Содержание
- 2. Affirmative
- 3. Negative Long Form I/You have not visited He/She/It has not visited We/You/They have not visited Short
- 4. Interrogative Have I/you visited? Has he/she/it visited? Have we/you/they visited?
- 5. Short answer Yes, I/you have. No, I/You haven’t. Yes, he/she/it has. No, he/she/it hasn’t. Yes, we/you/they
- 6. We form the present perfect with the auxiliary verb have/has and past participle of the main
- 7. We usually form the past participle of regular verbs by adding –ed to the verb. Stay-stayed
- 8. We form questions by putting have/has before the subject. f.E.Has she done her homework?
- 9. We form negations by putting not between have/has and the past participle. f.E. They haven’t phoned
- 10. Use We use the present perfect: for action which started in the past and continue up
- 11. to talk about a past action which has a visible result in the present. He has
- 12. for actions which happened at an unstated time in the past. The action is more important
- 13. with today, this morning/afternoon, etc when these periods of time are not finished at the time
- 15. Скачать презентацию












 Grammar review
Grammar review FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE
FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE DEATH PENALTY or CAPITAL PUNISHMENT
DEATH PENALTY or CAPITAL PUNISHMENT PASSIVE VOICE Подготовила учитель английского языка средней школы №35 Митякова Н.И.
PASSIVE VOICE Подготовила учитель английского языка средней школы №35 Митякова Н.И. Canada
Canada  Lost in translation
Lost in translation Презентация Сложное дополнение Complex object
Презентация Сложное дополнение Complex object My Body
My Body Презентация к уроку английского языка "Welcome to Wales" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Welcome to Wales" - скачать  Passive Voice Пассивный залог
Passive Voice Пассивный залог Farm animals Memory game
Farm animals Memory game Lesson 1
Lesson 1 National Park Elk Island
National Park Elk Island Grammar: verb -can
Grammar: verb -can School supplies
School supplies The River Thames
The River Thames There is, there are
There is, there are Let’s check your hometask
Let’s check your hometask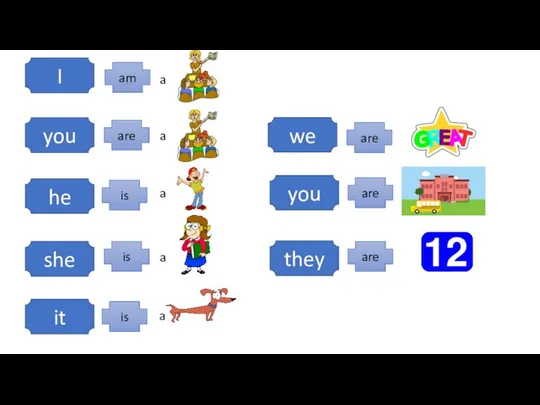 Personal pronouns and forms of to be icebreakers
Personal pronouns and forms of to be icebreakers Teddy Bear Day
Teddy Bear Day HEALTHY & UNHEALTHY FOOD
HEALTHY & UNHEALTHY FOOD Feelings and Emotions
Feelings and Emotions Косметические процедуры
Косметические процедуры Junk Food
Junk Food  My hobbies
My hobbies Фонетическая зарядка на английском языке. Сказка о язычке Выполнила: Абдрахимова Регина Ринатовна
Фонетическая зарядка на английском языке. Сказка о язычке Выполнила: Абдрахимова Регина Ринатовна  Letter
Letter Kate Vershinina Grade 11 “B” Dul’durga High school
Kate Vershinina Grade 11 “B” Dul’durga High school