_gumileva
20141229_tvorchestvo_nikolaya_gumileva Transporte. Personas. Mercancías
Transporte. Personas. Mercancías Билеты счастья
Билеты счастья Si-ФЭУ с улучшенными характеристиками
Si-ФЭУ с улучшенными характеристиками Одежда детская
Одежда детская Юбилейный вечер Николая Георгиевича Наумова
Юбилейный вечер Николая Георгиевича Наумова Программа комплексных геофизических исследований на лицензионном участке Южно-Русский
Программа комплексных геофизических исследований на лицензионном участке Южно-Русский Истории Великой Отечественной войны в средней школе
Истории Великой Отечественной войны в средней школе Искусство быть родителям
Искусство быть родителям