Содержание
- 2. REFERENCE Cryptography and Network Security Fifth Edition by William Stallings
- 3. This course covers the following topics : Introduction Networks vulnerabilities and attack Web security Wireless network
- 4. Aim of Course our focus is on Network Security which consists of measures to deter, prevent,
- 5. Standards Organizations National Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST) Internet Society (ISOC) International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication
- 6. Background Information Security requirements have changed in recent times traditionally provided by physical and administrative mechanisms
- 7. Computer Security the protection afforded to an automated information system in order to attain the applicable
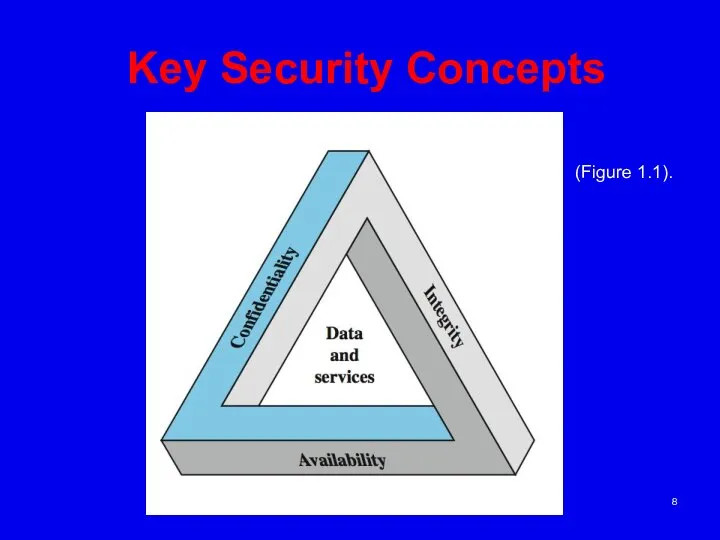
- 8. Key Security Concepts (Figure 1.1).
- 9. Key Security Concepts These three concepts form what is often referred to as the CIA triad
- 10. Key Security Concepts Confidentiality (covers both data confidentiality and privacy): preserving authorized restrictions on information access
- 11. Key Security Concepts • Integrity (covers both data and system integrity): Guarding against modification or destruction
- 12. Key Security Concepts • Availability: Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information. A
- 13. Key Security Concepts Although the use of the CIA triad to define security objectives is well
- 14. Key Security Concepts • Authenticity: The property of being genuine and being able to be verified
- 15. Levels of Impact can define 3 levels of impact from a security breach Low Moderate High
- 16. Levels of Impact • Low: The loss could be expected to have a limited adverse effect
- 17. Levels of Impact but the effectiveness of the functions is noticeably reduced; (ii) result in minor
- 18. Levels of Impact • Moderate: The loss could be expected to have a serious adverse effect
- 19. Levels of Impact (ii) result in significant damage to organizational assets; (iii) result in significant financial
- 20. Levels of Impact High: The loss could be expected to have a severe or catastrophic adverse
- 21. Levels of Impact • (ii) result in major damage to organizational assets; (iii) result in major
- 22. Definitions Computer Security - generic name for the collection of tools designed to protect data and
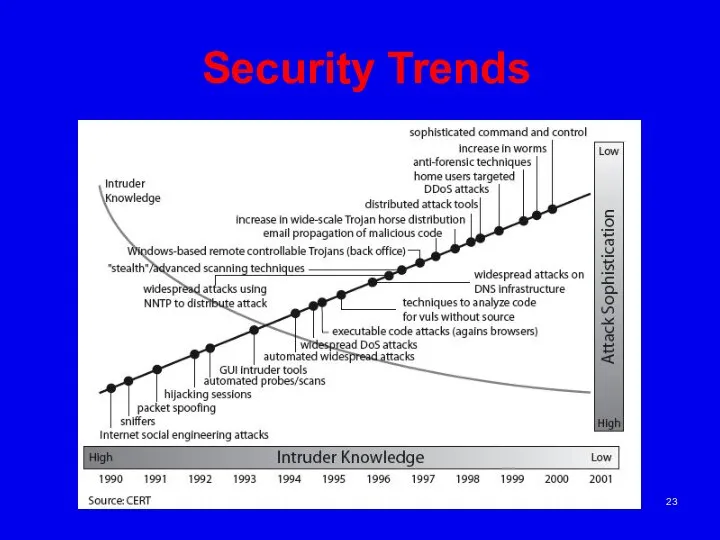
- 23. Security Trends
- 24. OSI Security Architecture ITU-T X.800 “Security Architecture for OSI” defines a systematic way of defining and
