Содержание
- 2. Gamma radiation (gamma rays, gamma-quanta) - a kind of electromagnetic radiation with a very short wavelength
- 3. Gamma-quanta are high-energy photons. On the scale of electromagnetic waves gamma rays bordered by X-rays, taking
- 4. Gamma-rays, in contrast to α-rays, β-rays are not deflected by electric and magnetic fields have greater
- 5. Gamma rays cause ionization of atoms of the substance. Main processes occurring during the passage of
- 6. Protection against gamma radiation can serve as a layer of material. The effectiveness of protection with
- 7. Application Gamma radiation is used in the art (eg., Inspection), radiation chemistry (for initiating chemical reactions,
- 9. Скачать презентацию






 Измерение размеров малых объектов с помощью микроскопа
Измерение размеров малых объектов с помощью микроскопа Термодинамика
Термодинамика Урок физики в 7 классе Тема: Выяснение условия равновесия рычага.
Урок физики в 7 классе Тема: Выяснение условия равновесия рычага. Постоянный электрический ток. Характеристики электрической цепи. Действие электрического тока и правила техники безопасности
Постоянный электрический ток. Характеристики электрической цепи. Действие электрического тока и правила техники безопасности Свойства водяного пара. Основные понятия и определения
Свойства водяного пара. Основные понятия и определения Творчий проект Кінематика
Творчий проект Кінематика  Қалпына келтірілетін жүйелер. Қалпына келтірілетін жүйелердің сенімділік көрсеткіштері
Қалпына келтірілетін жүйелер. Қалпына келтірілетін жүйелердің сенімділік көрсеткіштері Применение фотоэффекта
Применение фотоэффекта Задачи к ГОСам. Ж. д. путь
Задачи к ГОСам. Ж. д. путь Баллистика. Повторение. Равномерное движение
Баллистика. Повторение. Равномерное движение Разъемные соединения. Резьбовые соединения. Типы резьб. Детали резьбовых соединений. Основные расчетные случаи. Виды разрушений
Разъемные соединения. Резьбовые соединения. Типы резьб. Детали резьбовых соединений. Основные расчетные случаи. Виды разрушений Камера-обскура. Интересные факты
Камера-обскура. Интересные факты Презентация по физике "Учёные-физики" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Учёные-физики" - скачать  Магнетизм. ЭМ колебания и волны
Магнетизм. ЭМ колебания и волны Электрическое поле. Свойства электрического поля
Электрическое поле. Свойства электрического поля Уравнение состояния идеального газа Менделеева-Клапейрона. Газовые законы
Уравнение состояния идеального газа Менделеева-Клапейрона. Газовые законы Гидравлический пресс
Гидравлический пресс Магнитное поле
Магнитное поле Наука плазмохимия
Наука плазмохимия Магнит өрісі
Магнит өрісі Принципиальные электрические схемы
Принципиальные электрические схемы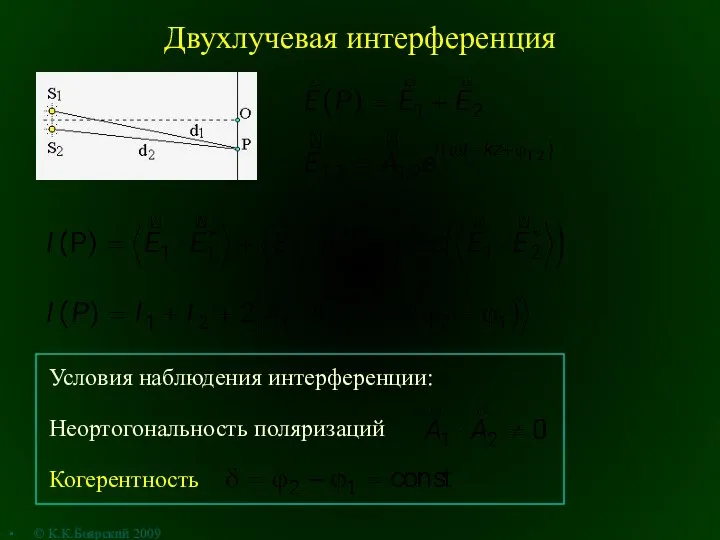 Двухлучевая интерференция
Двухлучевая интерференция Электромагниттік толқындар
Электромагниттік толқындар Различные подходы в определении информации
Различные подходы в определении информации Взаимное притяжение и отталкивание молекул
Взаимное притяжение и отталкивание молекул Интерференция света
Интерференция света Исследование точечных внешних воздействий на квазиодномерные структуры атомов переходных металлов
Исследование точечных внешних воздействий на квазиодномерные структуры атомов переходных металлов Механика. Законы сохранения в механике
Механика. Законы сохранения в механике