Содержание
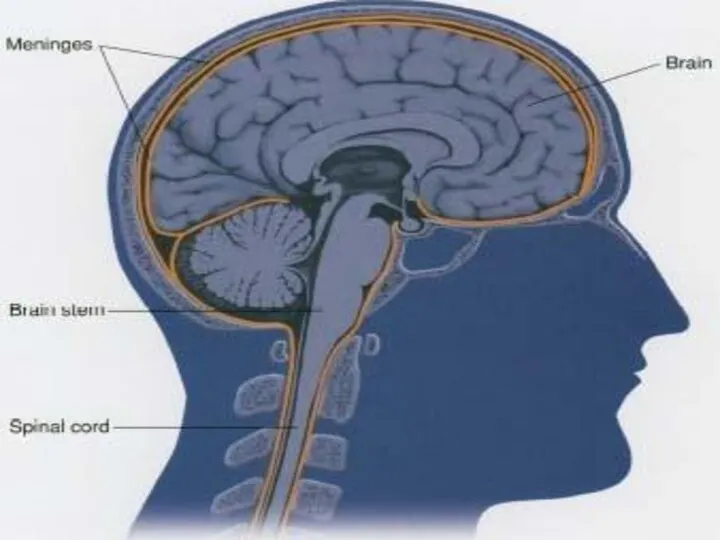
- 2. Increased Intracranial Pressure (pg. 666) The cranium consists of 1. Brain tissue 2. Blood 3. Cerebrospinal
- 4. Increased Intracranial pressure The skull cannot expand so a tumor, cerebral edema, brain abscess, or bleeding
- 5. Increased Intracranial Pressure If not recognized, the brainstem will herniate thru the foramen magnum brainstem controls
- 6. ICP Signs and symptoms develop rapidly or slowly If slow it may be over looked Keep
- 7. Level Of Consciousness Confusion, restlessness, disorientation and drowsiness may or may not be a symptom of
- 8. Headache Pain is usually intermittent--if constant condition usually grave coughing, sneezing, straining at stool increases headache
- 9. Vomiting and ICP Commonly occurs without warning of nausea and without a relationship to eating projectile
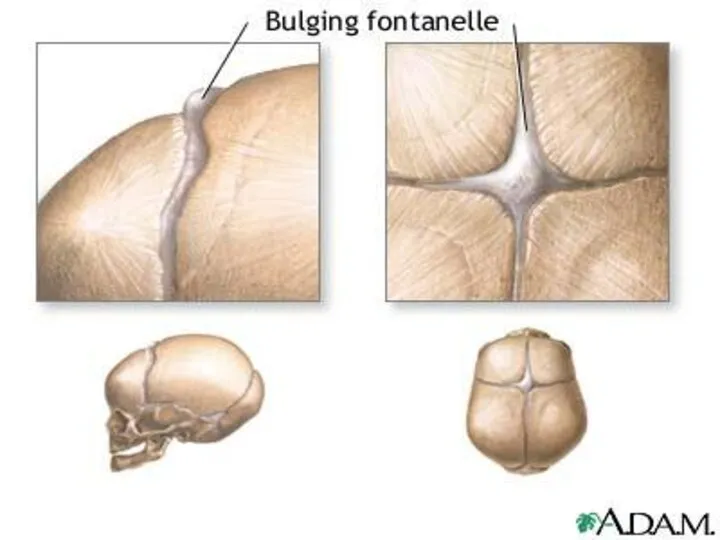
- 10. Papilledema Papilledema (edema of optic nerve caused by obstruction of venous drainage due to ICP Can
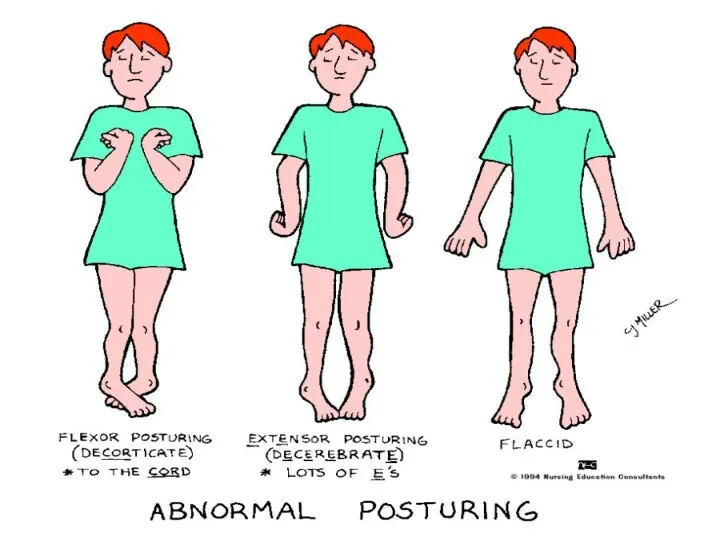
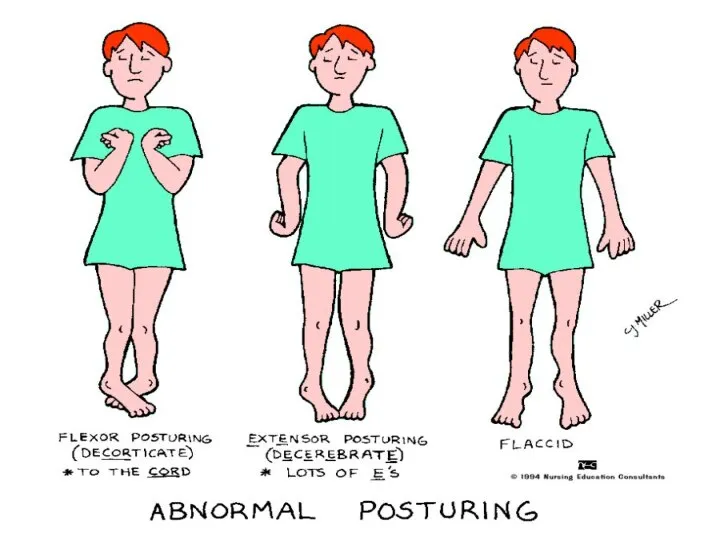
- 11. Posturing Decorticate--arms flexed--problem with cervical spinal tract or cerebral hemisphere Decerebrate--arms extended (more serious as brainstem
- 13. Symptoms of ICP Change in LOC headache vomiting papilledema vital signs--temp rises, b/p rises and pulse
- 14. Vital signs Temp rises, B/P rises and pulse pressure widens. These 3 s/s are called Cushing’s
- 15. Medical and surgical management Osmotic diuretics (mannitol, glycerol); steroids to reduce cerebral edema If clot then
- 16. Medical & surgical management Restrict fluids, lumbar punctures to remove CSF and hyperventilation via ventilator to
