Содержание
- 2. Formalized topological methods for the analysis of electrical circuits These methods are based on the use
- 3. The connection point of two or more electrical circuits is called a node or a node
- 4. A node is usually indicated by a dot in a circuit. If a short circuit (a
- 5. A loop is a closed path formed by starting at a node, passing through a set
- 6. The method of connecting branches and nodes of an electrical circuit, that is, a structural diagram
- 7. Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U. An electrical circuit graph is a conditional
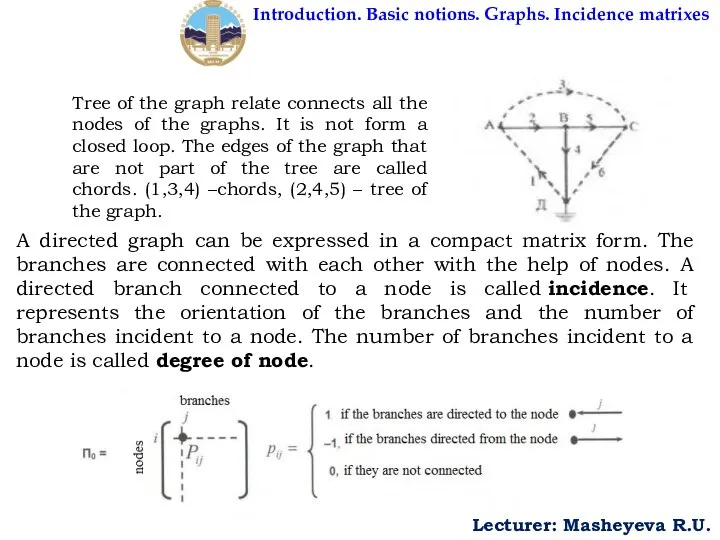
- 8. Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U. Tree of the graph relate connects all
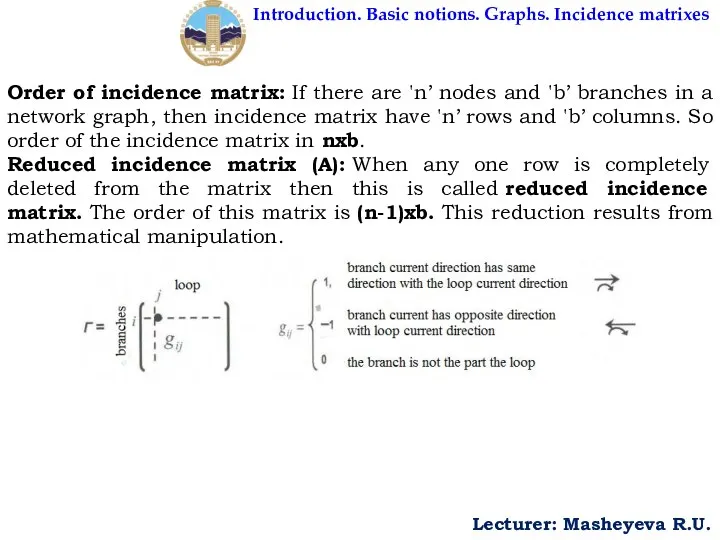
- 9. Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U. Order of incidence matrix: If there are
- 11. Скачать презентацию
Formalized topological methods for the analysis of electrical circuits
These methods are
Formalized topological methods for the analysis of electrical circuits
These methods are
The basis of electrical circuits are active two-terminal networks, which have equivalent resistances and EMF, and passive ones, which have only resistance, and the EMF is zero.
Auto two-pole networks are sources of EMF and current, batteries, generators, electric motors;
Passive two-pole networks are transformers, load resistance lines;
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
The connection point of two or more electrical circuits is called
The connection point of two or more electrical circuits is called
Links between nodes are called branches.
A branch represents a single element such as a voltage source or a resistor. In other words, a branch represents any two-terminal element.
The branches form loops. A loop is any closed path in a circuit.
