Содержание
- 2. Background The Declaration of Independence 1776 The War of Independence 1776-1783 The American Constitution 1789 Federal
- 3. State and Federal System Historically state and local government came first. The states have their own
- 4. The Legislative Branch: Congress Passes legislation and appropriates money The House of Representatives 435 members –according
- 5. The Executive Branch: The Presidency 4-year term - max two 4-year terms Protects the Constitution Proposes
- 6. The Executive Branch: The Cabinet No mention of it in the Constitution Subordinate to the President
- 7. The Supreme Court 9 members Life term appointment Interprets and guards the Constitution Interprets the law
- 8. Checks and Balances Congress: Power of the purse Can override presidential veto (2/3 majority) Power of
- 9. Elections and Political Parties Winner-take-all-election system The Electoral College Two party system- both appealing to the
- 10. The Electoral College Representatives of the people in presidential elections 534 electors, corresponding to the numbers
- 11. Democrats and Republicans And Their Voters Democrats supported by majority of black voters (Clinton 83%) Urban
- 13. Скачать презентацию










 Big city problems. Как написать эссе
Big city problems. Как написать эссе Green issues
Green issues Homework
Homework Spotlight 9. Module 5. Art &Literature
Spotlight 9. Module 5. Art &Literature Презентация к уроку английского языка "Seasons" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Seasons" - скачать  Презентация к уроку английского языка "What do you want to eat?" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "What do you want to eat?" - скачать  Groups and movements
Groups and movements Animals
Animals  United Kingdom Olga Novik Form 10-B
United Kingdom Olga Novik Form 10-B  Презентация к уроку английского языка "ПРАЗДНИК АНГЛИЙСКОЙ ПОЭЗИИ" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "ПРАЗДНИК АНГЛИЙСКОЙ ПОЭЗИИ" - скачать бесплатно Animal Sounds
Animal Sounds W.Shakespear’s heroines
W.Shakespear’s heroines Holidays and festivals in Britain выполнила учитель английского языка МОУ «СОШ №77», г. Омска, Тонких Т.А.
Holidays and festivals in Britain выполнила учитель английского языка МОУ «СОШ №77», г. Омска, Тонких Т.А. Birch is a symbol of Russia. Gusseva Tanya School №3 Class 8B
Birch is a symbol of Russia. Gusseva Tanya School №3 Class 8B Презентация к уроку английского языка "Root Words" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Root Words" - скачать бесплатно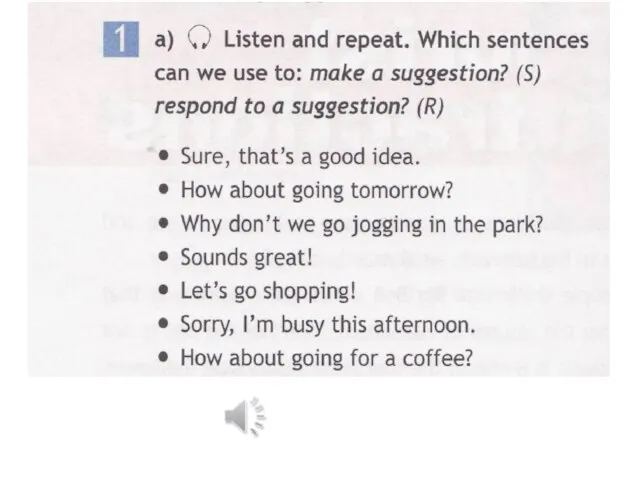 Презентация English
Презентация English Презентация к уроку английского языка "Голливуд" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Голливуд" - скачать бесплатно Чтение гласных в английском языке
Чтение гласных в английском языке One photo to describe (day 2)
One photo to describe (day 2) Vitamins for children: pros and cons
Vitamins for children: pros and cons Evolution of Youth Groups in Russia
Evolution of Youth Groups in Russia Презентация по английскому языку Past, Present, Future. 5 класс
Презентация по английскому языку Past, Present, Future. 5 класс  Глаголы put on и take off. Look and read
Глаголы put on и take off. Look and read MY HOUSE
MY HOUSE  Презентация к уроку английского языка "Техника запоминания иностранных слов" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Техника запоминания иностранных слов" - скачать  Презентация к уроку английского языка "Britain. The country and its people" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Britain. The country and its people" - скачать  Party games for esl
Party games for esl Презентация к уроку английского языка "Youth subculture" - скачать
Презентация к уроку английского языка "Youth subculture" - скачать