Содержание
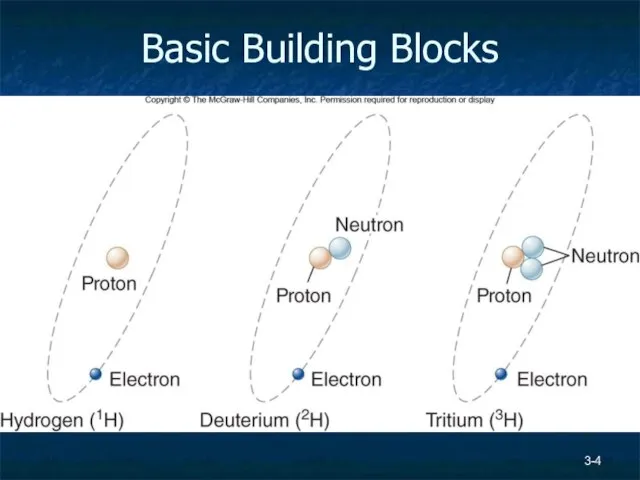
- 2. 3- Basic Building Blocks Atoms Nucleus contains protons and neutrons Electrons orbit the nucleus Elements Atoms
- 3. Basic Building Blocks Isotope – an atom with varying number of neutrons, some are unstable =
- 4. Basic Building Blocks 3-
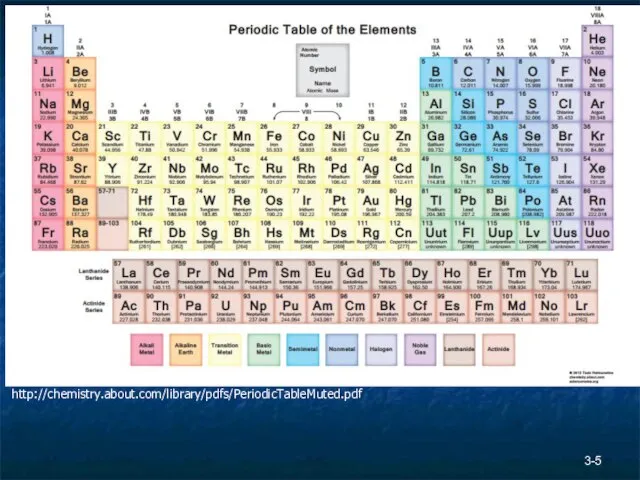
- 5. 3- http://chemistry.about.com/library/pdfs/PeriodicTableMuted.pdf
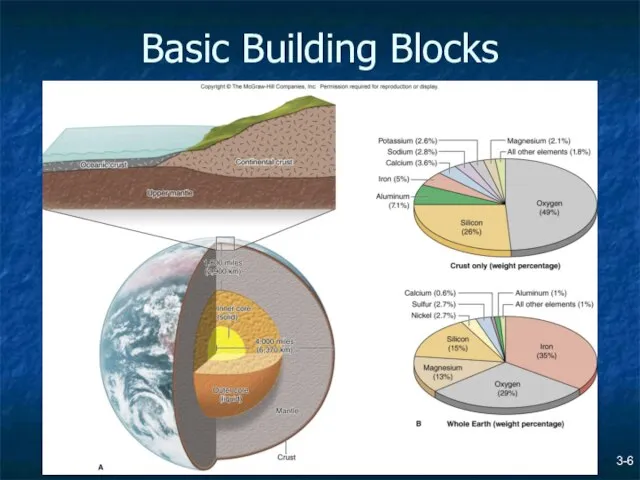
- 6. Basic Building Blocks 3-
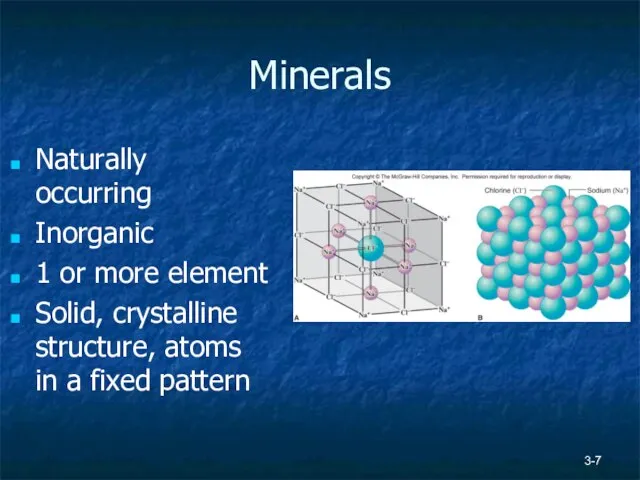
- 7. 3- Minerals Naturally occurring Inorganic 1 or more element Solid, crystalline structure, atoms in a fixed
- 8. 3- Minerals 4,000+ minerals Each has unique chemical and physical properties (for ex. - graphite vs
- 9. 3- Rock Forming Minerals Approximately 12 common minerals make up crust Pyroxene and Amphibole are ferromagnesian
- 10. Rock Forming Minerals Minerals classified on type of negatively charged ion within crystalline structure Sulfides contain
- 11. 3- Rocks Aggregate or assemblage of one or more types of minerals; many are composed of
- 12. 3- Igneous Rocks Form via cooling magma Intrusive cooled Coarse grained When magma breaches Earth’s surface
- 13. 3- Weathering Breaking down of rocks Physical weathering Frost wedging Plant roots Crystal growth – minerals
- 14. 3- Physical Weathering
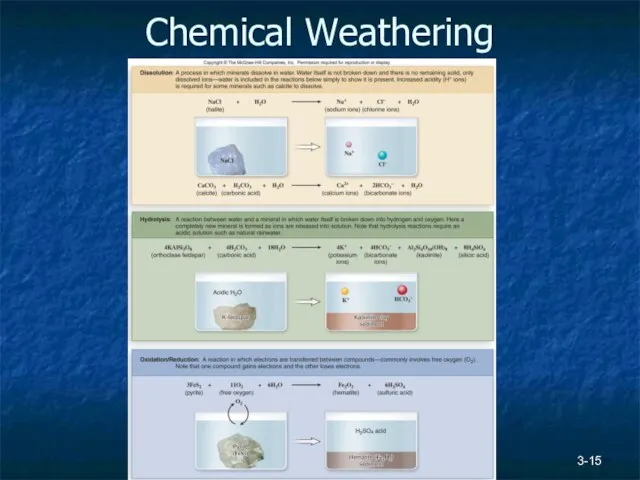
- 15. 3- Chemical Weathering
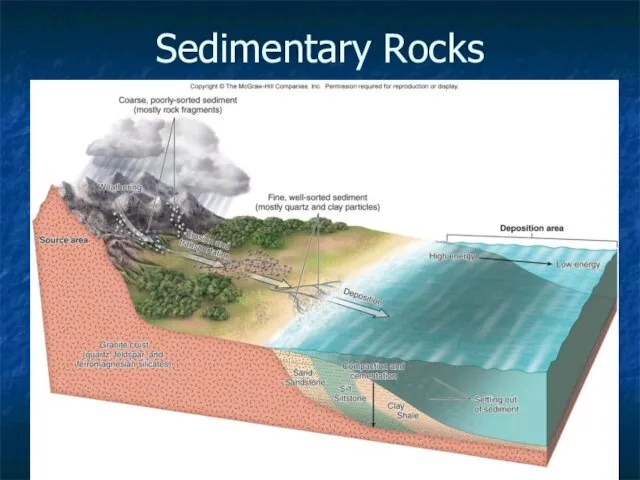
- 16. 3- Sedimentary Rocks Weathering results in sediment Compacted and cemented sediment = sedimentary rocks Erosion –
