Содержание
- 2. FERTILIZERS Function of elements Symptoms of lack of elements Elements in soil Strategy: Soil Fertigation Foliar
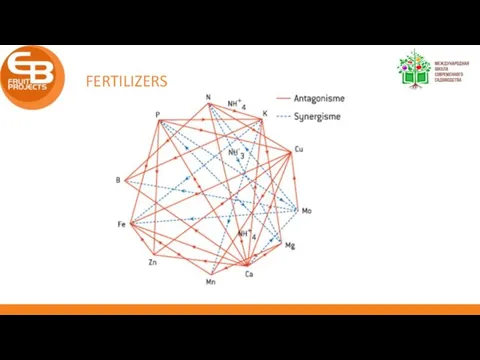
- 3. FERTILIZERS It is about balance between elements More of 1 element does NOT mean: more production
- 4. FERTILIZERS
- 5. FERTILIZERS Keep in mind: Roots are for uptake of elements and water Leaves are for assimilation
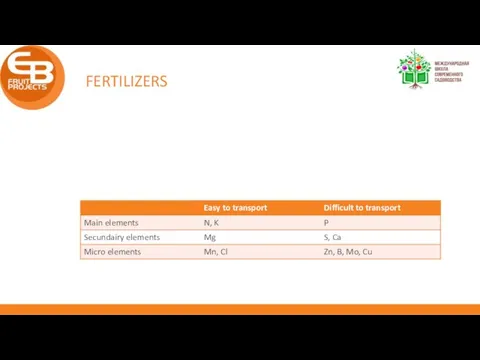
- 6. FERTILIZERS
- 7. FERTILIZERS
- 8. N = NITROGEN In quantity needed, the most important of all For metabolism of plant: Amino-acids
- 9. N = NITROGEN Uptake: ? by roots, little by leaves Uptake of: NO3 = nitrate NH4
- 10. N = NITROGEN If there is a lack: Small leaves ? not green, more yellow Weak
- 11. N = NITROGEN Too much N: Big leaves ? dark green Strong vegetative growth Big fruit
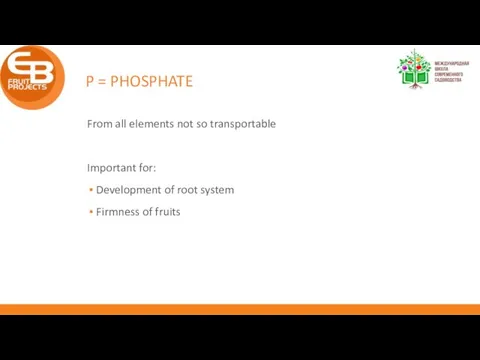
- 12. P = PHOSPHATE From all elements not so transportable Important for: Development of root system Firmness
- 13. P = PHOSPHATE Uptake difficult Should be enough P2O5 around rootsystem Lack: Smalller fruits Less and
- 14. K = POTASSIUM Important for water uptake And transport of other elements Very mobile Good for:
- 15. K = POTASSIUM Lack: Abnormal evaporation Small fruits More N in leaves
- 16. K = POTASSIUM K is concurrent for: Magnesium (Mg) Calcium (Ca) Borium (B) And also Natrium
- 17. MG = MAGNESIUM Magnesium is part of chlorofyll. 15% of all Mg is in het leaves.
