Содержание
- 2. Topic 11. Examination of innovative projects
- 3. P L A N Necessary of Examination Types of Testing (Examination)
- 4. Necessary of Examination Examination allows us to reveal the most effective innovative projects, and to estimate
- 5. Examination of innovative projects is limited to evaluation of the technological level of new products and
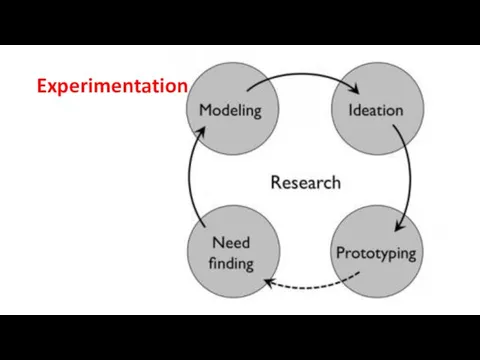
- 6. Experimentation The experimentation stage tests an idea, such as with a prototype or pilot test. Experimentation
- 7. Experimentation
- 8. Good ideas - Bad Products Not viable manufacturing techniques Expensive Apprehensive market Ahead of its time
- 9. up-to-date quality management techniques quality management systems; environment management systems; self-assessment; assessment results for quality contests.
- 10. What You Need to Know About Testing Project managers need to realize that only people can
- 12. Types of Testing (Examination) Unit testing Smoke testing Regression testing Conversion validation Integration testing UX /
- 13. What is Unit Testing? Unit testing, a testing technique using which individual modules are tested to
- 14. Unit Testing - Advantages: Reduces Defects in the Newly developed features or reduces bugs when changing
- 16. Unit Testing Techniques: Black Box Testing - Using which the user interface, input and output are
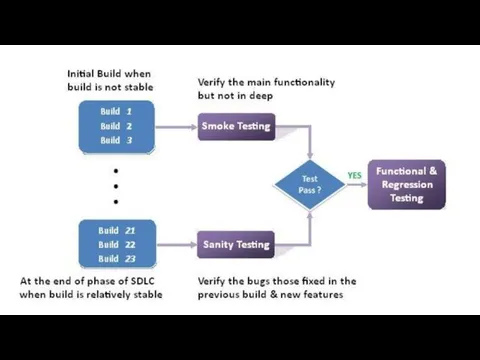
- 17. What is Smoke Testing? Smoke testing is the initial testing process exercised to check whether the
- 19. Advantages of Smoke testing: It helps to find issues introduced in integration of modules. It helps
- 20. What is Regression Testing? Regression Testing is defined as a type of software testing to confirm
- 21. Need of Regression Testing Change in requirements and code is modified according to the requirement New
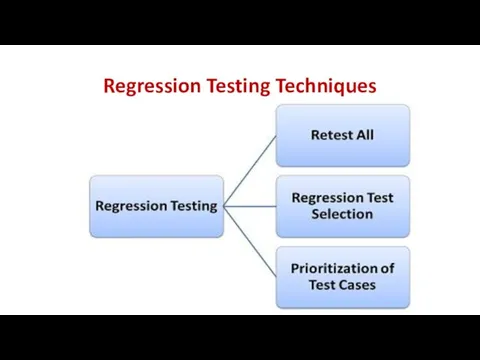
- 22. Regression Testing Techniques
- 23. Following are most important tools used for regression testing: Selenium: This is an open source tool
- 24. Following are the major testing problems for doing regression testing: With successive regression runs, test suites
- 25. Conversion validation When one “heritage” system is replaced with a newer system, it is common for
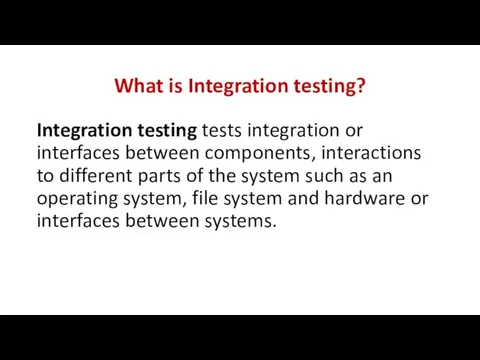
- 26. What is Integration testing? Integration testing tests integration or interfaces between components, interactions to different parts
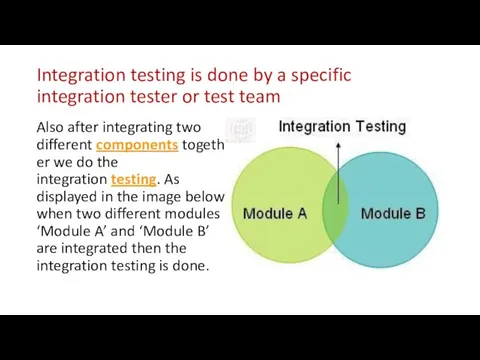
- 27. Integration testing is done by a specific integration tester or test team Also after integrating two
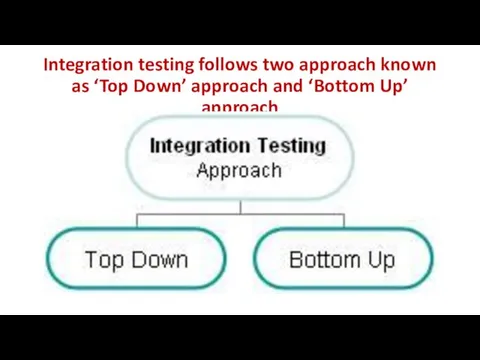
- 28. Integration testing follows two approach known as ‘Top Down’ approach and ‘Bottom Up’ approach
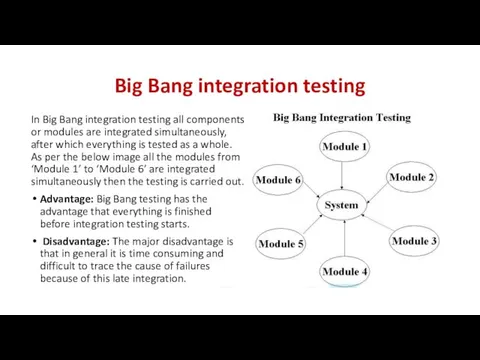
- 29. Big Bang integration testing In Big Bang integration testing all components or modules are integrated simultaneously,
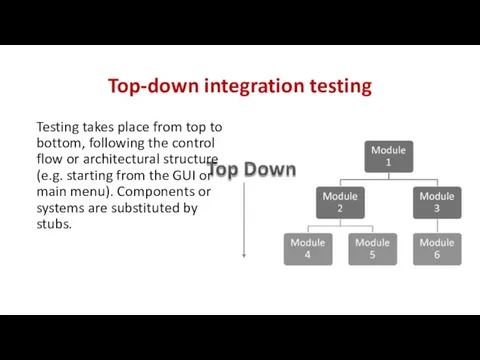
- 30. Top-down integration testing Testing takes place from top to bottom, following the control flow or architectural
- 31. Advantages of Top-Down approach: The tested product is very consistent because the integration testing is basically