- 17. Two Types of Sedimentary Rocks Detrital – made of preexisting rock & mineral fragments that have
- 18. Sedimentary Rocks 3-
- 19. 3- Metamorphic Rocks Changes through heat and pressure, not enough to melt rock. Contact metamorphism Heat,
- 20. Contact Metamorphism 3-
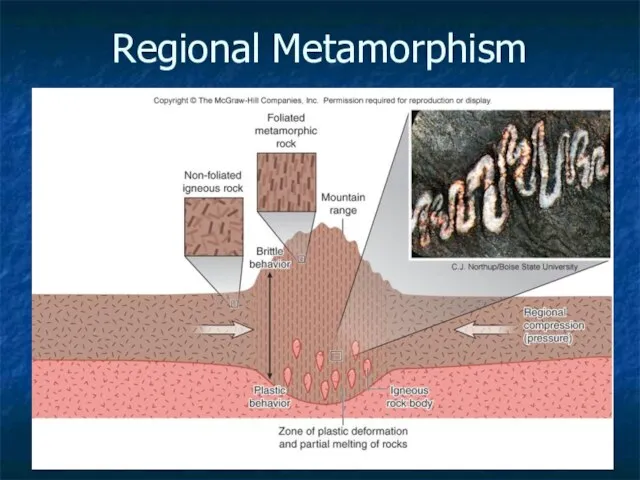
- 21. Regional Metamorphism 3-
- 22. Foliation 3- Figure 3.27, page 84
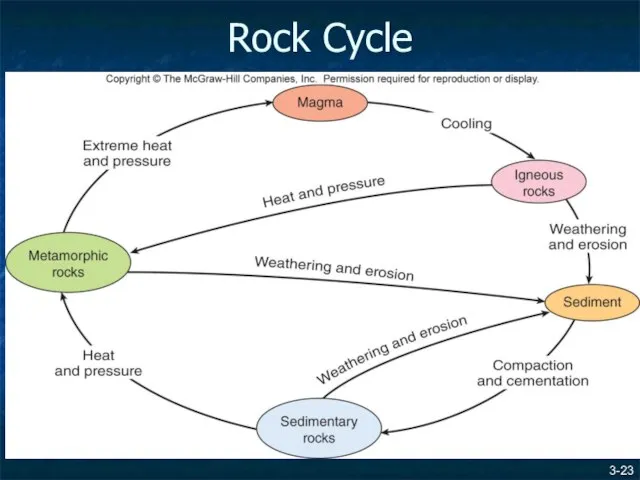
- 23. 3- Rock Cycle
- 24. 3- Rocks as Indicators of the Past Figure 3.30, page 87 Figure 3.31, page 88
- 26. Скачать презентацию















 Оборудование метеорологической станции Учебно-методическое пособие для учащихся 6-10 классов по теме «Атмосфера» учителя геогра
Оборудование метеорологической станции Учебно-методическое пособие для учащихся 6-10 классов по теме «Атмосфера» учителя геогра Центральная Россия
Центральная Россия Как обеспечить экологическую безопасность России
Как обеспечить экологическую безопасность России ТЕСТ "Природно-хозяйственные зоны России" 8 класс
ТЕСТ "Природно-хозяйственные зоны России" 8 класс Атмосферные фронты, циклоны, антициклоны. Интерактивная модель процесса
Атмосферные фронты, циклоны, антициклоны. Интерактивная модель процесса  Путешествие в кладовые Земли. Полезные ископаемые
Путешествие в кладовые Земли. Полезные ископаемые Воркута
Воркута география 6 класс
география 6 класс Признаки погоды
Признаки погоды Московский Кремль Тестово – обучающая система
