Содержание
- 2. Plan: Carbohydrates Classification of carbohydrates The biological function of carbohydrates Metabolism of carbohydrates Digestion of carbohydrates
- 3. What is carbohydrates? Carbohydrates are chemical compounds that contain only oxygen, hydrogen and carbon. They are
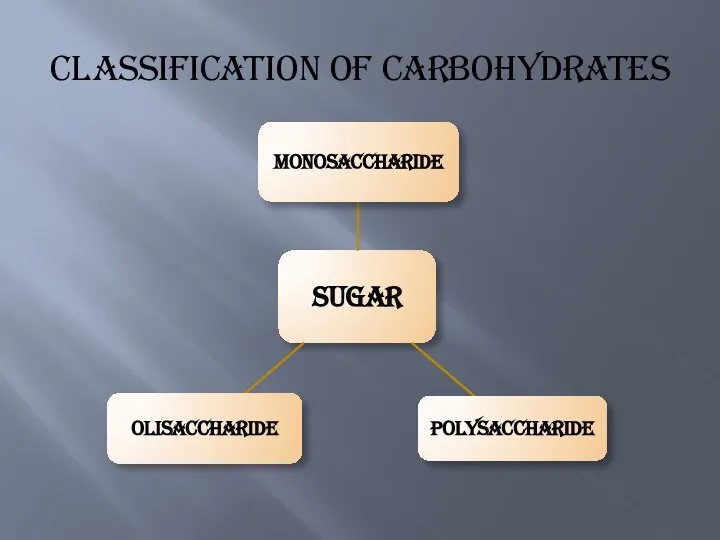
- 4. Classification of carbohydrates
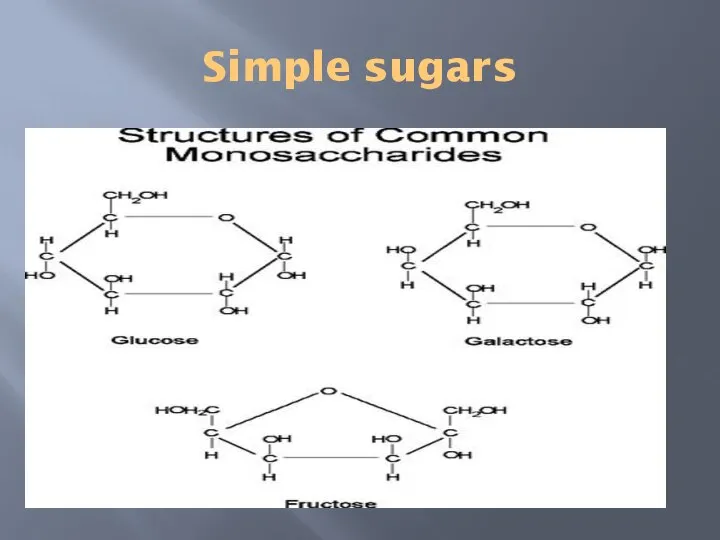
- 5. MONOsaccharide Monosaccharide are carbohydrates which can not be hydrolyze to small molecoles. Monosaccharides containing three (3)
- 6. Simple sugars
- 7. Glyceraldehyde and dihydroxy acetone are aldotriose and ketotriose are respectively.The phosphorylated forms are metabolic entermediate. H
- 8. Olisasaccharide Olisaccharides are polymerized monosaccharides, which contain more or two to ten residues on hydrolysis. They
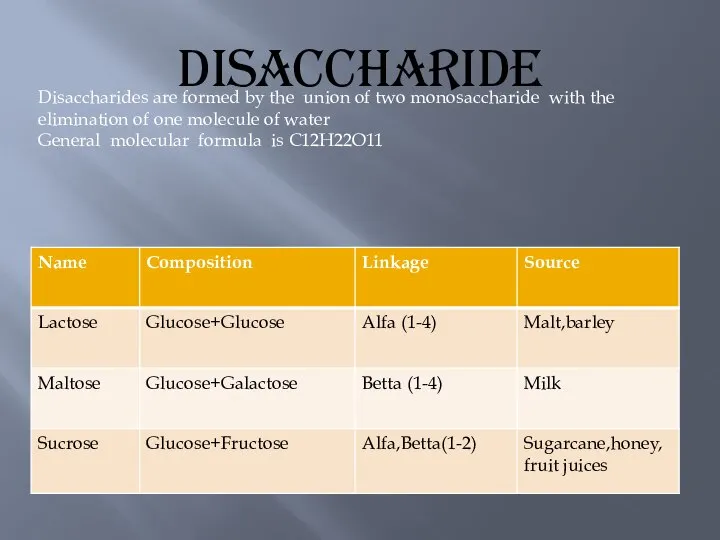
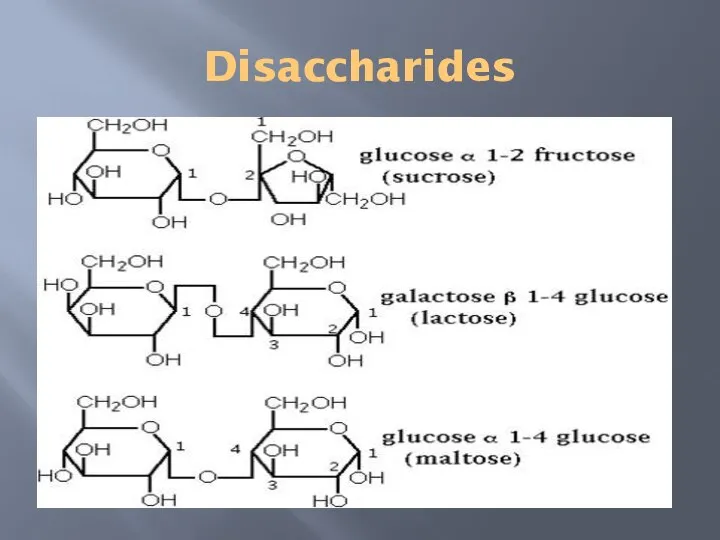
- 9. Disaccharide Disaccharides are formed by the union of two monosaccharide with the elimination of one molecule
- 10. Disaccharides
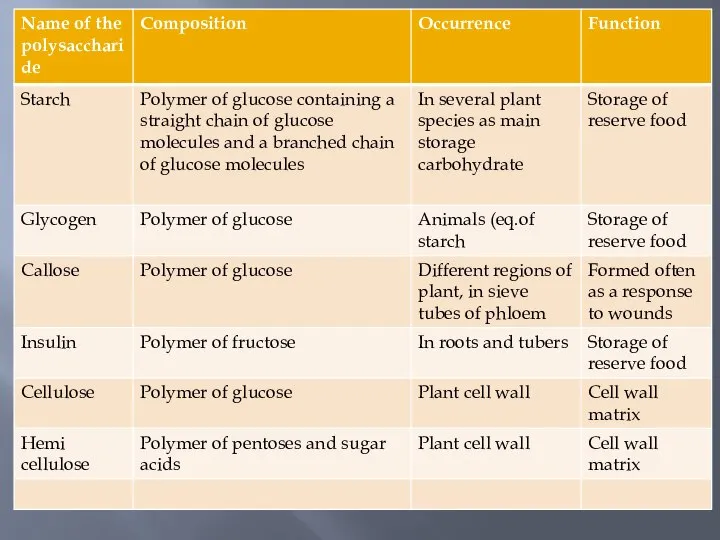
- 11. Polysaccharide Polysaccharide are polymeric anhydrides of monosaccharides. Polysaccharide are of two types based on their function
- 13. Biological function od carbohydrates Carbohydrates are defined as poly hydroxy alcohols function aldehyde or keto group.
- 14. Metabolism of carbohydrates METABOLISM The entire spectrum of chemical reactions, occuring in the living system are
- 16. Скачать презентацию








 Презентация Память
Презентация Память Производственно-коммерческая компания ООО «Техмашкомплект» г. Ульяновск
Производственно-коммерческая компания ООО «Техмашкомплект» г. Ульяновск Язык ASSEMBLER. Команды пересылки данных
Язык ASSEMBLER. Команды пересылки данных EasyPact TVS – выбор в пользу простоты и гибкости
EasyPact TVS – выбор в пользу простоты и гибкости Презентация Запреты и ограничения во внешней торговле стран членов Таможенного союза
Презентация Запреты и ограничения во внешней торговле стран членов Таможенного союза Решаем примеры и задачи в пределах 20 Выполнила: учитель начальных классов МКВ(с)ОУ г.Астрахани «О(с)ОШ №5» Милькина Юлия Алексеевн
Решаем примеры и задачи в пределах 20 Выполнила: учитель начальных классов МКВ(с)ОУ г.Астрахани «О(с)ОШ №5» Милькина Юлия Алексеевн Презентация "Инвестиционный фонд Российской Федерации как инструмент экономической политики и новые возможности для регионов&
