Содержание
- 2. Emma Shanley Adam Smith Scottish Economist 1723-1790 Born in Kirkcaldy, Scotland 5 June 1723 School in
- 3. Emma Shanley The Power of the Invisible Hand Pursue individual interest Result: Benefit society in general
- 4. Emma Shanley Laissez-Faire Promote free trade Build up the infrastructure of the country Provide a legal
- 5. Emma Shanley Productive and Non-productive Labour Productive Produced goods for sale Making money to reinvest E.g.
- 6. Emma Shanley The Labour Theory of Value Distinguished between value in use and value in exchange.
- 7. Emma Shanley The Canons of Taxation Equality– Tax payments should be proportional to income Certainty– Tax
- 8. Emma Shanley The Division of Labour Improve the productiveness of labour. For instance, the making of
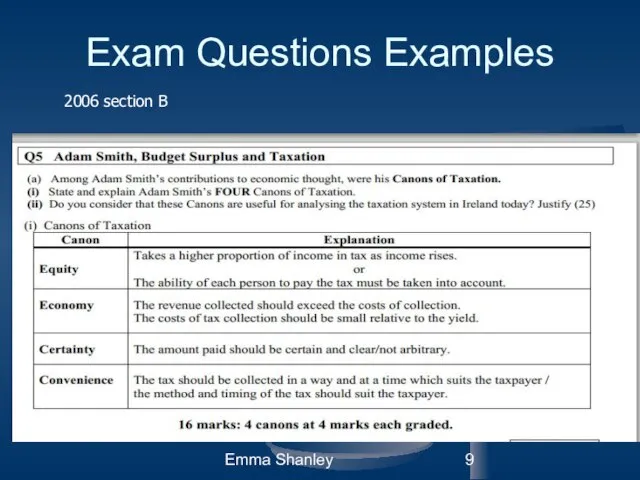
- 9. Emma Shanley Exam Questions Examples 2006 section B
- 10. Emma Shanley John Maynard Keynes British Economist 1883 - 1946 Born in Cambridge, England Son of
- 11. Emma Shanley Publications A Treatise on Money – 1930 Bestseller The General Theory of Employment, Interest
- 12. Emma Shanley Fiscal Policy Government controlled tax levels and public spending. E.g. an economy has slowed
- 13. Emma Shanley The Theory of the Multiplier Injection of money into a business. Creates more income
- 14. Emma Shanley The Liquidity Preference Theory of Interest Rates Rate of Interest fixed by the Central
- 15. Emma Shanley Saving and Investments Savings and Investments were not equal to each other. Savings were
- 16. Emma Shanley Exam Question Examples 2002 section A
- 18. Скачать презентацию














 Социально-экономическое положение Кааламского сельского поселения перспективы развития
Социально-экономическое положение Кааламского сельского поселения перспективы развития Особенности экономико-географического положения (ЭГП), природно-ресурсного потенциала Саратовской области
Особенности экономико-географического положения (ЭГП), природно-ресурсного потенциала Саратовской области Сущность и показатели эффективности деятельности предприятия
Сущность и показатели эффективности деятельности предприятия Глобализация мировой экономики и глобальные экономические проблемы современности
Глобализация мировой экономики и глобальные экономические проблемы современности Международные валютно-кредитные отношения и мировая валютная система
Международные валютно-кредитные отношения и мировая валютная система Префектура Акита
Префектура Акита Презентация Макроэкономика
Презентация Макроэкономика Формирование цены. Отражение целей фирмы в политике ценообразования
Формирование цены. Отражение целей фирмы в политике ценообразования Харчові продукти. Позиції галузі на світовому ринку. (Тема 6)
Харчові продукти. Позиції галузі на світовому ринку. (Тема 6) Научно-исследовательская работа на тему: «Корова на балконе». 4 класс
Научно-исследовательская работа на тему: «Корова на балконе». 4 класс Московская областная дума. Отчет о деятельности комитета по имущественным отношениям и землепользованию за 2017 год
Московская областная дума. Отчет о деятельности комитета по имущественным отношениям и землепользованию за 2017 год Динамика структуры экспорта и импорта России Подготовили: Цьопа Дарья Симонян Кирилл
Динамика структуры экспорта и импорта России Подготовили: Цьопа Дарья Симонян Кирилл История экономической мысли
История экономической мысли Стратегии развития Нижегородской области
Стратегии развития Нижегородской области Толкотт Парсонс «Понятие о политической власти»
Толкотт Парсонс «Понятие о политической власти» Сценарии социально-экономического развития России. Перспективы до 2030 г
Сценарии социально-экономического развития России. Перспективы до 2030 г Монополия как тип рыночной структуры
Монополия как тип рыночной структуры Макроекономічний огляд. Січень, 2016
Макроекономічний огляд. Січень, 2016 Методы экономических исследований. (Лекция 2)
Методы экономических исследований. (Лекция 2) Североамериканская интеграция
Североамериканская интеграция Факторы удовлетворенности жизнью в пожилом возрасте и политика государства
Факторы удовлетворенности жизнью в пожилом возрасте и политика государства Методы краткосрочного прогнозирования экономических явлений. Сглаживание и экстраполяция
Методы краткосрочного прогнозирования экономических явлений. Сглаживание и экстраполяция Совместное общество (общество участия)
Совместное общество (общество участия) Памятка проектировщикам часть II
Памятка проектировщикам часть II Формирование объемов деятельности предприятия
Формирование объемов деятельности предприятия Ограниченность ресурсов и безграничность потребностей
Ограниченность ресурсов и безграничность потребностей Рынок труда и доходы населения в Волгоградской области
Рынок труда и доходы населения в Волгоградской области Қазақстандағы рухани жаңғыру қажеттіліктері мен жолдары
Қазақстандағы рухани жаңғыру қажеттіліктері мен жолдары