- 25. Aspects of Security consider 3 aspects of information security: security attack security mechanism security service note
- 26. Security Attack any action that compromises the security of information owned by an organization information security
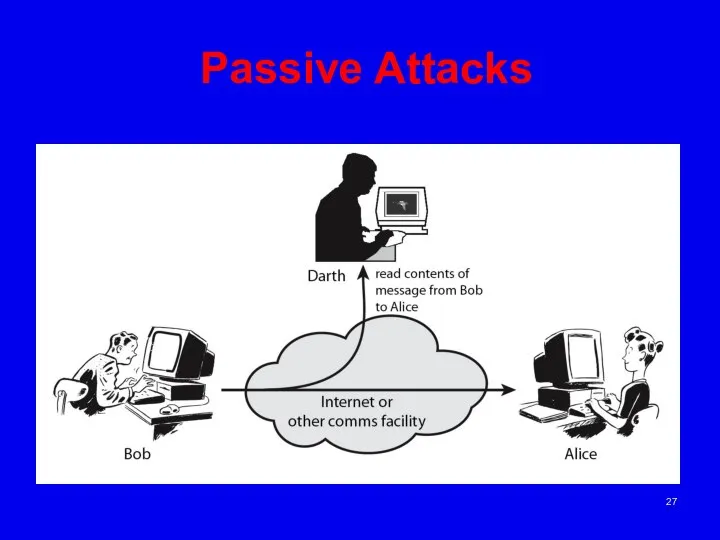
- 27. Passive Attacks
- 28. Passive Attacks Have “passive attacks” which attempt to learn or make use of information from the
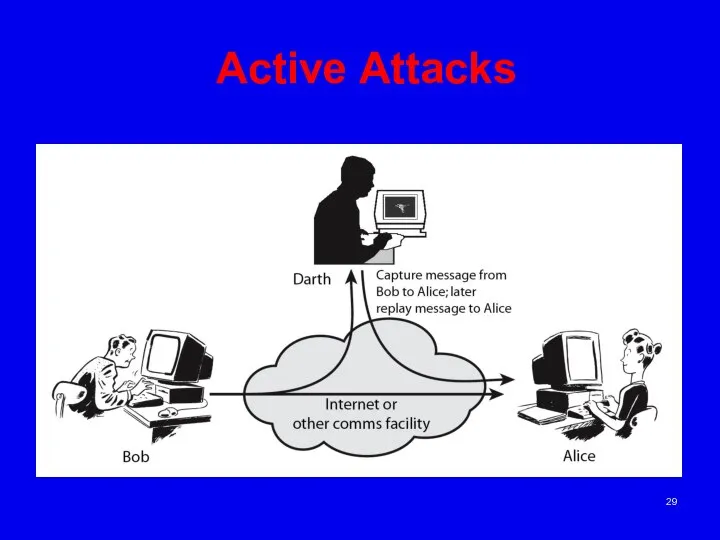
- 29. Active Attacks
- 30. Active Attacks “active attacks” which attempt to alter system resources or affect their operation. By modification
- 31. Active Attacks Active attacks present the opposite characteristics of passive attacks. Whereas passive attacks are difficult
- 32. Security Service enhance security of data processing systems and information transfers of an organization intended to
- 33. Security Mechanism feature designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack no single mechanism
- 34. Security Services X.800: “a service provided by a protocol layer of communicating open systems, which ensures
- 35. Security Services (X.800) Authentication - assurance that the communicating entity is the one claimed Access Control
- 36. Security Mechanisms (X.800) specific security mechanisms: encipherment, digital signatures, access controls, data integrity, authentication exchange, traffic
- 37. Model for Network Security
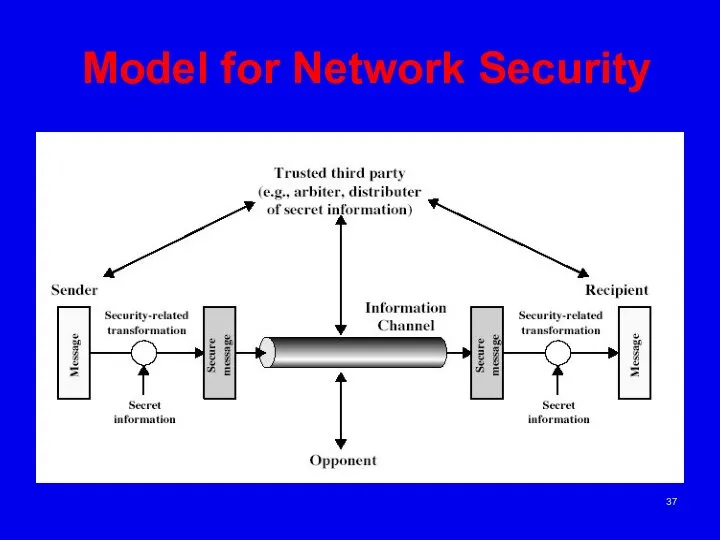
- 38. Model for Network Security In considering the place of encryption, its useful to use the following
- 39. Model for Network Security using this model requires to:(there are four basic tasks in designing a
- 40. Model for Network Security The second, illustrated in Figure 1.6, model is concerned with controlled access
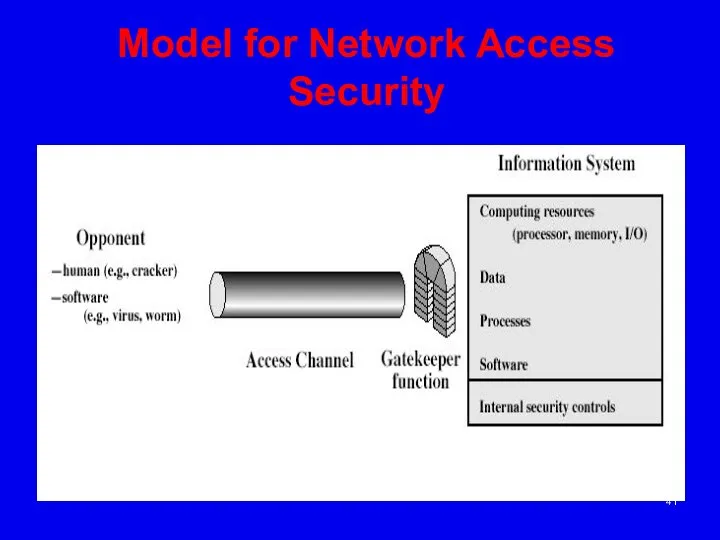
- 41. Model for Network Access Security
- 42. Model for Network Access Security using this model requires us to: select appropriate gatekeeper functions to
- 44. Скачать презентацию

































 Презентация Основы таможенного дела
Презентация Основы таможенного дела Рекомендации по монтажу преобразователей частоты для повышения их ЭМС
Рекомендации по монтажу преобразователей частоты для повышения их ЭМС Радиобиология
Радиобиология  Потоки и файлы
Потоки и файлы Мораль. Религия
Мораль. Религия Сенатская Площадь
Сенатская Площадь  «Вредные советы Оратору». Юмористически-познавательная работа для всех кто выступает с презентациями