- 18. MG = MAGNESIUM Lack: Especially on soil with lower pH After dry period Low temperatures during
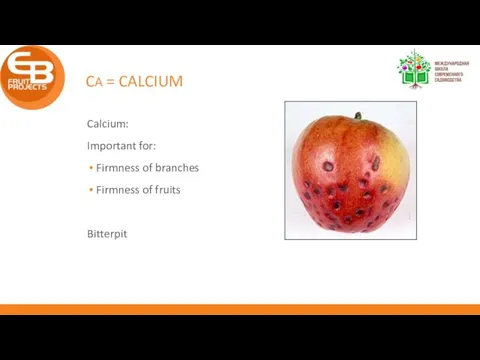
- 19. CA = CALCIUM Calcium: Important for: Firmness of branches Firmness of fruits Bitterpit
- 20. CA = CALCIUM Calcium: Bitterpit: Too much vegetative growth Ca transported to new leaves, not to
- 21. B = BORIUM Borium important for: Formation of flower buds Quality of flower buds ? winter
- 22. MN = MANGANE Important for: Fotosynthesis ? growth Firmness of fruits In plant not easy to
- 23. ZN = ZINC Important for: Growth Winterhardness Lack: Small leaves
- 24. FE = IRON Important for: Basic colour of fruits ? better storage Assimiliation ? green leaves
- 25. STRATEGY What do we need? We give per hectare Better is per kilogram or ton per
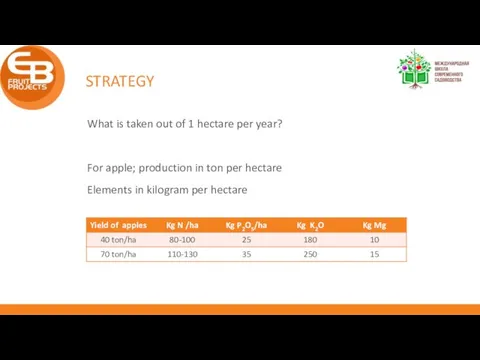
- 26. STRATEGY What is taken out of 1 hectare per year? For apple; production in ton per
- 27. ON THE SOIL On light, sandy soils: Shortly for flowering On other soils: 35-50 kg N
- 28. ON THE SOIL Potassium: Not necessary before flowering During the season Phosphate: On good soil: not
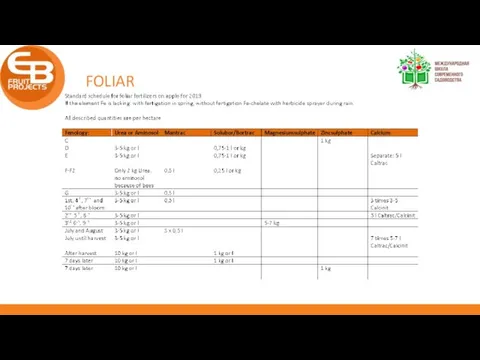
- 29. FOLIAR Just additional Never the basic Especcially the elements which are difficult to transport by the
- 30. FOLIAR
- 31. WATER AND FERTIGATION Without water: not possible with M9 Not necessary the whole year Water and
- 32. WATER AND FERTIGATION Often used: Tensiometers: amount of water in kPa Also tensiometers that give %
- 33. WATER AND FERTIGATION What does it means for tree?
- 34. WATER AND FERTIGATION Recommended during growing season: Depending on: Climate: dry or rain Production
- 35. WATER AND FERTIGATION Fertigation = additional, especially older trees N during spring important: 50-60% needed. Advantage:
- 36. WATER AND FERTIGATION From 3rd year; on production trees Fertigationscheme, often used: (in combination with spring
- 37. WATER AND FERTIGATION Example for standard fertilizers In 1.000 liters:
- 38. WATER AND FERTIGATION Calcium: always separate from other elements Only with N possible EC must not
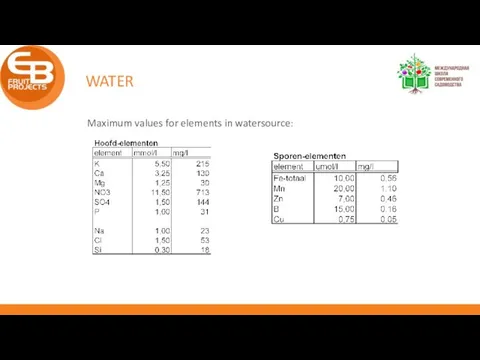
- 39. WATER Maximum values for elements in watersource:
- 40. WATER pH in water: Range at drip point: between 5 and 7 Low pH: better uptake
- 41. WATER pH in water: If too high: use acid to decrease Like: fosfor acid, nitrate-acid If
- 42. WATER EC = Electric Conductivity Measure of content of salt in water In many cases, EC
- 43. WATER EC formula: Gram N/tree/day X EC Fertilizer X 100 %N fertilizer X liters/tree/day = EC
- 44. ANALYSIS Soil: Before planting Each 3 years Leaves: Begin of June: possible to adapt, but not
- 46. Скачать презентацию



