- 17. Medical Management May order: insertion of foley NG tube for gastric decompression or feedings Stool softener
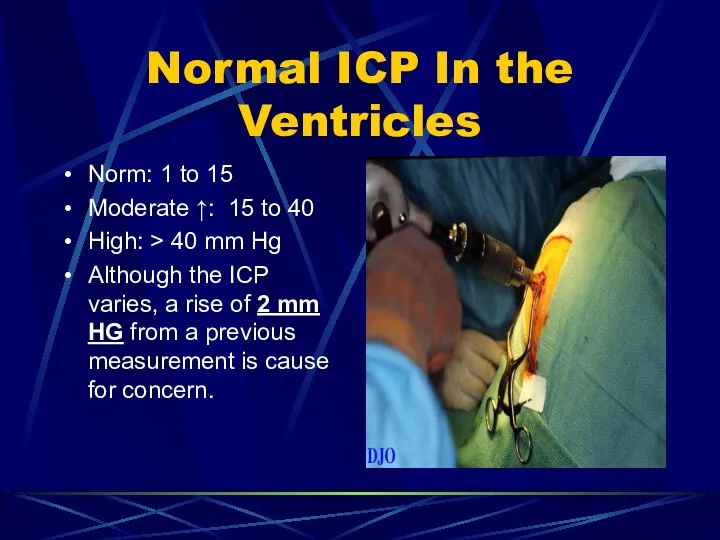
- 18. Normal ICP In the Ventricles Norm: 1 to 15 Moderate ↑: 15 to 40 High: >
- 19. Nursing care ICP Teach to remain quiet in bed and not to turn in bed without
- 20. Nursing Care ICP ICP can affect temp regulation so cooling blanket may be needed Neuro assessment
- 21. Nursing Care ICP A neurologic flow sheet that includes the Glasgow Coma Scale or Ranchos Los
- 22. Nursing Care ICP Laboratory findings such as serum electrolyte levels and arterial blood gas measurements are
- 23. Nursing Care ICP Keep head straight and head of bed slightly elevated If a basal skull
- 24. Activities That increase ICP Coughing range of motion exercises sneezing hip flexion of 90 degrees or
- 25. Activities that increase ICP Straining to have a BM (valsalva maneuver holding breath digging heels into
- 26. Nursing Care ICP Hourly I&O may be done If steroids given, monitor glucose as ordered test
- 27. Nursing Care ICP Monitor I&O…fluids may be restricted to reduce cerebral edema and prevent vomiting and
- 28. Infectious & Inflammatory Disorders Meningitis Encephalitis Gullian-Barre Syndrome Poliolmyelitis Brain Abscess
- 29. Meningitis (Covering of the Brain) pg 669 Inflammation of meninges (three membranes that cover the brain-dura,
- 31. Meningitis Most adults with bacterial meningitis recover without permanent neurologic damage or dysfunction. When complications do
- 32. Meningitis S/S Fever, nuchal rigidity (pain and stiffness of neck); inability to place chin on chest
- 33. Kernig’s Sign Positive Kernig’s sign ( inability to extend the leg when the thigh is flexed
