Содержание
- 2. Contents: From the Big Bang theory to Inflationary Cosmology Eternal inflation and string theory landscape
- 3. Two major cosmological discoveries: The new-born universe experienced rapid acceleration (inflation) A new (slow) stage of
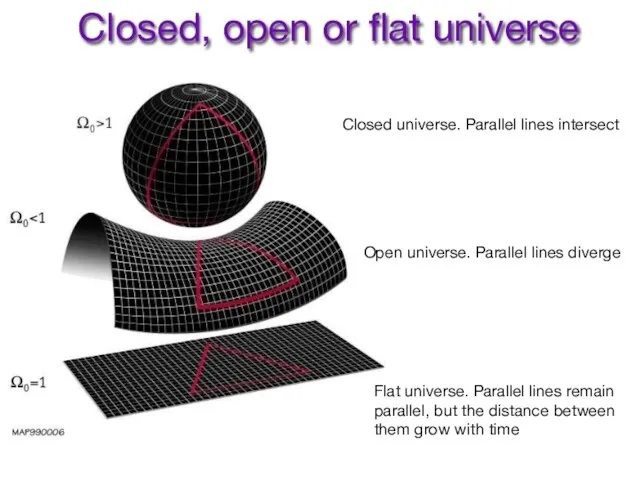
- 4. Closed, open or flat universe Closed universe. Parallel lines intersect Open universe. Parallel lines diverge Flat
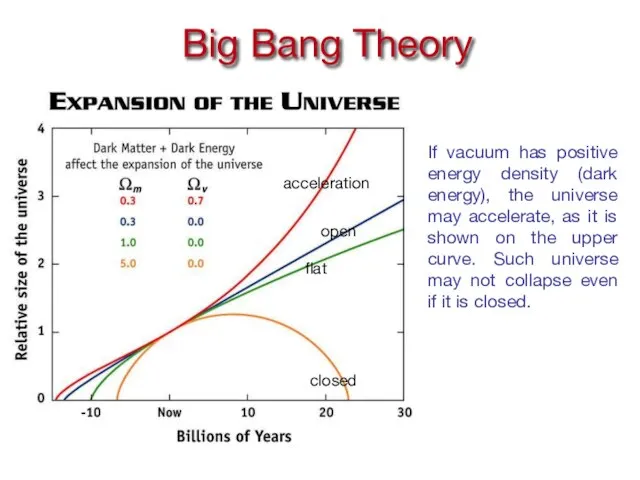
- 5. Big Bang Theory acceleration closed flat open If vacuum has positive energy density (dark energy), the
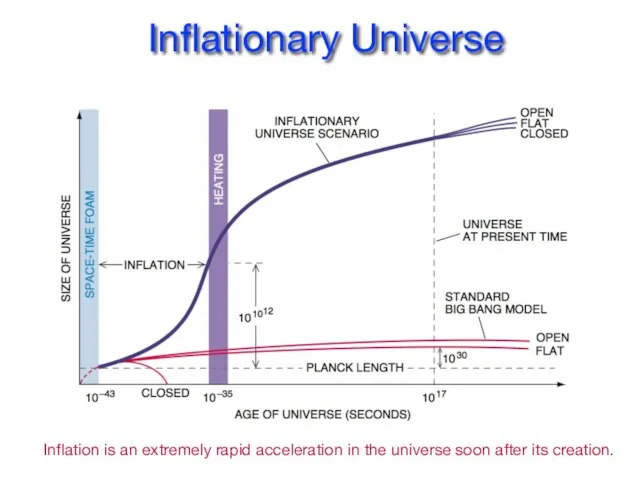
- 6. Inflationary Universe Inflation is an extremely rapid acceleration in the universe soon after its creation.
