Содержание
- 2. Why meet? Meetings are held in all types of businesses Meetings are a great tool in
- 3. Meetings are held for variety of purposes: To co-ordinate or arrange activities To give information to
- 4. Types of Meetings: Formal Meetings Have set rules and guidelines. Formal record of them must be
- 5. Types of Meetings: Informal Meetings They are not bound by regulations as formal meetings. An agenda
- 6. Why Meetings Fail? Managers spend about 60% of their time in meetings. If held effectively, meetings
- 7. Attending Meetings Try to understand the meeting’s purpose and your role in it. Do your homework.
- 8. Roles Our role in meetings is a set of behaviors expected of us by the group.
- 10. Successful Team Will contain a balance of all nine roles. Several people may share the same
- 11. Committed Members Devote time and energy to team Support final decision Perform needed functions Necessary for
- 12. Group Task Functions Initiate Give information Seek information Give opinion Seek opinion Elaborate Energize Review Record
- 13. Group Maintenance Functions Encourage Harmonize Relieve tension Gatekeep Microsoft Image
- 14. Nonfunctional Behaviors Blocking Aggression Storytelling Recognition seeking Dominating Confessing Special-interest pleading Distracting Withdrawing Cause unproductive conflict
- 15. Handling Nonfunctional People Plan opening remarks carefully Seat nonfunctional person next to leader Avoid direct eye
- 16. Nonfunctional People (con’t) Break in Place talkative member between quiet members Encourage withdrawers Give praise and
- 17. Member Skills Active Listening Open-mindedness Microsoft Image Communication skills for group members include . . .
- 18. Leadership Defined: Leadership is the use of power to promote the goal accomplishment and maintenance of
- 19. Leadership in Meetings The best soldier is not soldierly The best fighter is not ferocious The
- 20. Trait Theory of Leadership Do you believe that some people are “born leaders”? Basically, that’s what
- 21. Trait Theory of Leadership Microsoft Image Successful leaders are more likely to be . . .
- 22. Leader Responsibilities Inform members of meetings Select place for meeting Check that everything needed is in
- 23. Leader Responsibilities (con’t) Encourage discussion Ask questions skillfully See to task and maintenance functions Listen carefully
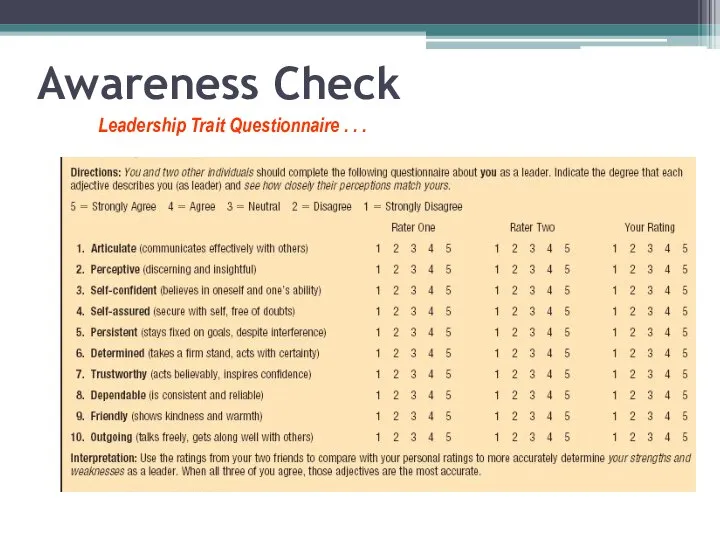
- 24. Awareness Check Leadership Trait Questionnaire . . .
- 25. Function Theory of Leadership “There are certain functions that must be performed if a group is
- 26. Awareness Check Leadership Function Questionnaire . . .
- 27. Three-Dimension Theory To be a good leader, you should be aware of your leadership style (the
- 28. Situational Contingency Theory Situation dictates leadership style Leadership depends on: Power Task Relationship Microsoft Image
- 29. Situational Contingency Theory states that… Autocratic Leadership Style works best when: Group agreement is not required
- 30. Situational Contingency Theory states that… Democratic Leadership is best when: Greater employee satisfaction is needed. Group
- 31. Situational Leadership Theory Definition: “A good leader is flexible and can change styles when needed .”
- 32. Situational Leadership Theory Delegating style. Employees make and implement decisions on their own. This style works
- 33. Situational Leadership Theory Participating Style. Employees and leader share in decision making. This style works best
- 35. Скачать презентацию































 Урок английского языка по теме «The British monarchy and a parliamentary democracy” (По учебнику К.И.Кауфман, М.Ю.Кауфман для 8 кл Happy English.ru) Учитель: Корнилова Наталья Геннадьевна МБОУ «ДСОШ №3»
Урок английского языка по теме «The British monarchy and a parliamentary democracy” (По учебнику К.И.Кауфман, М.Ю.Кауфман для 8 кл Happy English.ru) Учитель: Корнилова Наталья Геннадьевна МБОУ «ДСОШ №3»  Time
Time УЧИТЕЛЬ АНГЛИЙСКОГО ЯЗЫКА МБОУ «МАЛО-УРУССИНСКАЯ ООШ» ШАМСУЛЛИНА АЛИНА ФАВАРИСОВНА
УЧИТЕЛЬ АНГЛИЙСКОГО ЯЗЫКА МБОУ «МАЛО-УРУССИНСКАЯ ООШ» ШАМСУЛЛИНА АЛИНА ФАВАРИСОВНА  Исполнителя Петриковской Валерии
Исполнителя Петриковской Валерии Education in Australia
Education in Australia  WE ARE WHAT WE EAT
WE ARE WHAT WE EAT Seasons
Seasons Презентация к уроку английского языка "Lie to Me" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Lie to Me" - скачать  How are you?
How are you? Practice 1
Practice 1 Презентация к уроку английского языка "Презентация вставь пропущенную букву" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Презентация вставь пропущенную букву" - скачать бесплатно Welcome
Welcome Презентация к уроку английского языка "Вашингтон- столица США" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Вашингтон- столица США" - скачать  Презентация к уроку английского языка "Clothes" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Clothes" - скачать бесплатно Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland Have something done
Have something done THE ALMANAC “Nature’s seven greatest wonders” Работу выполнила Королева Алена ученица 6 «в» класса МАОУ «Сузунская СОШ № 2» Новосибирской области Руководитель: Шмальц Н. В., учитель иностранных языков
THE ALMANAC “Nature’s seven greatest wonders” Работу выполнила Королева Алена ученица 6 «в» класса МАОУ «Сузунская СОШ № 2» Новосибирской области Руководитель: Шмальц Н. В., учитель иностранных языков My favorite movie
My favorite movie Презентация к уроку английского языка "James Fenimore Cooper" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "James Fenimore Cooper" - скачать бесплатно Модальные глаголы Must и Have to
Модальные глаголы Must и Have to Упаковка и маркировка пищевых продуктов
Упаковка и маркировка пищевых продуктов Colours
Colours Almost all people are fond of travelling
Almost all people are fond of travelling How We Take Care of the Environment
How We Take Care of the Environment  The 25th of February “Tourism. Jobs in tourism”
The 25th of February “Tourism. Jobs in tourism” Find the mistake
Find the mistake Risk Management
Risk Management Vincent Van Gogh
Vincent Van Gogh