- 34. Brudzinsi’s Sign Brudzinski’s sign--flexion of neck produces flexion of knees and hips
- 35. Diagnostic findings: Meningitis Lumbar puncture done if bacterial meningitis the CSF is cloudy and pressure is
- 37. Medical Management IV fluids, antibiotics, anticonvulsants are used to treat sulfonamide given to people who are
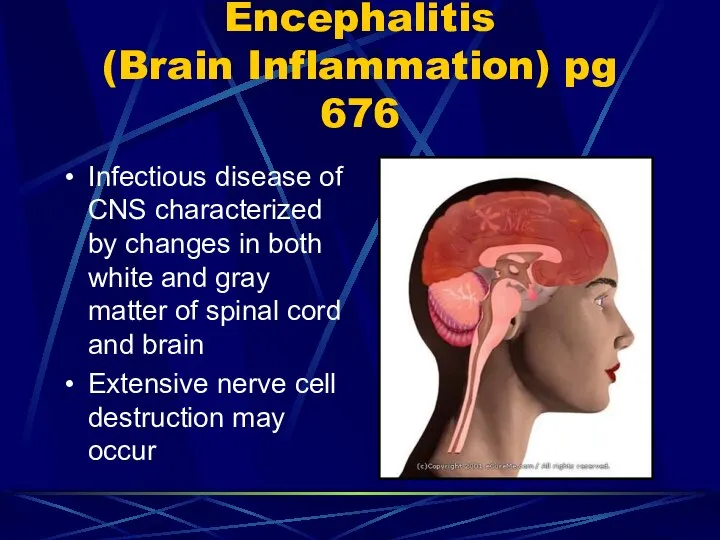
- 38. Encephalitis (Brain Inflammation) pg 676 Infectious disease of CNS characterized by changes in both white and
- 39. Encephalitis (brain inflammation) Symptoms similar to meningitis Caused by bacteria, fungi, or virus cause virus: Polio,
- 40. Encephalitis occurs after a viral infection elsewhere (measles or vaccinations) Poisoning by drugs and chemicals, such
- 41. Encephalitis Onset of viral is sudden with fever, severe headache, stiff neck, vomiting and drowsiness lethargy
- 42. Encephalitis Muscle weakness, incoordination, incontinence and visual disturbances (photophobia, involuntary eye movement, double or blurred vision
- 43. Encephalitis--brain inflammation Lumbar puncture done…CSF pressure elevated but fluid clear EEG has slow wave forms treatment
- 44. Encephalitis Mild cases are common and may go unrecognized complications and deaths are more common in
- 45. Guillain-Barre’ syndrome Pg.677 Rare, inflammatory condition involving the CNS that causes rapid weakness and loss of
- 46. Guillain-Barre’ Syndrome May be autoimmune response to viral infection Takes approx 1 month to start improving
- 47. Guillain Barre’ Syndrome Weakness, tingling, and numbness in arms and legs may be 1st symptoms Weakness
- 48. Medical Management Guillian Barre’ Plasmaphoresis removal of plasma from the blood and reinfusion of the cellular
