Содержание
- 2. Plan Project Introduction. Definition Of Iislamic Legal System. Origin Of Islamic Law. General characteristic of Islamic
- 3. Introduction The Islamic legal system of Sharia (Islamic law) and Fiqh (Islamic jurisprudence) is the most
- 4. DEFINITION OF ISLAMIC LEGAL SYSTEM THE ISLAMIC LEGAL SYSTEM (or Sharia law) : is a religious
- 5. ORIGIN OF ISLAMIC LAW ORIGIN OF ISLAMIC LAW Traditional theory of Islamic jurisprudence recognizes four sources
- 7. General characteristic of Islamic legal system After a lot of researches concerning Islamic law, the scholars
- 8. Second : it is comprehensive in terms of its ruling, methods, and ethics. therefore It covers
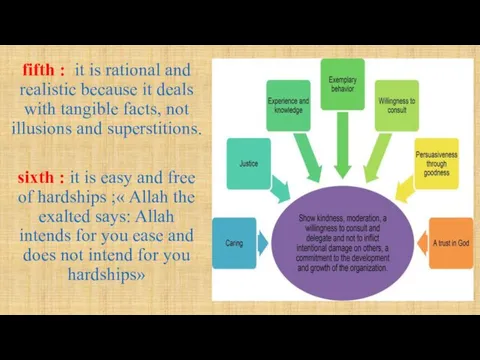
- 9. fifth : it is rational and realistic because it deals with tangible facts, not illusions and
- 10. History of its development Before Islam, the nomadic tribes inhabiting the Arabian peninsula worshiped idols.Each tribe
- 11. The history of Islam concerns the political, social, economic and cultural developments of Islamic civilization. Most
- 12. In the modern era, traditional laws in the Muslim world have been widely replaced by statutes
- 13. The structure of Islamic law The Qur'an is the principal source of Islamic law, the Sharia.
- 14. The sources of Islamic law The body of islamic laws was the shariaa. There are four
- 15. The Holy Quran Muslims believe the Quran to be the direct words of Allah, as revealed
- 16. The Sunnah Sunnah are the traditions or known practices of the Prophet Muhammad . Many Hadiths
- 17. People also asked the Prophet directly for rulings on various matters, and he would pronounce his
- 18. ljma (Consensus) In situations when Muslims have not been able to find a specific legal ruling
- 19. Qiyas (Analogy) In cases when something needs a legal ruling, but has not been clearly addressed
- 20. The Egyptian Legal System The Egyptian legal system is built on the combination of Islamic (Shariah)
- 21. The Egyptian legal system, being considered as a civil law system, is based upon a well-established
- 23. Скачать презентацию


















 Гражданское общество и государство
Гражданское общество и государство Формирование комфортной городской среды
Формирование комфортной городской среды Права и обязанности ребенка
Права и обязанности ребенка Заседание Комиссии по координации деятельности и контролю в сфере формирования доступной среды жизнедеятельности для инвалидов
Заседание Комиссии по координации деятельности и контролю в сфере формирования доступной среды жизнедеятельности для инвалидов Конституционные основы правового регулирования охраны здоровья граждан в РФ. Источники правового регулирования
Конституционные основы правового регулирования охраны здоровья граждан в РФ. Источники правового регулирования Объявление несовершеннолетнего полностью дееспособным (эмансипация). (Глава 32 ГПК РФ)
Объявление несовершеннолетнего полностью дееспособным (эмансипация). (Глава 32 ГПК РФ) Порядок осуществления закупок способом запроса предложений
Порядок осуществления закупок способом запроса предложений Стандарт готовой продукции СТ-ГП-14
Стандарт готовой продукции СТ-ГП-14 Международное частное право
Международное частное право Гражданское право
Гражданское право Презентация _ЭДО_в_маркировке_молока_партнерам
Презентация _ЭДО_в_маркировке_молока_партнерам О выборах депутатов МПСО
О выборах депутатов МПСО Прохождение производственной практики в Петровск-Забайкальском РО
Прохождение производственной практики в Петровск-Забайкальском РО Содержание предпринимательской деятельности
Содержание предпринимательской деятельности Право и его роль в жизни общества и государства
Право и его роль в жизни общества и государства Контроль загрязняющих веществ в объектах окружающей среды в зоне действия предприятий по добыче и переработке углей
Контроль загрязняющих веществ в объектах окружающей среды в зоне действия предприятий по добыче и переработке углей Управление акционерным капиталом и органы управления АО
Управление акционерным капиталом и органы управления АО Нарушение авторских и смежных прав. Пиратство
Нарушение авторских и смежных прав. Пиратство Операционная работа на стадионе. Общая информация
Операционная работа на стадионе. Общая информация Права ребёнка
Права ребёнка Право социального обеспечения. Тема 1
Право социального обеспечения. Тема 1 Периодизация и системы римского права
Периодизация и системы римского права Источники Римского права
Источники Римского права Конституция – основной закон государства
Конституция – основной закон государства Красная книга Республики Калмыкия
Красная книга Республики Калмыкия Виды и тактика действий служебных нарядов по охране общественного порядка и безопасности. (Тема 20)
Виды и тактика действий служебных нарядов по охране общественного порядка и безопасности. (Тема 20) Министерство иностранных дел
Министерство иностранных дел Развитие общества
Развитие общества