«Вредные советы Оратору». Юмористически-познавательная работа для всех кто выступает с презентациями Основы объектно-ориентированного программирования
Основы объектно-ориентированного программирования Древняя Керкинитида. Средневековый Гезлёв. Современная Евпатория
Древняя Керкинитида. Средневековый Гезлёв. Современная Евпатория Конструкционные и функциональные волокнистые композиты. Неорганические матрицы
Конструкционные и функциональные волокнистые композиты. Неорганические матрицы Дорожный бетон
Дорожный бетон Число. Имя числительное - презентация по Алгебре_
Число. Имя числительное - презентация по Алгебре_ Франсиско Гойя(1746-1828гг.)
Франсиско Гойя(1746-1828гг.) Метрологическое обеспечение строительства. (Лекция 1)
Метрологическое обеспечение строительства. (Лекция 1) Цифровой логический уровень
Цифровой логический уровень  В музеях искусства. Пейзаж. 3 класс
В музеях искусства. Пейзаж. 3 класс Эскизы декорации
Эскизы декорации Русское деревянное культовое зодчество
Русское деревянное культовое зодчество Мейрамханада қызметкерлерді басқару
Мейрамханада қызметкерлерді басқару Тема 11. Особенности экономической политики государства Вопросы: 1. Экономическая политика: принципы, цели, инструменты 2. Финан
Тема 11. Особенности экономической политики государства Вопросы: 1. Экономическая политика: принципы, цели, инструменты 2. Финан Население и трудовые ресурсы
Население и трудовые ресурсы Закон об энергосбережении и о повышении энергетической эффективности и о внесении изменений в отдельные законодательные акты
Закон об энергосбережении и о повышении энергетической эффективности и о внесении изменений в отдельные законодательные акты Образование поверхностей и решение задач на пересечение поверхностей. (Лекция 4.2)
Образование поверхностей и решение задач на пересечение поверхностей. (Лекция 4.2) Пауки не являются насекомыми, а принадлежат к классу паукообразных. В отличие от насекомых, у них восемь ног. - презентация
Пауки не являются насекомыми, а принадлежат к классу паукообразных. В отличие от насекомых, у них восемь ног. - презентация Устройство и эксплуатация систем передачи с частотным разделением каналов. Аппаратура каналообразования П-303-ОБ. (Тема 3.2)
Устройство и эксплуатация систем передачи с частотным разделением каналов. Аппаратура каналообразования П-303-ОБ. (Тема 3.2) Франсуа Виет
Франсуа Виет Инженерно-геодезические изыскания
Инженерно-геодезические изыскания Плоскостные элементы благоустройства территории. Дорожки и площадки
Плоскостные элементы благоустройства территории. Дорожки и площадки