- 50. Nursing Management Monitory respiratory status/distress Use IS R/T incapacitated by immobility, provide meticulous skin care and
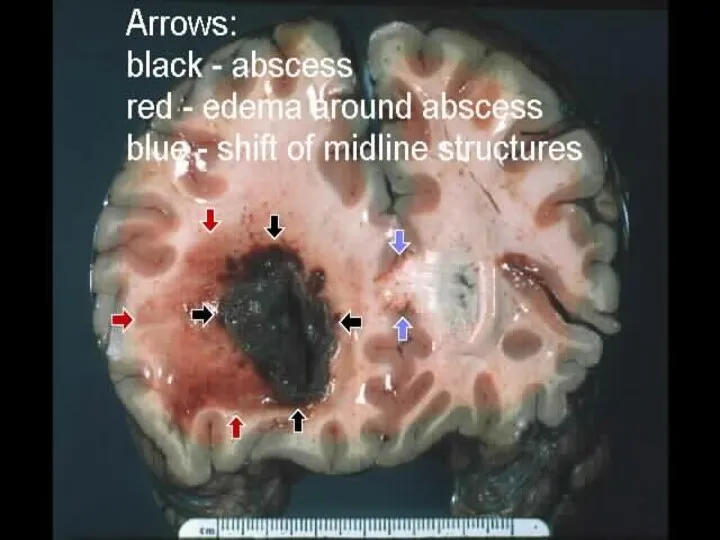
- 51. Brain abscess Pg. 678 A collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection in the brain—if
- 53. Brain abscess May occur from infection of teeth, sinus, middle ear, or from an infection in
- 54. Brain abscess Risk increases with head injury, illness that lowers resistance (esp. diabetes) recent infection (esp
- 55. Brain abscess I&O fluids may be restricted as over-hydration may cause cerebral edema antibiotics usually given
- 56. General Nursing Care for Inflammatory Disorders Swallowing may be affected---give PO drugs slowly…no narcotics REPORT sudden
- 57. Nursing Care for Inflammatory Disorders Monitor vitals…complete care neuro checks…use Glasgow Coma scale Seizure precautions—insert a
- 58. Neuromuscular disorders PG 678 Involves the nervous system and indirectly affects the muscles Multiple Sclerosis Myasthenia
- 59. Multiple sclerosis PG 678 Chronic, progressive disease of the peripheral nerves. Onset in young adult and
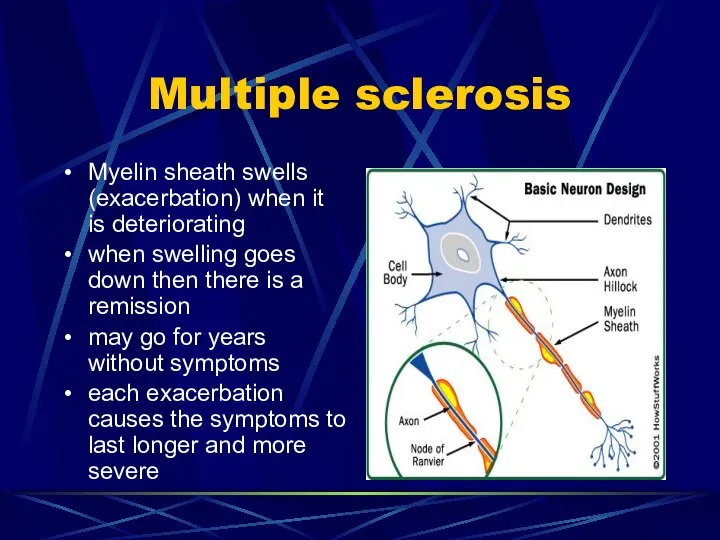
- 60. Multiple sclerosis Permanent degeneration as patchy destruction of myelin sheath of nerve fibers of brain and
- 61. Multiple sclerosis Myelin sheath swells (exacerbation) when it is deteriorating when swelling goes down then there
- 62. Multiple sclerosis Weakness of arms and legs may progress to paraplegia may be incontinent visual disturbances
- 63. Multiple sclerosis Intellectual functioning may be impaired late in disease loss of memory, impaired judgment shallow
- 64. Drugs for MS Lioresal and Dantrium--muscle spasticity and rigidity Antibiotics, urinary infectives, tranquilizers for mood swings