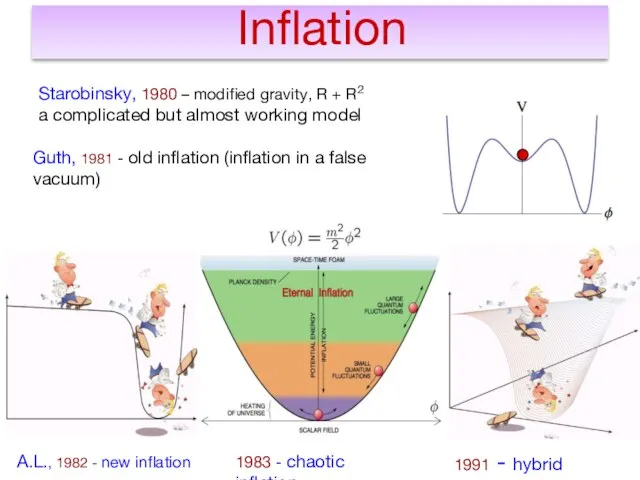
- 7. Inflation Starobinsky, 1980 – modified gravity, R + R2 a complicated but almost working model Guth,
- 8. What was before the Big Bang? Why is our universe so homogeneous (better than 1 part
- 9. Where did the energy come from? Some basic facts: 1) Energy of matter in the universe
- 10. Energy of matter in the Big Bang theory According to the Big Bang theory, the total
- 11. solves many problems of the old Big Bang theory, and explains how the whole universe could
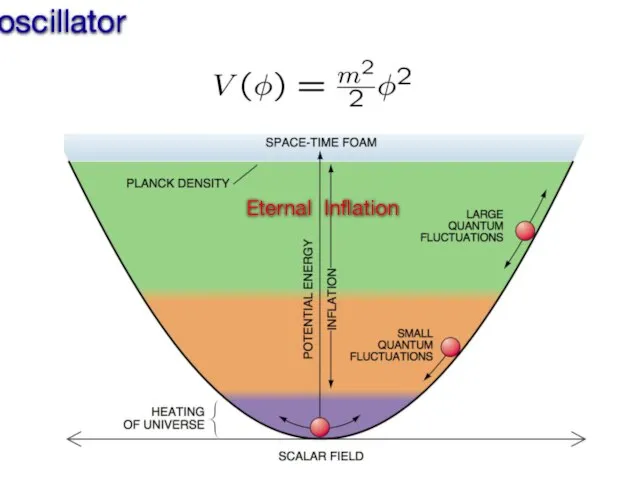
- 12. Inflation as a theory of a harmonic oscillator Eternal Inflation
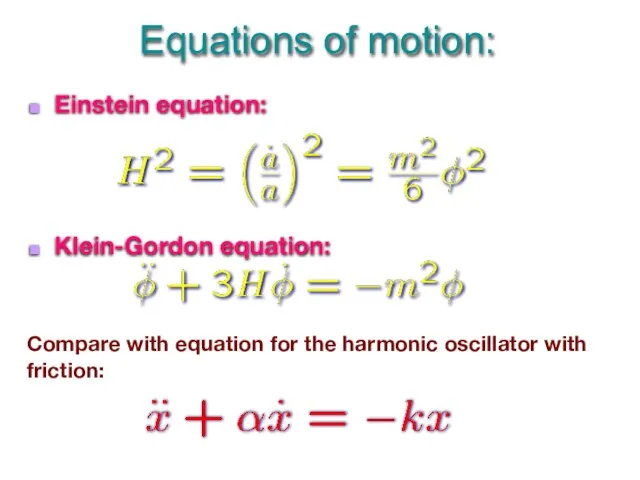
- 13. Einstein equation: Klein-Gordon equation: Equations of motion: Compare with equation for the harmonic oscillator with friction:
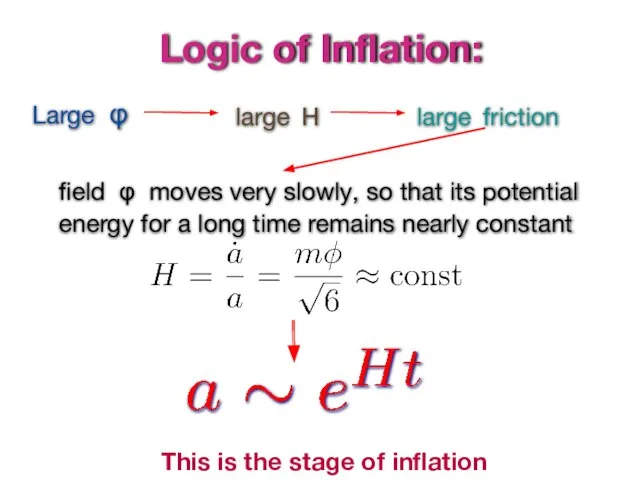
- 14. Logic of Inflation: Large φ large H large friction field φ moves very slowly, so that