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
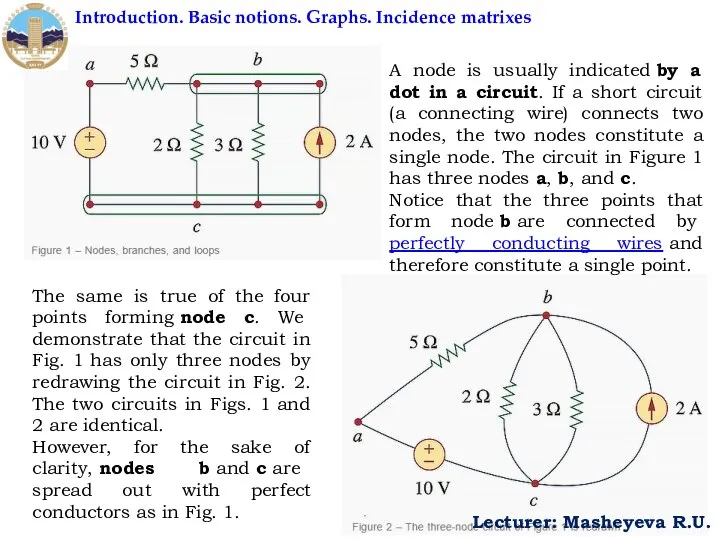
A node is usually indicated by a dot in a circuit. If
A node is usually indicated by a dot in a circuit. If
Notice that the three points that form node b are connected by perfectly conducting wires and therefore constitute a single point.
The same is true of the four points forming node c. We demonstrate that the circuit in Fig. 1 has only three nodes by redrawing the circuit in Fig. 2. The two circuits in Figs. 1 and 2 are identical.
However, for the sake of clarity, nodes b and c are spread out with perfect conductors as in Fig. 1.
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
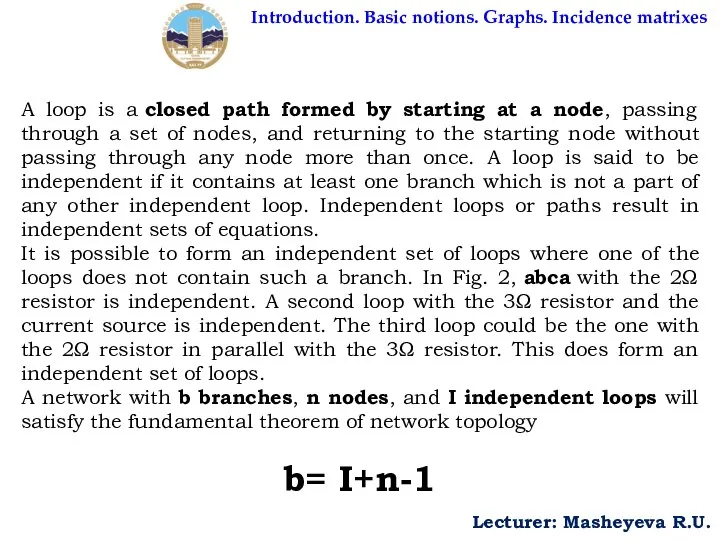
A loop is a closed path formed by starting at a node,
A loop is a closed path formed by starting at a node,
It is possible to form an independent set of loops where one of the loops does not contain such a branch. In Fig. 2, abca with the 2Ω resistor is independent. A second loop with the 3Ω resistor and the current source is independent. The third loop could be the one with the 2Ω resistor in parallel with the 3Ω resistor. This does form an independent set of loops.
A network with b branches, n nodes, and I independent loops will satisfy the fundamental theorem of network topology
b= I+n-1
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
The method of connecting branches and nodes of an electrical circuit,
The method of connecting branches and nodes of an electrical circuit,
Sources of EMF, current, resistance do not show in this graphs but only take into account the nodes and their circuits.
For each branch, its orientation (positive direction) is set, in accordance with which the positive directions of the current and voltage of the branch are taken. We will take the direction of the current in the branch to the node as a positive direction. For loop currents, we take the clockwise direction as positive. Under these conditions, any electrical circuit can be represented in the form of a graph and P matrix, connections that uniquely reflects the structural diagram of the graph.
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
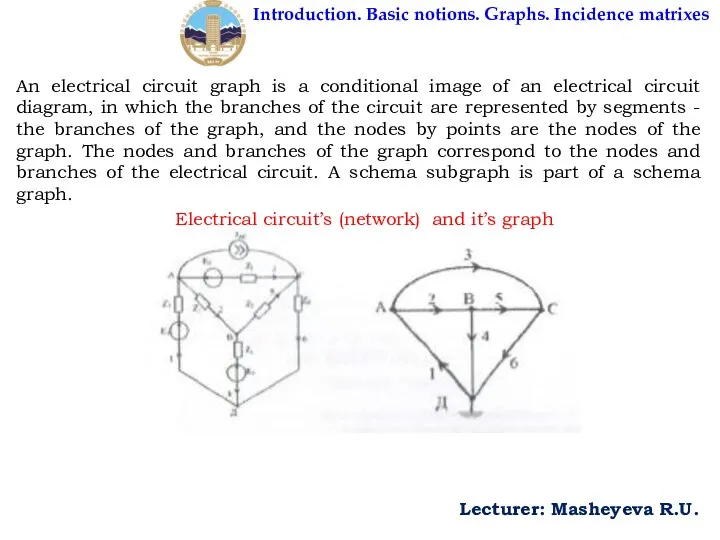
An electrical circuit graph
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
An electrical circuit graph
Electrical circuit’s (network) and it’s graph
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
Tree of the graph
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
Tree of the graph
A directed graph can be expressed in a compact matrix form. The branches are connected with each other with the help of nodes. A directed branch connected to a node is called incidence. It represents the orientation of the branches and the number of branches incident to a node. The number of branches incident to a node is called degree of node.