- 65. Nursing Sensory impairment: be careful with hot, cold, avoid injury REST, conserve energy Polyunsaturated fate, linoleic
- 66. Myasthenia Gravis pg 681 Disorder of muscles, with increasing fatigue and weakness as muscles are used
- 67. Myasthenia Gravis Most common symptoms are ptosis of eyelids, difficulty chewing and swallowing, diplopia, voice weakness,
- 68. Myasthenia Gravis Diagnosed by giving IV Tensilon which relieves symptoms in a few seconds if it
- 69. Myasthenia gravis Treatment is Mesitonon or Myelelase Atropine is antidote for mestinon and other anticholinesterase drugs
- 70. Mestinon or Mytelase Observe for drug overdose….abdominal cramps, clenched jaws, muscle rigidity Give drug at exact
- 71. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis--Lou Gehrig’s Disease 682 Progressive, fatal neuro disorder of unknown cause Degeneration of motor
- 72. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis--Lou Gehrig’s Disease 682 Periods of inappropriate laughter or crying Causes resp failure and
- 73. Cranial Nerve disorders Pg. 683 Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux) Bell’s palsy Temporomandibular Disorder (TMD)
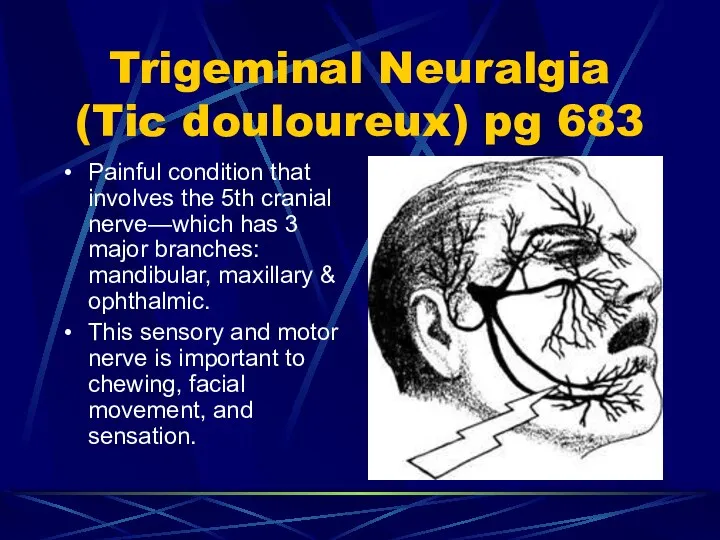
- 74. Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux) pg 683 Painful condition that involves the 5th cranial nerve—which has 3
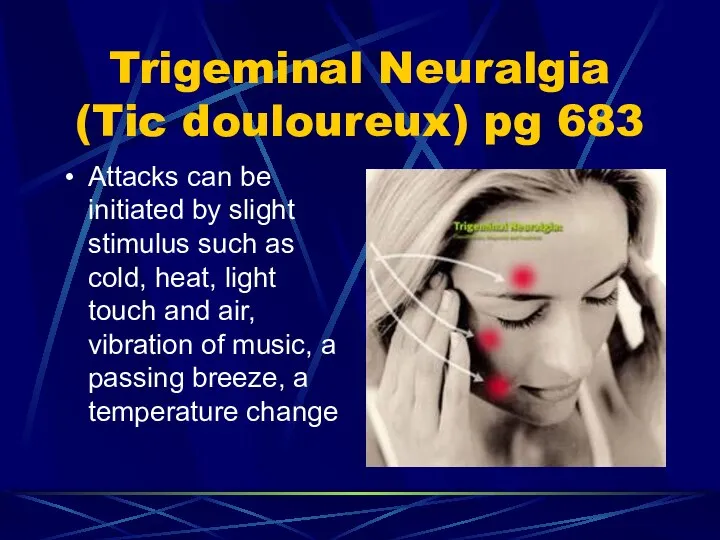
- 75. Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic douloureux) pg 683 Attacks can be initiated by slight stimulus such as cold,
- 76. Trigeminal Neuralgia The pain is described as sudden, severe, and burning It ends as quickly as
- 77. Trigeminal Neuralgia Analgesics, surgery on nerve root or branches post op there is no feeling in