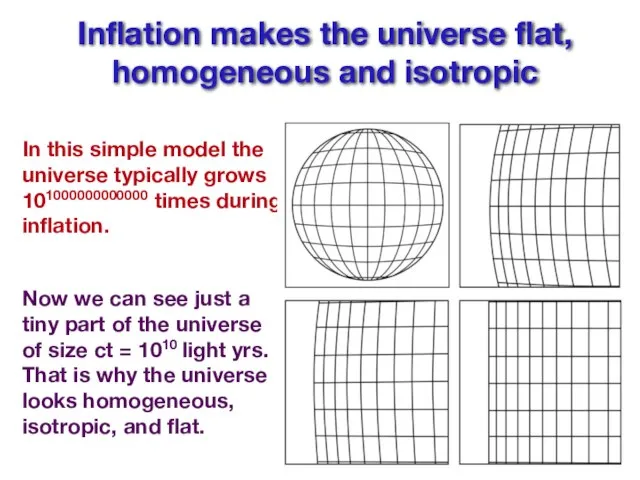
- 15. Inflation makes the universe flat, homogeneous and isotropic In this simple model the universe typically grows
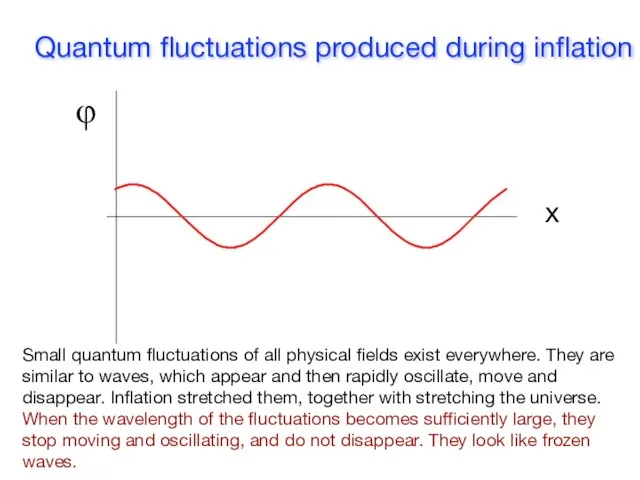
- 16. Quantum fluctuations produced during inflation φ x Small quantum fluctuations of all physical fields exist everywhere.
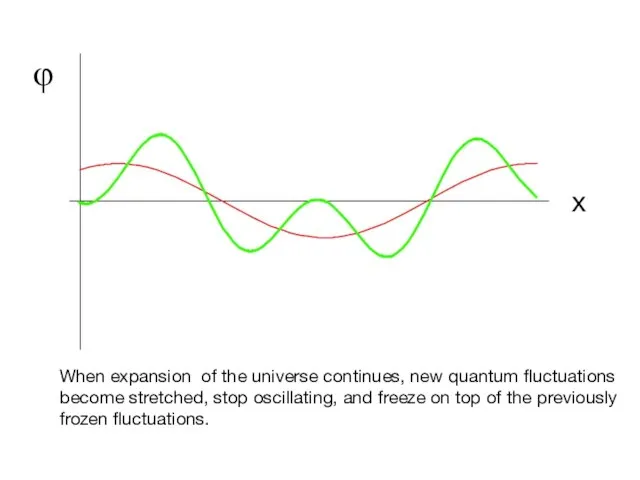
- 17. φ x When expansion of the universe continues, new quantum fluctuations become stretched, stop oscillating, and
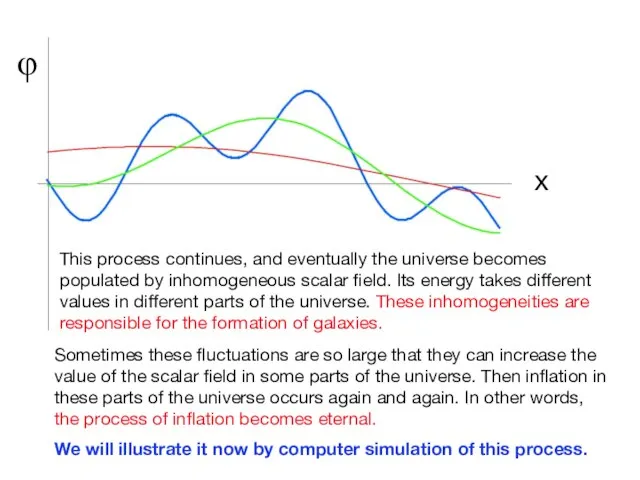
- 18. φ x This process continues, and eventually the universe becomes populated by inhomogeneous scalar field. Its
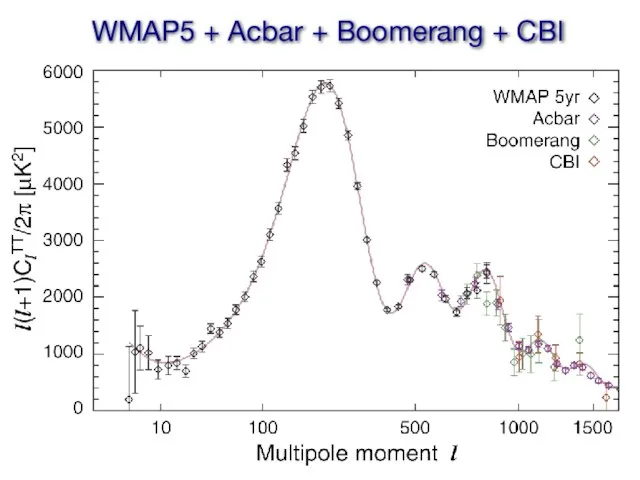
- 19. WMAP5 + Acbar + Boomerang + CBI
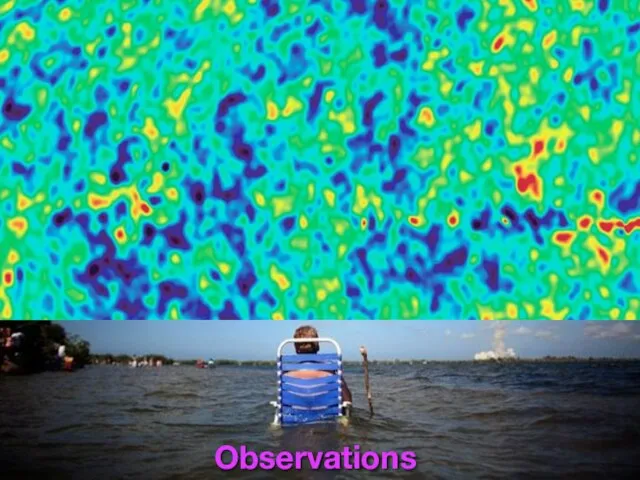
- 20. Observations
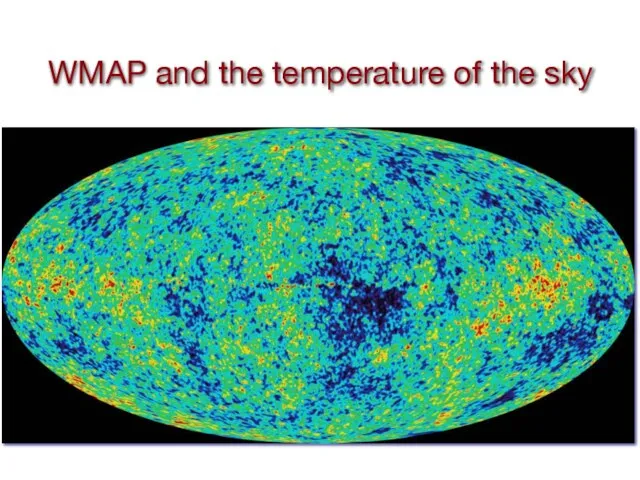
- 21. WMAP and the temperature of the sky
- 22. This is a photographic image of quantum fluctuations blown up to the size of the universe
