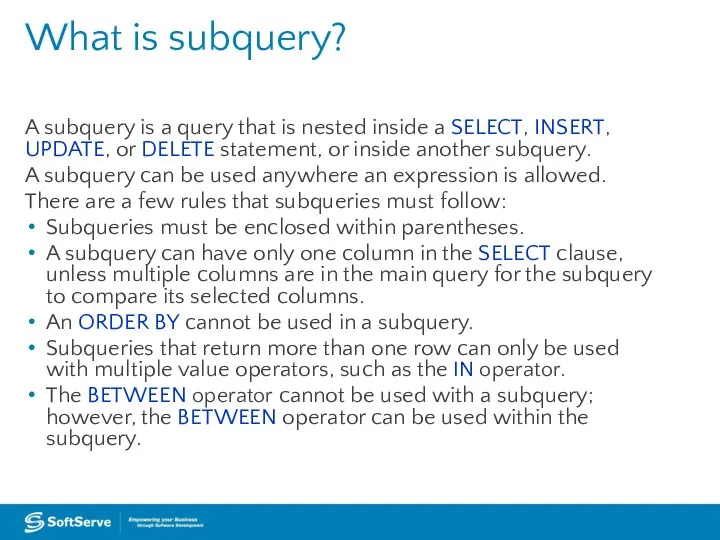
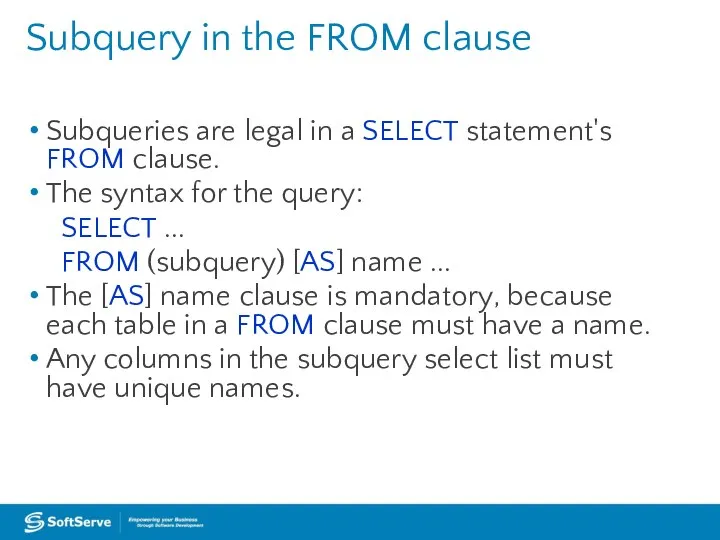
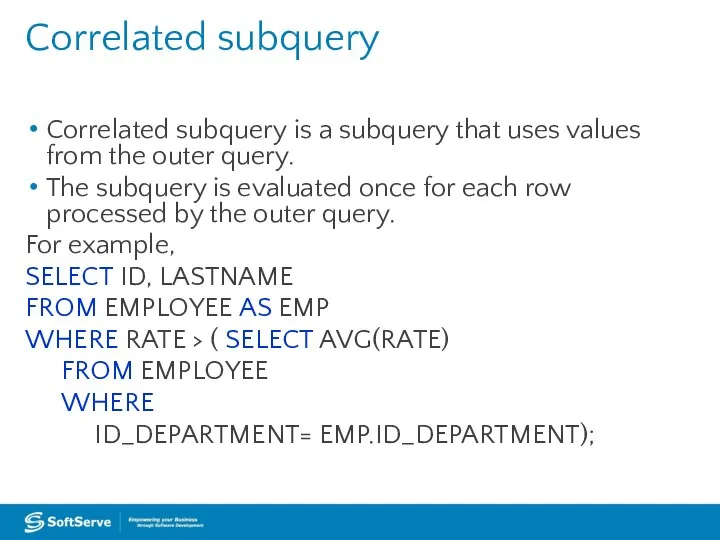
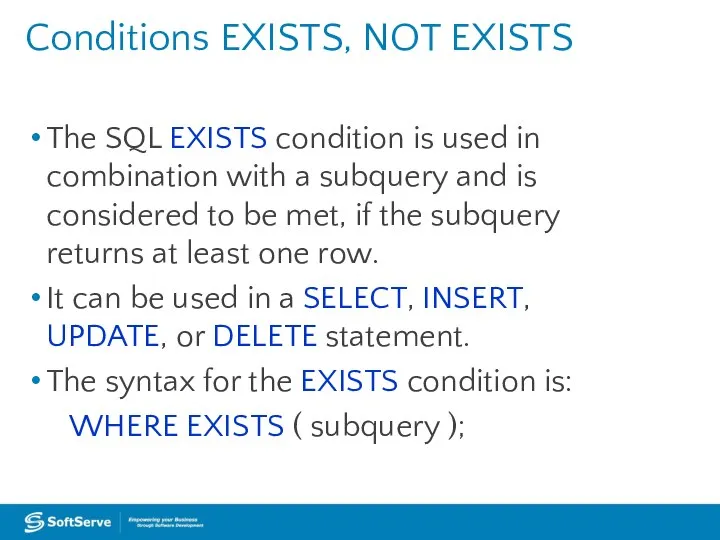
A subquery is a query that is nested inside a SELECT,
INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement, or inside another subquery.