- 78. Trigeminal Neuralgia Slightest stimulus may start attack (vibration from music, breeze, temp change they avoid washing
- 79. Trigeminal Neuralgia Post-op eating may be a problem as may bite tongue without knowing it food
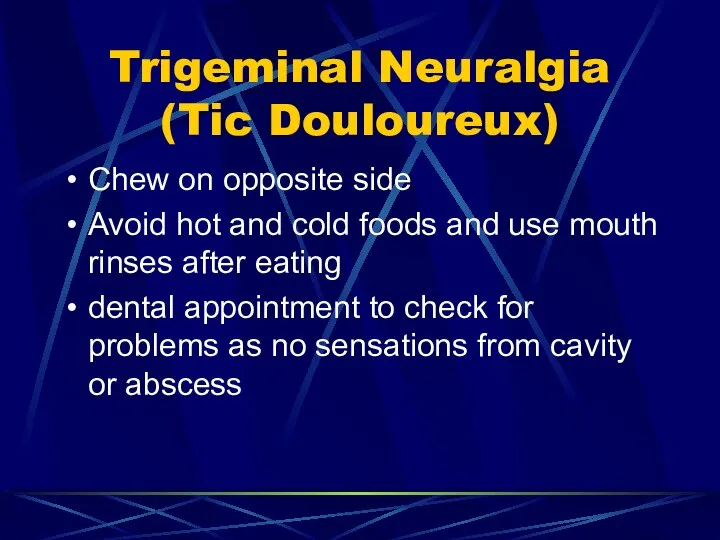
- 80. Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic Douloureux) Chew on opposite side Avoid hot and cold foods and use mouth
- 81. Trigeminal Neuralgia Dilantin and tegretol used to reduce pain as analgesics not too successful narcotics may
- 82. Bell’s Palsy 7th cranial nerve—responsible for movement of the facial muscles facial nerve usually affects one
- 83. Bell’s Palsy causes weakness and paralysis of facial muscles and eyelid facial pain, pain behind ear,
- 84. Bell’s Palsy Speech and chewing difficulty may occur Must rule out CVA, tumor no specific test
- 85. Bell’s palsy If ptosis and blinking reflex affected must wear eye patch corneal ulcerations and infection
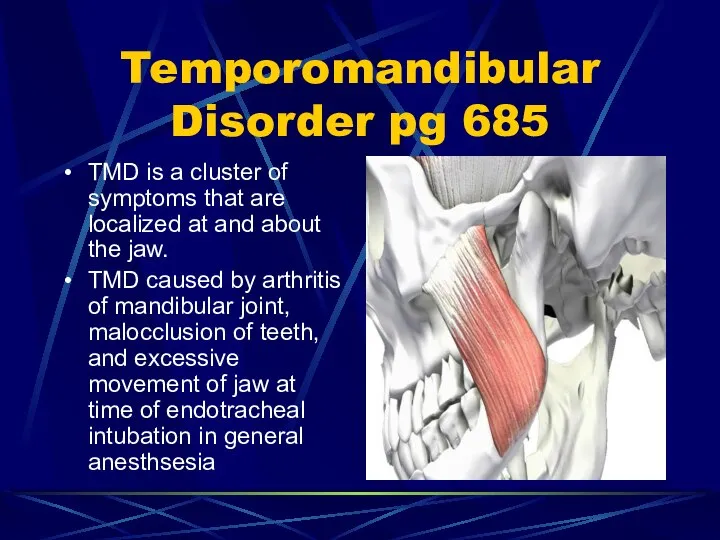
- 86. Temporomandibular Disorder pg 685 TMD is a cluster of symptoms that are localized at and about
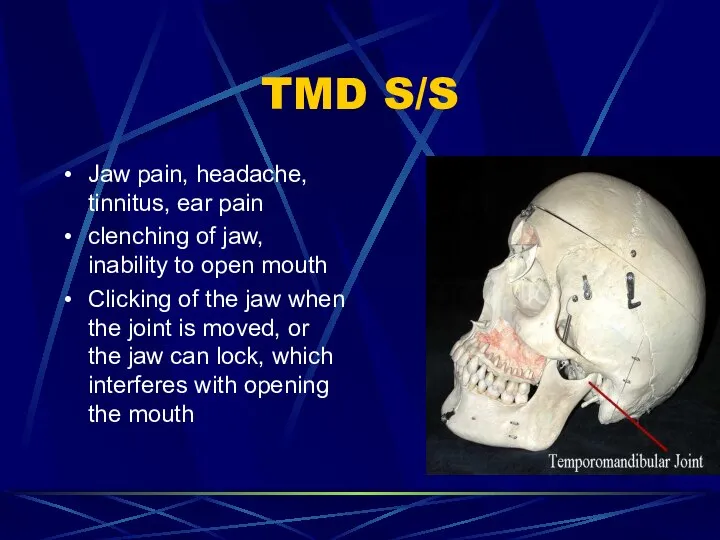
- 87. TMD S/S Jaw pain, headache, tinnitus, ear pain clenching of jaw, inability to open mouth Clicking
- 88. TMD S/S Pronounced spasm and tenderness of the masseter and temporalis muscles Dental x-rays help with
- 89. TMD Medical Management Treatment is referred to a dentist Analgesics are prescribed Custom-fitted mouth guard is
- 90. TMD Medical Management TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), injection of a local anesthetic to relieve muscle
- 91. Extrapyramidial disorders pg 686 Parkinson’s disease Huntington’s disease One primary characteristic is abnormal movement.