- 23. On a much, much larger scale… Inflationary multiverse
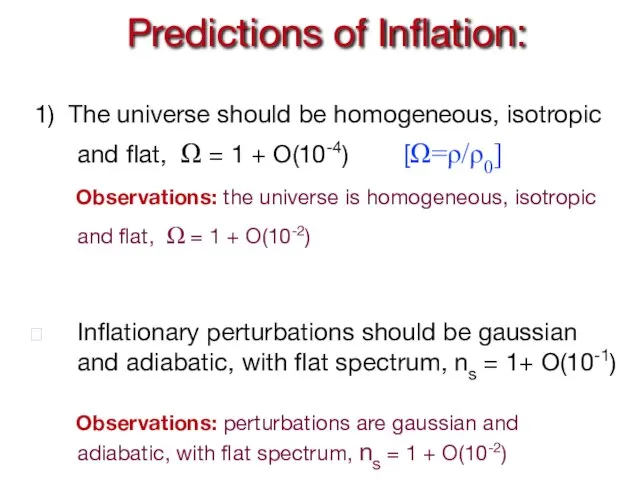
- 24. Predictions of Inflation: 1) The universe should be homogeneous, isotropic and flat, Ω = 1 +
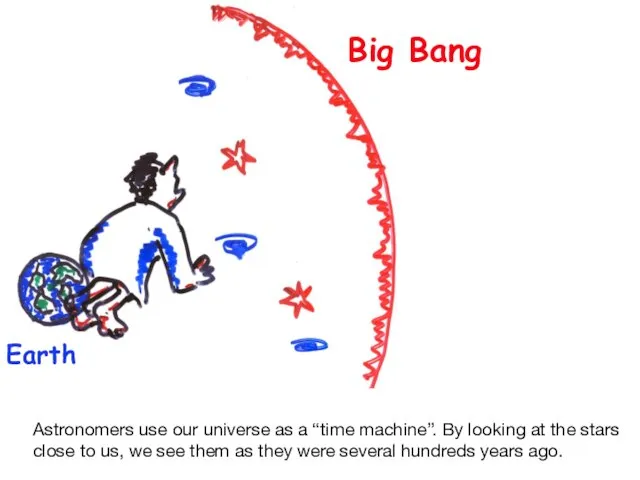
- 25. Big Bang Earth Astronomers use our universe as a “time machine”. By looking at the stars
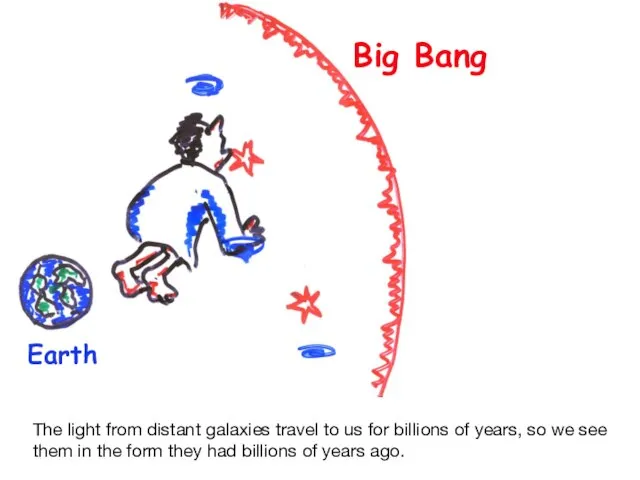
- 26. Big Bang Earth The light from distant galaxies travel to us for billions of years, so
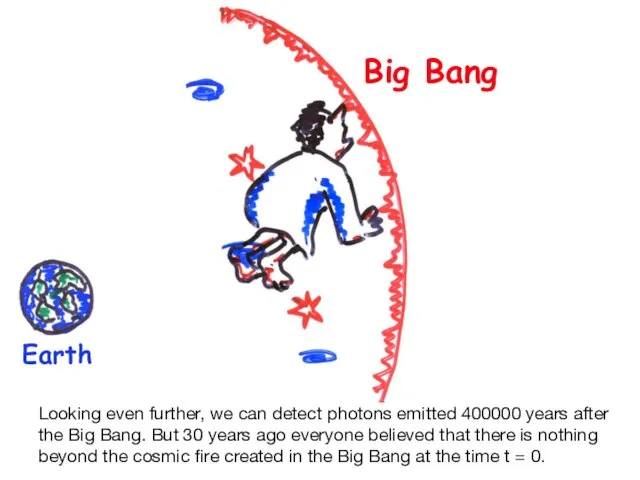
- 27. Big Bang Earth Looking even further, we can detect photons emitted 400000 years after the Big
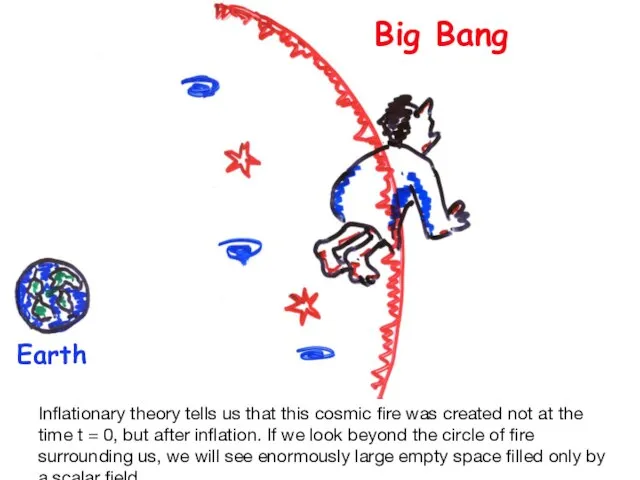
- 28. Big Bang Earth Inflationary theory tells us that this cosmic fire was created not at the
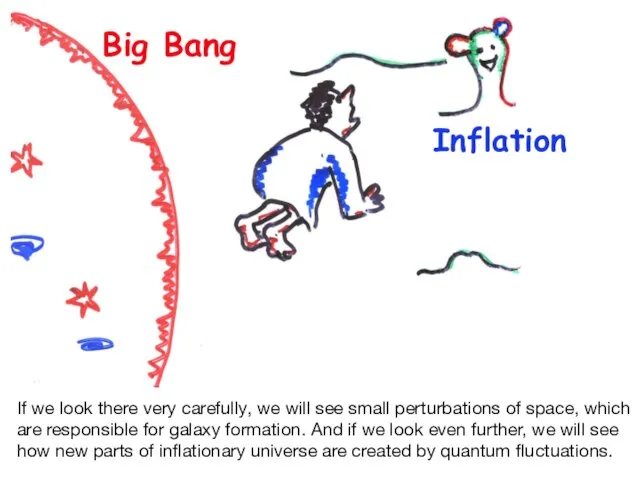
- 29. Big Bang Inflation If we look there very carefully, we will see small perturbations of space,