A subquery can be used anywhere an expression is allowed.
There are a few rules that subqueries must follow:
Subqueries must be enclosed within parentheses.
A subquery can have only one column in the SELECT clause, unless multiple columns are in the main query for the subquery to compare its selected columns.
An ORDER BY cannot be used in a subquery.
Subqueries that return more than one row can only be used with multiple value operators, such as the IN operator.
The BETWEEN operator cannot be used with a subquery; however, the BETWEEN operator can be used within the subquery.
What is subquery?




 Презентация Понятие и назначение административно-правового режима (АПР) защиты государственной тайны.
Презентация Понятие и назначение административно-правового режима (АПР) защиты государственной тайны.  Мехатронные модули
Мехатронные модули Automatics and automatic control
Automatics and automatic control Европейский суд по правам человека
Европейский суд по правам человека Дагестан – край белых роз и черных гор
Дагестан – край белых роз и черных гор «Предпосылки возникновения и этапы развития науки» Выполнили студентки 1-го курса ФТД Бекенова Кымбат Эрмекова Айжан
«Предпосылки возникновения и этапы развития науки» Выполнили студентки 1-го курса ФТД Бекенова Кымбат Эрмекова Айжан Презентация «ОБЩИЕ ПОЛОЖЕНИЯ О ПРАВАХ НА РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ИНТЕЛЛЕКТУАЛЬНОЙ ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТИ И СРЕДСТВА ИНДИВИДУАЛИЗАЦИИ»
Презентация «ОБЩИЕ ПОЛОЖЕНИЯ О ПРАВАХ НА РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ ИНТЕЛЛЕКТУАЛЬНОЙ ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТИ И СРЕДСТВА ИНДИВИДУАЛИЗАЦИИ» Эффект Мессбауэра.
Эффект Мессбауэра. Проект пульсатора распределителя для заборного устройства вихревого типа
Проект пульсатора распределителя для заборного устройства вихревого типа ПОЛЬША И ЕС Подготовила: Клеутина С.А. Группа МЭ-092
ПОЛЬША И ЕС Подготовила: Клеутина С.А. Группа МЭ-092  Презентация по МХК Гончарное искусство.
Презентация по МХК Гончарное искусство.  Презентация "Горнодобывающая промышленность РФ: 50 инвестиционных проек" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Горнодобывающая промышленность РФ: 50 инвестиционных проек" - скачать презентации по Экономике Проект «Комфортная городская среда» на 2018 год
Проект «Комфортная городская среда» на 2018 год Смена слайдов производится по щелчку или при нажатии клавиши «пробел», все остальные действия выполняются автоматически. Приятно
Смена слайдов производится по щелчку или при нажатии клавиши «пробел», все остальные действия выполняются автоматически. Приятно Теория управления портфелем
Теория управления портфелем  Кодирование текстовой информации
Кодирование текстовой информации Материалы для оклеивания поверхностей
Материалы для оклеивания поверхностей Применение линейного программирования в математических моделях
Применение линейного программирования в математических моделях Эмпиризм
Эмпиризм Презентация по продукту Мобильное приложение для ЮЛ и ИП
Презентация по продукту Мобильное приложение для ЮЛ и ИП Списки. Элемент списка. (Лекция 2)
Списки. Элемент списка. (Лекция 2) Стили одежды
Стили одежды Вирус Ласса
Вирус Ласса Доклад на московскои__ конференции(с англ)-1 с комм
Доклад на московскои__ конференции(с англ)-1 с комм Простейшие движения твердых тел
Простейшие движения твердых тел Доказательство происхождения человека от животных
Доказательство происхождения человека от животных  Культурное наследие Древней Греции. Музыка, танцы
Культурное наследие Древней Греции. Музыка, танцы Контактор. Виды контакторов
Контактор. Виды контакторов