- 92. Parkinson’s Usually begins after age 50 early signs include stiffness, tremors of hands, pill rolling and
- 93. Parkinson’s Intention tremor: when tremors increase during voluntary movement…may be seen in some patients Later, tremors
- 94. Parkinson’s Have difficulty turning or redirecting forward motion arms seldom swing while walking rigidity develops more
- 95. Parkinson’s Levodopa and cogentin are drugs of choice physical therapy…in extreme cases surgery done to destroy
- 96. Parkinson’s Symptoms usually begin on one side and may take 15 years to spread bilaterally late
- 97. Huntington’s Disease pg. 689 Hereditary, degeneration of basal ganglia and cerebral cortex Causes mental apathy, emotional
- 98. Huntington’s Treatment is supportive, no cure tranquilizers and antiparkinsonian drugs to relieve choreiform movements late in
- 99. Huntington’s 1/2 children of affected parent will develop the disease but will not find out about
- 100. Huntington’s Personality changes (obstinanacy, moodiness and lack of interest Inappropriate behavior may start before the involuntary
- 101. Huntington’s chorea Difficulty chewing and swallowing, speech difficulty, intellectual decline loss of bowel and bladder control
- 102. Nursing care extrapyramidial 43-2 pg 690 Offer fluids hourly I&O, keep suction available to prevent aspiration
- 103. Nursing Care extrapyramidial Avoid stress, fatigue bowel and bladder incontinent retraining program may be helpful early,
- 104. Seizure disorders pg 692 Abnormal electrical discharge of neurons can be focal or generalized idiopathic (no
- 106. Seizure disorders Epilepsy is a permanent, recurrent seizure disorder causes include brain injury at birth, head
- 107. Seizure disorders Too much electrical discharges from nerve cells in the brain Different types: partial or
- 108. Seizure disorder Jacksonian: begins at one place and spreads to another in an orderly fashion psychomotor
- 109. Seizures Generalized seizure: Entire brain involved; can last several minutes, loss of consciousness absence; brief change
- 110. Generalized seizure Myoclonic: brief involuntary muscular jerks of extremities or body Tonic-clonic: Grand mal--emotional changes, aura
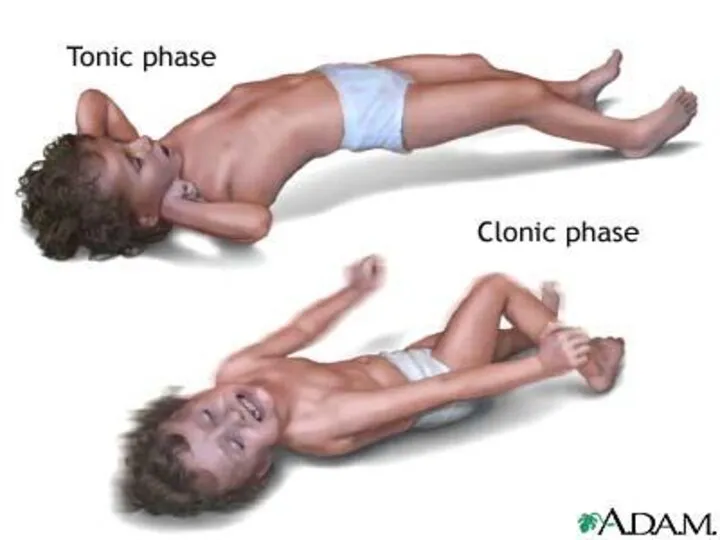
- 111. Seizure--Grand mal Clonic phase; alternating spasms and relaxations---thrashing and jerking breathing is spasmodic frothing saliva, jaws
- 113. Grand mal seizure Postictal stage: consciousness is regained, does not remember seizure confused, difficulty speaking, headache
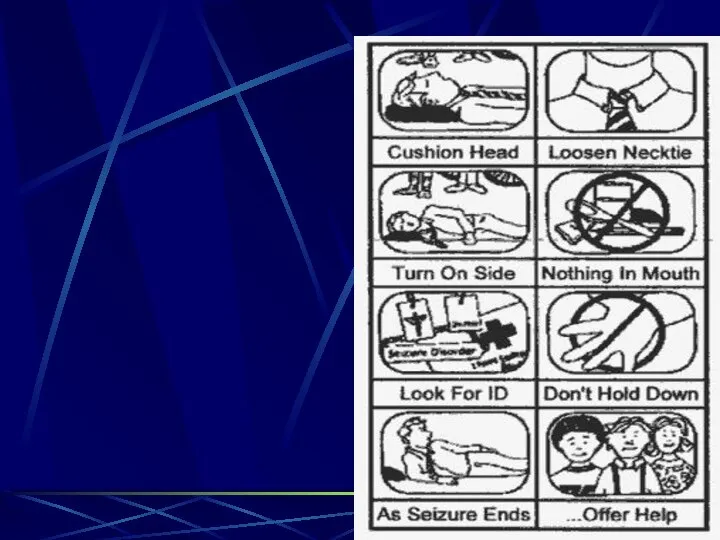
- 114. During a seizure Turn to side to keep airway patent and to prevent aspiration of saliva
- 116. During a Seizure Protect from injury…do not forcibly restrain arms, legs or head stay with patient
- 118. After a seizure Keep bed flat; turn to side until awake and responding keep room lighting
- 120. Nursing Observe closely and chart activity before and after turn on side--prevent aspiration, protect from injury
- 121. Nursing Assess for injury, allow to rest, report activity, time elapsed and client reaction pad side
- 123. Status Epilepticus Several tonic-clonic seizures without consciousness returning this is an emergency may be from stopping
- 125. Medications for seizures Dilantin phenobarbital Tegretol Zarontin depakene Valium drug of choice to stop status epilepticus
- 126. Brain Tumor pg. 697 Can result in death even if benign They take up space and
- 127. Brain tumor Projectile type vomiting without nausea, speech difficulty, double vision, paralysis Causes brain stem herniation
- 128. Brain Tumor Keep as pain free as possible IV fluids and TPN may be needed--keep I&O
- 129. Brain Tumor Chemotherapy, radiation and surgery used to treat craniotomy (incision thru skull) or craniectomy (part
- 132. Скачать презентацию













































































































 азбука - презентация для начальной школы
азбука - презентация для начальной школы Презентация на тему "Часть 3 (С2.2). Сочинение-рассуждение (собственное высказывание на основе прочитанного текста)" - скачать пр
Презентация на тему "Часть 3 (С2.2). Сочинение-рассуждение (собственное высказывание на основе прочитанного текста)" - скачать пр Презентация «Предмет квантовой механики. Место квантовой механики среди наук о движении.»