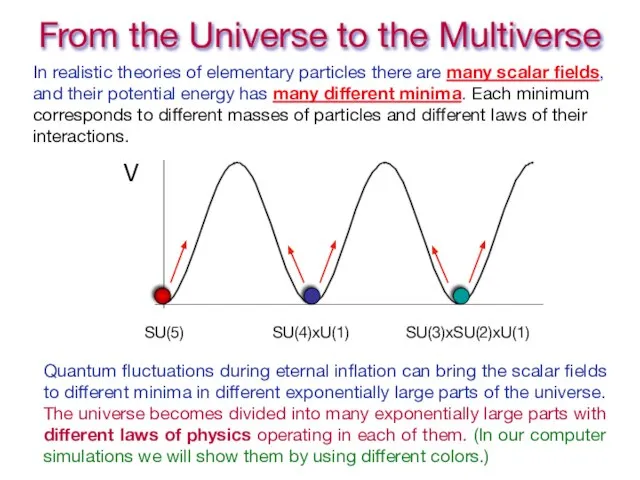
- 30. From the Universe to the Multiverse In realistic theories of elementary particles there are many scalar
- 31. Genetic code of the Universe There may be one fundamental law of physics, like a single
- 32. In string theory, genetic code is written in the properties of compactification of extra dimensions Up
- 33. String Theory Landscape Perhaps 10100 - 101000 different minima in string theory
- 34. Kandinsky Universe
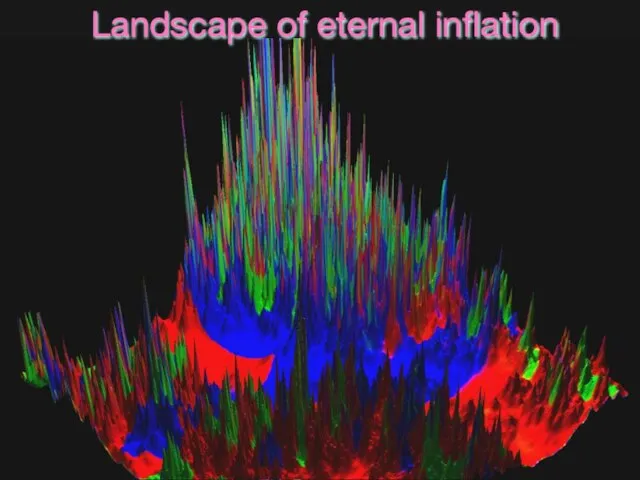
- 35. Landscape of eternal inflation
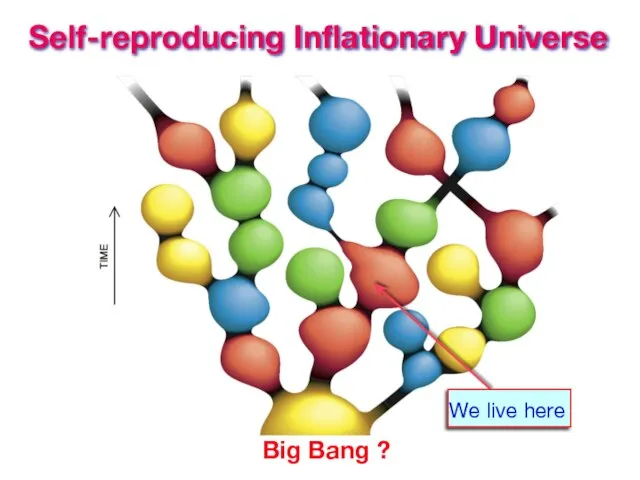
- 36. Self-reproducing Inflationary Universe Big Bang ? We live here
- 37. "It is said that there is no such thing as a free lunch. But the universe
- 39. Скачать презентацию













 Полеты на Луну
Полеты на Луну Корональный выброс масс на Солнце
Корональный выброс масс на Солнце Луна. Фазы луны. Лунные затмения
