Содержание
- 2. What does it mean when we hear: “He has bought a new motorcycle.”? He bought a
- 3. What does it mean when we hear: “He has bought a new motorcycle.”? He bought a
- 4. “He bought a new motorcycle.” He bought a new motorcycle in the past. The motorcycle is
- 5. “He bought a new motorcycle.” He bought a new motorcycle in the past. The motorcycle is
- 6. “Kenny has baked a cake.” Kenny baked a cake in the past. There is cake in
- 7. “Kenny has baked a cake.” Kenny baked a cake in the past. There is cake in
- 8. “Kenny baked a cake.” Kenny baked a cake in the past. There is cake in the
- 9. “Kenny baked a cake.” Kenny baked a cake in the past. There is cake in the
- 10. “Betty has broken her leg.” Betty broke her leg in the past. Her leg is broken
- 11. “Betty has broken her leg.” Betty broke her leg in the past. Her leg is broken
- 12. “Betty broke her leg.” Betty broke her leg in the past. Her leg is broken now.
- 13. “Betty broke her leg.” Betty broke her leg in the past. Her leg is broken now.
- 14. “They have cleaned the car.” They cleaned the car in the past. The car is clean
- 15. “They have cleaned the car.” They cleaned the car in the past.. The car is clean
- 16. “They cleaned the car.” They cleaned the car in the past. The car is clean now.
- 17. “They cleaned the car.” They cleaned the car in the past. The car is clean now.
- 18. “Simon and Clare have set up the dominoes.” Simon and Clare set them up in the
- 19. “Simon and Clare have set up the dominoes.” Simon and Clare set them up in the
- 20. “Simon and Clare set up the dominoes.” Simon and Clare set them up in the past.
- 21. “Simon and Clare set up the dominoes.” Simon and Clare set them up in the past.
- 22. “Ben has recieved his salary.” Ben recieved his salary in the past. Ben has some money
- 23. “Ben has recieved his salary.” Ben recieved his salary in the past. Ben has some money
- 24. “Harry recieved his salary.” Harry recieved his salary in the past. Harry has some money now.
- 25. “Harry recieved his salary.” Harry recieved his salary in the past. Harry has some money now.
- 26. Basically Present Perfect is providing information about a past event and the current result we have
- 28. Скачать презентацию

























 Millionaire
Millionaire Action verbs and abilities
Action verbs and abilities Город и село. City and village
Город и село. City and village Домашние обязанности
Домашние обязанности Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin  lexical_expressive_means
lexical_expressive_means Sport is fun!
Sport is fun! Composition Your opinion
Composition Your opinion What do they have for lunch
What do they have for lunch My Room A game for the 6th form Done by Kara Ludmila A teacher of English School 2 Artemovsky Sverdlovsk Region
My Room A game for the 6th form Done by Kara Ludmila A teacher of English School 2 Artemovsky Sverdlovsk Region  Интерактивный тренажер к уроку английского языка Animals
Интерактивный тренажер к уроку английского языка Animals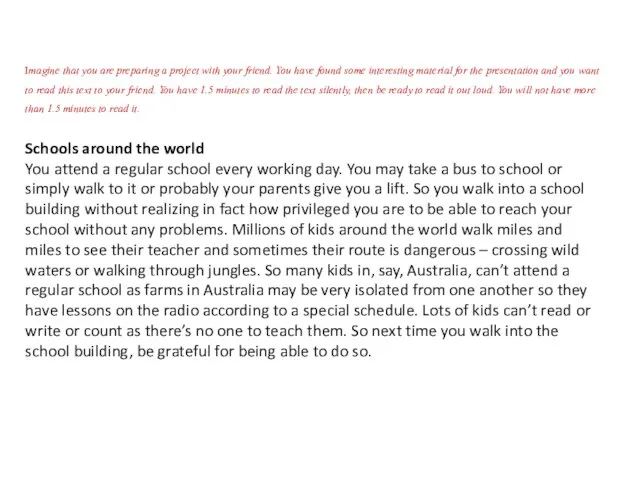 Schools around the world
Schools around the world Презентация к уроку английского языка "Graffiti L Hostel" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Graffiti L Hostel" - скачать  Grammar rain
Grammar rain What would you like to see in the
What would you like to see in the Language for Entertainment
Language for Entertainment My family
My family Healthy lifestyle. Your choice!
Healthy lifestyle. Your choice! Праздники Англии
Праздники Англии  Major world religions
Major world religions Step-by-step recipe of buckwheat with forcemeat
Step-by-step recipe of buckwheat with forcemeat Презентация к уроку английского языка "Иностранные языки" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Иностранные языки" - скачать бесплатно Past Tense
Past Tense Reported speech. Косвенная речь
Reported speech. Косвенная речь Ах, юбилей!
Ах, юбилей! Придаточные обстоятельственные предложения
Придаточные обстоятельственные предложения М.З. Биболетова «Enjoy English» 4 класс Lesson
М.З. Биболетова «Enjoy English» 4 класс Lesson Стратегии письменного экзамена: аудирование
Стратегии письменного экзамена: аудирование