Презентация «Предмет квантовой механики. Место квантовой механики среди наук о движении.» Робер Дуано – ироничный наблюдатель, лиричный и великий фотограф-гуманист
Робер Дуано – ироничный наблюдатель, лиричный и великий фотограф-гуманист Преза Шашихин
Преза Шашихин Вентильді және интегральды сұлбалар. Биттік байланыстар логикасы. Блоктарға интеграцияланатын сұлба деңгейлері
Вентильді және интегральды сұлбалар. Биттік байланыстар логикасы. Блоктарға интеграцияланатын сұлба деңгейлері Историческая трансформация пылесоса
Историческая трансформация пылесоса Магические числа» и кЛАССИЧЕСКОЕ использования констант
Магические числа» и кЛАССИЧЕСКОЕ использования констант Читаем. Вспомним местоимения. Спряжение глаголов. Познакомимся с числами от 1 до 12
Читаем. Вспомним местоимения. Спряжение глаголов. Познакомимся с числами от 1 до 12 Презентация Виски
Презентация Виски Хорошее настроение - презентация для начальной школы_
Хорошее настроение - презентация для начальной школы_ Иконопись
Иконопись Военизированная спортивно-экстремальная игра «Зарница»
Военизированная спортивно-экстремальная игра «Зарница» Оборудование МС производства и ср-ва автоматизации
Оборудование МС производства и ср-ва автоматизации Подбор номенклатуры полупроводниковых приборов в поисковой системе «Дейтрон»
Подбор номенклатуры полупроводниковых приборов в поисковой системе «Дейтрон» Построение третьего вида по двум данным
Построение третьего вида по двум данным КИСЛОТА – вещество, принимающее электроны в пары при образовании химической связи. ОСНОВАНИЕ – вещество, предоставляющее электро
КИСЛОТА – вещество, принимающее электроны в пары при образовании химической связи. ОСНОВАНИЕ – вещество, предоставляющее электро Подростковый возраст Родительское собрание
Подростковый возраст Родительское собрание Переходные процессы приводящие к потере устойчивости ЭТС. Промежуточно-устойчивые режимы
Переходные процессы приводящие к потере устойчивости ЭТС. Промежуточно-устойчивые режимы Fashion and function
Fashion and function Етика мовної комунікації
Етика мовної комунікації Бауэрсокс Д.ДЖ., Клосс Д.ДЖ. Логистика. Интегрированная цепь поставок. - М : ЗАО "ОЛИМП-БИЗНЕС", 2001. Бауэрсокс Д.ДЖ., Клосс Д.
Бауэрсокс Д.ДЖ., Клосс Д.ДЖ. Логистика. Интегрированная цепь поставок. - М : ЗАО "ОЛИМП-БИЗНЕС", 2001. Бауэрсокс Д.ДЖ., Клосс Д. Дисциплина Информатики
Дисциплина Информатики  Преступления в сфере служебной деятельности
Преступления в сфере служебной деятельности Метрологическое обеспечение строительства. (Лекция 1)
Метрологическое обеспечение строительства. (Лекция 1) Женские образы в поэмах Гомера. Живопись и скульптура
Женские образы в поэмах Гомера. Живопись и скульптура Религия античного мира
Религия античного мира Attractions Kushchyovsky District
Attractions Kushchyovsky District