Луна. Фазы луны. Лунные затмения Занимательная ономастика для дошкольников
Занимательная ономастика для дошкольников Кометы и метеоры - презентация по Астрономии скачать
Кометы и метеоры - презентация по Астрономии скачать  Марс
Марс Планета Марс Підготувала учениця 11-Б класу ЗОШ І-ІІІ ст. №11 Відняк Людмила
Планета Марс Підготувала учениця 11-Б класу ЗОШ І-ІІІ ст. №11 Відняк Людмила  Астрономия и другие естественные науки
Астрономия и другие естественные науки Загадки звёздного неба
Загадки звёздного неба САТУРН - презентация по Астрономии скачать бесплатно
САТУРН - презентация по Астрономии скачать бесплатно Space exploration
Space exploration Карликовые планеты
Карликовые планеты Планета Марс
Планета Марс Історія про Юпітер та Сатурн
Історія про Юпітер та Сатурн Астрономія та визначення часу. Типи календарів. Видимий рух Сонця. Видимі рухи планет Підготувала: Учениця 11-М класу Грідіна В
Астрономія та визначення часу. Типи календарів. Видимий рух Сонця. Видимі рухи планет Підготувала: Учениця 11-М класу Грідіна В Плутон
Плутон Зачем летают в космос? - презентация по Астрономии скачать _
Зачем летают в космос? - презентация по Астрономии скачать _ Физические характеристики солнца Выполнила: Терешко Елена 11-Б
Физические характеристики солнца Выполнила: Терешко Елена 11-Б  Будова Всесвіту
Будова Всесвіту Галилеевы спутники Юпитера - презентация по Астрономии скачать
Галилеевы спутники Юпитера - презентация по Астрономии скачать  Основные характеристики звезд
Основные характеристики звезд КУРС ГЕОДЕЗИЧЕСКОЙ АСТРОНОМИИ
КУРС ГЕОДЕЗИЧЕСКОЙ АСТРОНОМИИ  Карликовые планеты
Карликовые планеты Планета Уран
Планета Уран Плутон - презентация по Астрономии скачать
Плутон - презентация по Астрономии скачать  День космонавтики презентация
День космонавтики презентация История открытия Плутона и Нептуна
История открытия Плутона и Нептуна Астероид
Астероид