Содержание
- 2. TOTAL STATION
- 3. Harry Williams, Cartography X Y Z NORTH EAST
- 4. The total station works by firing an infrared laser beam at a reflector mounted on a
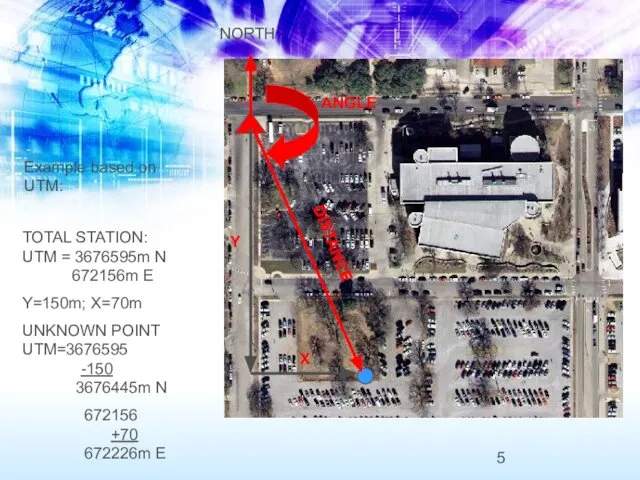
- 5. Example based on UTM: NORTH ANGLE DISTANCE X Y TOTAL STATION: UTM = 3676595m N 672156m
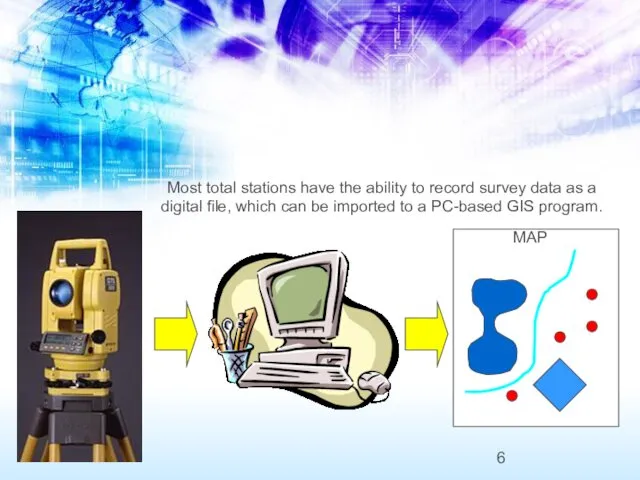
- 6. Most total stations have the ability to record survey data as a digital file, which can
- 7. Why use a total station? 1. Field work is carried out very fast. 2. Accuracy of
- 8. When do you use a total station? For mapping small areas (the range of a total
- 11. Comparison of total station and GPS
- 12. SMART STATION Benefits of SmartStation: ■ Control points are not needed; ■ No awkward traversing required;
- 13. Robotic total stations Allows the operator to control the instrument from a distance via remote control
- 15. Скачать презентацию










 Дифракция света
Дифракция света  Теоретическая (техническая) механика
Теоретическая (техническая) механика Определение потока и индукции магнитного поля. (Лабораторная работа 4.1)
Определение потока и индукции магнитного поля. (Лабораторная работа 4.1) Многоэлектронный атом (Лекция 8)
Многоэлектронный атом (Лекция 8) Вырождение влияния критериев
Вырождение влияния критериев Изобретение радио А.С. Поповым
Изобретение радио А.С. Поповым Динамика поступательного движения
Динамика поступательного движения Релятивистская динамика
Релятивистская динамика Серебряно-цинковые, щелочные аккумуляторные батареи
Серебряно-цинковые, щелочные аккумуляторные батареи Явления смачивания и капиллярности
Явления смачивания и капиллярности Атмосферные явления
Атмосферные явления Спектроскопические методы анализа
Спектроскопические методы анализа Строение вещества Повторение и обобщение темы
Строение вещества Повторение и обобщение темы Измерение атмосферного давления. Опыт Торричелли
Измерение атмосферного давления. Опыт Торричелли Внутренняя энергия
Внутренняя энергия Максвелл Джеймс Клерк Работу выполнила Ученица 10В класса гимназии №4 им.А.С.Пушкина г.Йошкар-Олы Галиуллина Диана 2008-2009г.г
Максвелл Джеймс Клерк Работу выполнила Ученица 10В класса гимназии №4 им.А.С.Пушкина г.Йошкар-Олы Галиуллина Диана 2008-2009г.г НОВЫЕ ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИЯ ДЛЯ ТЕОРИИ ОТНОСИТЕЛЬНОСТИ
НОВЫЕ ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИЯ ДЛЯ ТЕОРИИ ОТНОСИТЕЛЬНОСТИ Первое начало термодинамики
Первое начало термодинамики Основные понятия. Цепи постоянного тока
Основные понятия. Цепи постоянного тока Принцип відносності А.Ейнштейна. Основні положення спеціальної теорії відносності (СТВ). Виконала Учениця 10 – Б класу ЕНВК №
Принцип відносності А.Ейнштейна. Основні положення спеціальної теорії відносності (СТВ). Виконала Учениця 10 – Б класу ЕНВК № Явление тяготения. Сила тяжести
Явление тяготения. Сила тяжести Расчет дисковой овощеочистительной машины
Расчет дисковой овощеочистительной машины Самофокусировка света: физическая картина
Самофокусировка света: физическая картина Окружающий мир. Тест
Окружающий мир. Тест Соединения деталей
Соединения деталей Эмилий Христианович Ленц
Эмилий Христианович Ленц Детали механизмов и машин. Подшипники скольжения
Детали механизмов и машин. Подшипники скольжения Принцип действия реактивного двигателя
Принцип действия реактивного двигателя