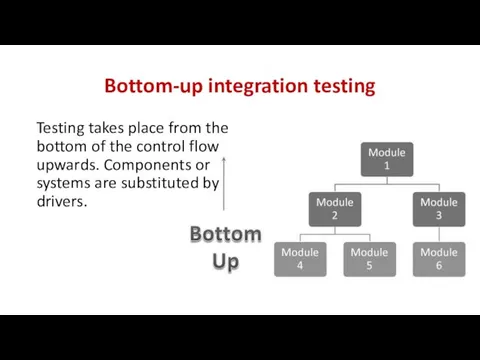
- 32. Bottom-up integration testing Testing takes place from the bottom of the control flow upwards. Components or
- 33. Advantage of Bottom-Up approach: In this approach development and testing can be done together so that
- 34. UX / usability testing – Increasingly, we’re as concerned about the ability of the user to
- 35. Survivability testing – Different systems have different availability requirements. Those with high availability or continuity of
- 37. Скачать презентацию

























 Рабочее пространство, где есть все для роста и развития бизнеса
Рабочее пространство, где есть все для роста и развития бизнеса Секреты сервиса в салоне красоты
Секреты сервиса в салоне красоты Клуб Магистр TianDe
Клуб Магистр TianDe Помощь в создании бизнеса
Помощь в создании бизнеса Business growth on hyper speed
Business growth on hyper speed Цели и задачи бизнес-плана АТП
Цели и задачи бизнес-плана АТП Обзор компании EGGTEC CO., LTD
Обзор компании EGGTEC CO., LTD Разработка бизнес-плана предприятия общественного питания на примере закусочной
Разработка бизнес-плана предприятия общественного питания на примере закусочной Бизнес-план. Организация производства крафт-пакетов
Бизнес-план. Организация производства крафт-пакетов Внедрение системы управления рабочим временем для сотрудников организации
Внедрение системы управления рабочим временем для сотрудников организации SWOT аналіз Apple
SWOT аналіз Apple Бизнес-идеи. Багажный трекер. Магазин стикеров и открыток. Доставка еды квадрокоптером
Бизнес-идеи. Багажный трекер. Магазин стикеров и открыток. Доставка еды квадрокоптером BPMN Business Process Model and Notation
BPMN Business Process Model and Notation Бизнес-идея. Развитие ее в бизнес-концепции (бизнес-плане)
Бизнес-идея. Развитие ее в бизнес-концепции (бизнес-плане) Навигатор инноватора
Навигатор инноватора Бизнес-проект. Тактильные книги для слабовидящих детей
Бизнес-проект. Тактильные книги для слабовидящих детей We are your inspiration InCase. Dane o przedsiębiorstwie
We are your inspiration InCase. Dane o przedsiębiorstwie Бизнес-презентация Уверенность в завтрашнем дне
Бизнес-презентация Уверенность в завтрашнем дне Сектор Ярославль-3
Сектор Ярославль-3 Почтовый бизнес
Почтовый бизнес Организация ускоренного движения электропоездов на участке Москва-Одинцово
Организация ускоренного движения электропоездов на участке Москва-Одинцово Международные контрактные обязательства
Международные контрактные обязательства Enhanced oil recovery
Enhanced oil recovery Теоретические основы автоматизации бухгалтерского учета
Теоретические основы автоматизации бухгалтерского учета Проект производства рекламного мыла
Проект производства рекламного мыла Unlocking Value in Rwanda’s Extractive Industries Sappera
Unlocking Value in Rwanda’s Extractive Industries Sappera Формирование и оценка общих и профессиональных компетенций в реализации дисциплины Индивидуальный проект
Формирование и оценка общих и профессиональных компетенций в реализации дисциплины Индивидуальный проект Тренинг Конструктор бизнес-плана
Тренинг Конструктор бизнес-плана