 Переливание крови Сергеев , Рощупкина Илья Елена 8 «Б» класс МОУ«Средняя общеобразовательная школа №30»
Переливание крови Сергеев , Рощупкина Илья Елена 8 «Б» класс МОУ«Средняя общеобразовательная школа №30» Регуляция обмена веществ
Регуляция обмена веществ Презентация на тему "Клас черевоногі" - скачать бесплатно презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Клас черевоногі" - скачать бесплатно презентации по Биологии Исследование сосудистой системы. Лабораторное занятие №3
Исследование сосудистой системы. Лабораторное занятие №3 Презентация на тему "Как мы приучаем нашего попугая" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Как мы приучаем нашего попугая" - скачать презентации по Биологии Отдел Моховидные
Отдел Моховидные Пищевое поведение
Пищевое поведение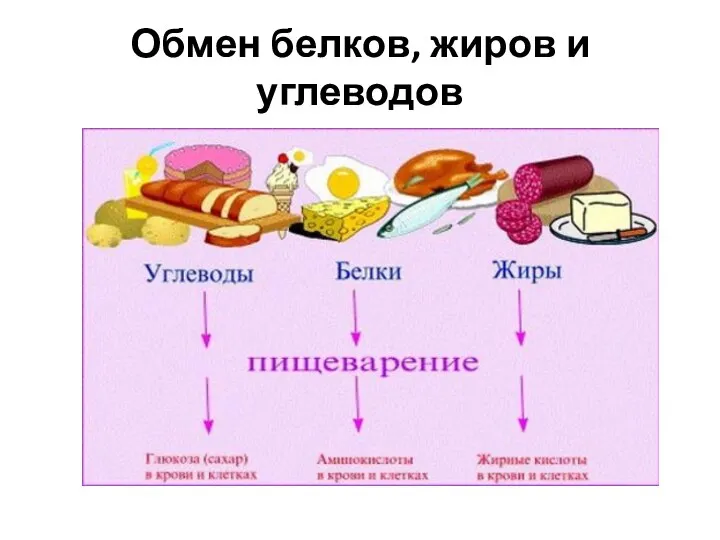 Обмен белков, жиров и углеводов
Обмен белков, жиров и углеводов Митоз
Митоз Топографическая анатомия области груди. Границы, внешние ориентиры
Топографическая анатомия области груди. Границы, внешние ориентиры Решение задач с использованием таблицы генетического кода
Решение задач с использованием таблицы генетического кода ТКАНИ И ОРГАНЫ ЧЕЛОВЕКА Урок по биологии 8 класс Учитель Жданова Оксана Викторовна
ТКАНИ И ОРГАНЫ ЧЕЛОВЕКА Урок по биологии 8 класс Учитель Жданова Оксана Викторовна  Физиология центральной нервной системы (цнс): торможение
Физиология центральной нервной системы (цнс): торможение Презентация на тему "Эндокринная система человека" - скачать бесплатно презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Эндокринная система человека" - скачать бесплатно презентации по Биологии Гипотезы происхождения жизни на Земле
Гипотезы происхождения жизни на Земле Царство Грибы. Грибы-паразиты.
Царство Грибы. Грибы-паразиты.  Животные смешанных и лиственных лесов. Заповедники
Животные смешанных и лиственных лесов. Заповедники Презентация на тему "Неврология" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Неврология" - скачать презентации по Биологии Редкие и исчезающие виды животных нашего края
Редкие и исчезающие виды животных нашего края Дыхательная система человека
Дыхательная система человека 3. Происхождение и эволюция человека
3. Происхождение и эволюция человека 1 закон Менделя
1 закон Менделя Нормальная микрофлора
Нормальная микрофлора Тварини червоної книги
Тварини червоної книги Экосистемы Биогеоценозы
Экосистемы Биогеоценозы Презентация на тему Отходы большого города: как их собирают, удаляют и перерабатывают
Презентация на тему Отходы большого города: как их собирают, удаляют и перерабатывают  Тема урока: Понятие о систематике растений
Тема урока: Понятие о систематике растений  Глаза – органы зрения. Строение глаза
Глаза – органы зрения. Строение глаза