Содержание
- 2. Microbiology Microbiology - The science that studies very small living things Usually requires a magnification tool
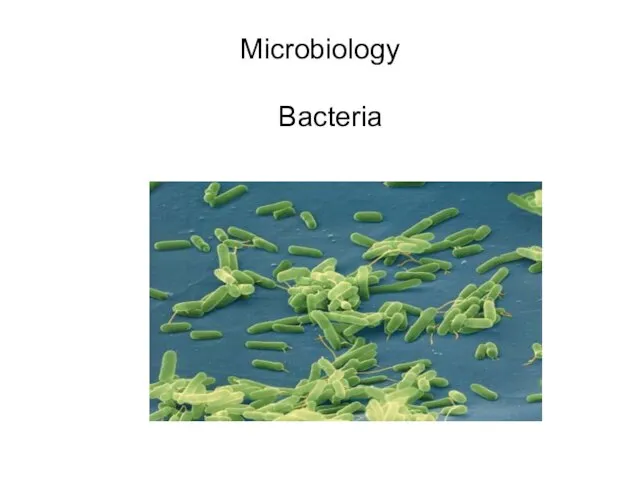
- 3. Microbiology Bacteria
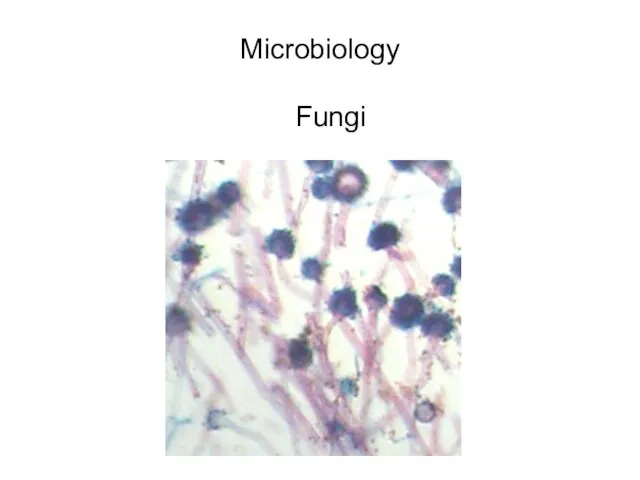
- 4. Microbiology Fungi
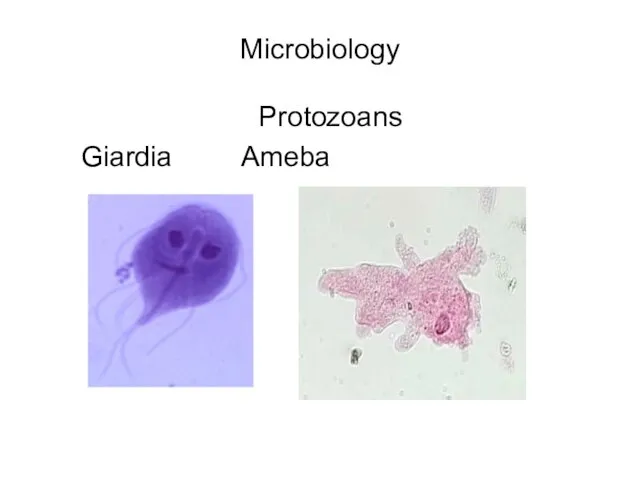
- 5. Microbiology Protozoans Giardia Ameba
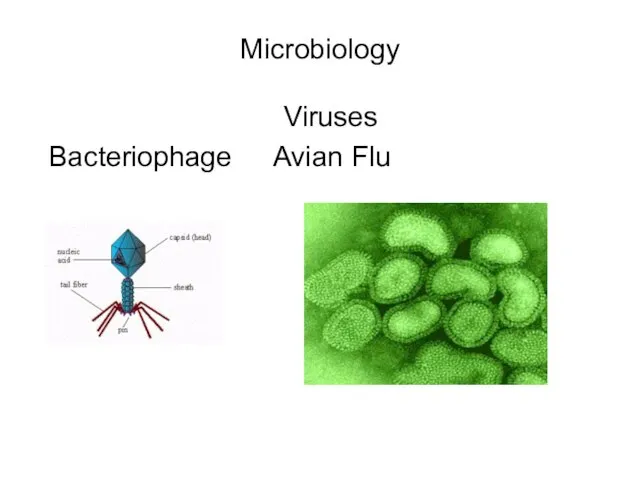
- 6. Microbiology Viruses Bacteriophage Avian Flu
- 7. Microbiology Various disciplines of study within microbiology: Bacteriology, Mycology, Parisitology, Immunology, Epidemiology, Biotechnology Virology Environmental Microbiology
- 8. Microbiology Historical review of the Science of Microbiology Robert Hook – 1665 – Englishman, used a
- 9. Microbiology Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek –1673 - probably the first person to observe living cells with a
- 10. Microbiology Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek
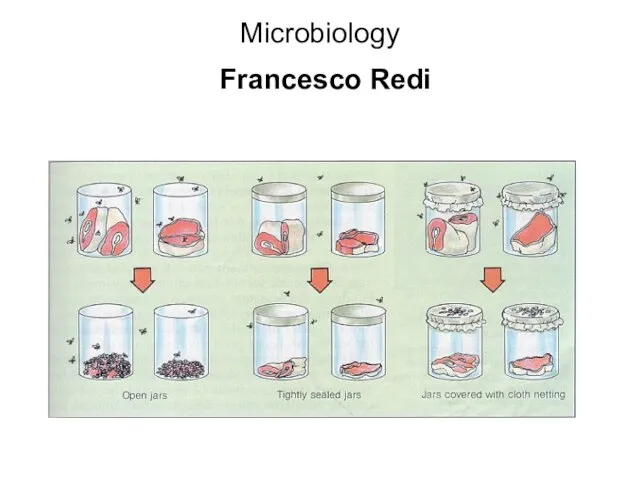
- 11. Microbiology Francesco Redi – 1668 – opposed the prevailing theory of Spontaneous Generation, maggots in meat
- 12. Microbiology Francesco Redi
- 13. Microbiology Pasteur – French sceintist that dealt the death blow to the spontaneous generation theory. He
- 14. Microbiology 1. He developed process we call Pasteuriztion – he heated wine to kill contaminating microbes
- 15. Microbiology Robert Koch - Developed Koch’s postulates – important technique for determining the actual microbial cause
- 16. Microbiology Koch’s and Pasteur’s work helped establish the “Germ Theory of Disease” - that microorganisms cause
- 17. Domain Archaea Archaea are single- celled organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus. - Prokaryote Archaea can
- 18. Domain Bacteria Bacteria are single- celled organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus. (Prokaryote also) Bacteria are
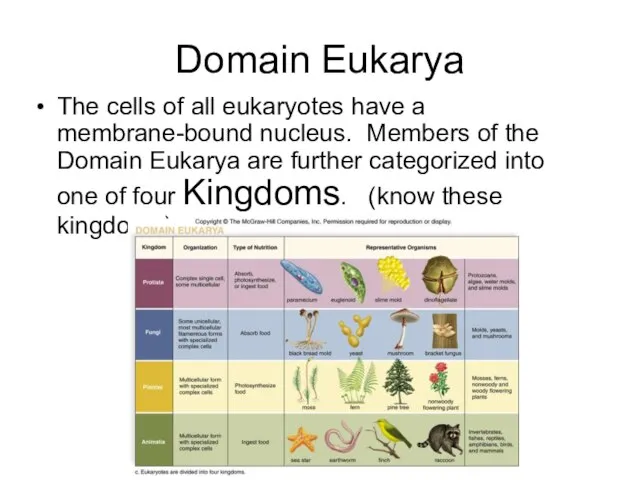
- 19. Domain Eukarya The cells of all eukaryotes have a membrane-bound nucleus. Members of the Domain Eukarya
- 21. Скачать презентацию












 История биологии. Научный метод
История биологии. Научный метод Основные признаки представителей царства животные. Простейшие
Основные признаки представителей царства животные. Простейшие Расы и их происхождение
Расы и их происхождение  Экология и мифы и коралловые рифы
Экология и мифы и коралловые рифы Ткани растений
Ткани растений Структурно-функциональная организация биологических мембран