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
Order of incidence matrix: If
Introduction. Basic notions. Graphs. Incidence matrixes
Lecturer: Masheyeva R.U.
Order of incidence matrix: If
Reduced incidence matrix (A): When any one row is completely deleted from the matrix then this is called reduced incidence matrix. The order of this matrix is (n-1)xb. This reduction results from mathematical manipulation.


 Лекция № 1. Основные понятия и законы электротехники. Классификация электрических цепей
Лекция № 1. Основные понятия и законы электротехники. Классификация электрических цепей Физические задачи,приводящие к дифференциальным уравнениям
Физические задачи,приводящие к дифференциальным уравнениям Зачем нужны ускорители элементарных частиц
Зачем нужны ускорители элементарных частиц Развитие понятия функции в 17 веке
Развитие понятия функции в 17 веке Специальная теория относительности Эйнштейна
Специальная теория относительности Эйнштейна Механічна енергія та її види
Механічна енергія та її види Метод подобия явлений. Числа подобия. Критерии подобия
Метод подобия явлений. Числа подобия. Критерии подобия Движение и его относительность Ключникова Н.В.
Движение и его относительность Ключникова Н.В.  Динамика. Законы Ньютона. (Лекция 2)
Динамика. Законы Ньютона. (Лекция 2) Электротехника, как отрасль науки и техники
Электротехника, как отрасль науки и техники TES, TEC, KES salīdzinājums un klasifikācija, galvenās prasības
TES, TEC, KES salīdzinājums un klasifikācija, galvenās prasības Презентация по физике "Использование ИКТ на уроках физики" - скачать
Презентация по физике "Использование ИКТ на уроках физики" - скачать  §8. Плоскопараллельное движение твердого тела (плоское)
§8. Плоскопараллельное движение твердого тела (плоское) Інфразвук. Джерела інфразвуку
Інфразвук. Джерела інфразвуку История отечественных космических ядерных установок
История отечественных космических ядерных установок Презентация Плотность вещества Взаимодействие тел
Презентация Плотность вещества Взаимодействие тел Закон Кулона. Единица электрического заряда
Закон Кулона. Единица электрического заряда Удельная теплота парообразования
Удельная теплота парообразования Ракеты. Современная космическая ракета
Ракеты. Современная космическая ракета Fyzika - Physics - Physik
Fyzika - Physics - Physik Магнитные свойства вещества. Диамагнетики.
Магнитные свойства вещества. Диамагнетики. Дифракція світла
Дифракція світла  Приводы подвагонных генераторов
Приводы подвагонных генераторов Основы теории процесса сушки зерна
Основы теории процесса сушки зерна Умови рівноваги тіла
Умови рівноваги тіла НАСЫЩЕННЫЙ И НЕНАСЫЩЕННЫЙ ПАР ВЛАЖНОСТЬ ВОЗДУХА КИПЕНИЕ УРОК МОДЕЛИРОВАНИЯ УМЕНИЙ И НАВЫКОВ УЧИТЕЛЬ ФИЗИКИ ЛЕВЧУК М.В. МАКЕ
НАСЫЩЕННЫЙ И НЕНАСЫЩЕННЫЙ ПАР ВЛАЖНОСТЬ ВОЗДУХА КИПЕНИЕ УРОК МОДЕЛИРОВАНИЯ УМЕНИЙ И НАВЫКОВ УЧИТЕЛЬ ФИЗИКИ ЛЕВЧУК М.В. МАКЕ Презентация по физике Основное уравнение молекулярно-кинетической теории идеальных газов. Статистические распределение.
Презентация по физике Основное уравнение молекулярно-кинетической теории идеальных газов. Статистические распределение. Научные революции в естествознании и формирование научной картины мира
Научные революции в естествознании и формирование научной картины мира