Презентация "Инвестиционный фонд Российской Федерации как инструмент экономической политики и новые возможности для регионов& Степ аэробика. Фитнес-студия "Body Balance"
Степ аэробика. Фитнес-студия "Body Balance" Базовый комплект комплекса разведки, управления и связи БК КРУС-М. Изделие 83т415
Базовый комплект комплекса разведки, управления и связи БК КРУС-М. Изделие 83т415 Организация, вооружение мотострелкового (танкового) батальона
Организация, вооружение мотострелкового (танкового) батальона Спортивные сооружения. Лекция 4. Спортивные залы. Тренажерные устройства спортивного зала
Спортивные сооружения. Лекция 4. Спортивные залы. Тренажерные устройства спортивного зала История развития ислама и исламского права
История развития ислама и исламского права Презентация по алгебре Линейные уравнения с одной переменной 7 класс
Презентация по алгебре Линейные уравнения с одной переменной 7 класс Национальная технологическая инициатива РФ
Национальная технологическая инициатива РФ Правовое регулирование недропользования, правовой режим недр
Правовое регулирование недропользования, правовой режим недр Техногенные опасности
Техногенные опасности  Массивы
Массивы Основные понятия алгебры логики
Основные понятия алгебры логики Аттестационная работа. Проект по созданию мобильных экскурсионных групп
Аттестационная работа. Проект по созданию мобильных экскурсионных групп Животные и растения в устном народном творчестве
Животные и растения в устном народном творчестве Презентация по ОБЖ Пожарная безопасность в России
Презентация по ОБЖ Пожарная безопасность в России  Muslim brotherhood
Muslim brotherhood Векторные пространства
Векторные пространства Презентация "Основы рыночной экономики" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Основы рыночной экономики" - скачать презентации по Экономике Языковые средства организации научного знания в логическом позитивизме
Языковые средства организации научного знания в логическом позитивизме Физический и духовный терроризм
Физический и духовный терроризм Фразеологизмы в литературе
Фразеологизмы в литературе Механика материалов. Теории прочности и разрушения. (Лекция 23)
Механика материалов. Теории прочности и разрушения. (Лекция 23)