Структурно-функциональная организация биологических мембран Презентация на тему "Негативное воздействие шума " - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Негативное воздействие шума " - скачать презентации по Биологии Разнообразен и прекрасен мир растений Мхи, водоросли, папоротники, плауны И семенные: сосны, туя, пихты, ели Но властелин
Разнообразен и прекрасен мир растений Мхи, водоросли, папоротники, плауны И семенные: сосны, туя, пихты, ели Но властелин Класс млекопитающие. Отряды Парнокопытные, Непарнокопытные
Класс млекопитающие. Отряды Парнокопытные, Непарнокопытные ПТИЦЫ 2010-2011учебный год Потапова Полина ученица 6 «Б» класса ГОУ гимназии №42 Приморског
ПТИЦЫ 2010-2011учебный год Потапова Полина ученица 6 «Б» класса ГОУ гимназии №42 Приморског Тип Членистоногие
Тип Членистоногие Тема урока: «Цветок, его строение и значение»
Тема урока: «Цветок, его строение и значение»  Клеточная инженерия в современной селекции и семеноводстве растений
Клеточная инженерия в современной селекции и семеноводстве растений Жизнь и творческая деятельность В.Н. Ремесло
Жизнь и творческая деятельность В.Н. Ремесло Аттестационная работа. Методическая разработка по выполнению исследовательской работы Фитоиндикация
Аттестационная работа. Методическая разработка по выполнению исследовательской работы Фитоиндикация Человек как биосоциальное существо. Происхождение человека
Человек как биосоциальное существо. Происхождение человека Пищевые добавки в жизни человека
Пищевые добавки в жизни человека Движущие силы антропогенеза.Ф. Энгельс о роли труда в процессе превращения обезьяны в человека
Движущие силы антропогенеза.Ф. Энгельс о роли труда в процессе превращения обезьяны в человека Белковые вещества
Белковые вещества Основные методы исследования генетики человека
Основные методы исследования генетики человека Из истории животноводства
Из истории животноводства Презентация на тему "Особенности строения и жизнедеятельности птиц как высокоорганизованных позвоночных." - скачать презент
Презентация на тему "Особенности строения и жизнедеятельности птиц как высокоорганизованных позвоночных." - скачать презент Молекулярный уровень организации жизни
Молекулярный уровень организации жизни Опыление. Самоопыление
Опыление. Самоопыление Презентация на тему "Виноград" - скачать презентации по Биологии
Презентация на тему "Виноград" - скачать презентации по Биологии Фила Proteobacteria
Фила Proteobacteria Жабы
Жабы Птицы. Выполнила ученица 7 класса: Пашко Екатерина. Учитель: Волчкова Л.К
Птицы. Выполнила ученица 7 класса: Пашко Екатерина. Учитель: Волчкова Л.К