Московский Кремль Тестово – обучающая система Особенности природы Крыма
Особенности природы Крыма Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенный пар. Влажность воздуха
Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенный пар. Влажность воздуха Тропики. Субтропики
Тропики. Субтропики Тема: Индия: насильственное разрушение традиционного общества.
Тема: Индия: насильственное разрушение традиционного общества.  Состав и строение гидросферы
Состав и строение гидросферы Презентация на тему Открытия русских путешественников
Презентация на тему Открытия русских путешественников  Заповедники Красноярского края
Заповедники Красноярского края География России. Население и хозяйство. Введение
География России. Население и хозяйство. Введение Обобщающий урок В 9 классе
Обобщающий урок В 9 классе Игра Ямал - край Земли - презентация к уроку Географии
Игра Ямал - край Земли - презентация к уроку Географии Цели,задачи, структура РСЧС. подсистемы, уровни РСЧС
Цели,задачи, структура РСЧС. подсистемы, уровни РСЧС Презентация по географии Природные зоны России.Тайга.
Презентация по географии Природные зоны России.Тайга.  Travelling around Russia
Travelling around Russia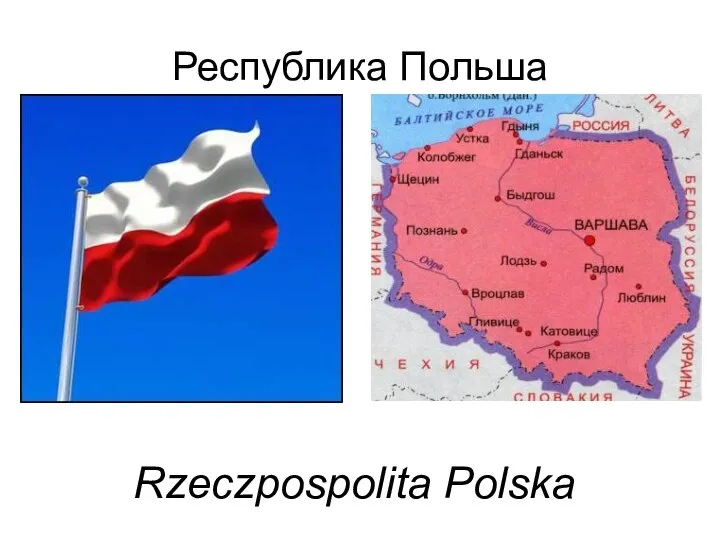 Республика Польша Rzeczpospolita Polska
Республика Польша Rzeczpospolita Polska Египет Выполнила ученица 11 б класса Крылова Анна
Египет Выполнила ученица 11 б класса Крылова Анна Горизонт. Линия горизонта - презентация к уроку Географии_
Горизонт. Линия горизонта - презентация к уроку Географии_ ПОЛЕВЫЕ МЕТОДЫ ГЕОЛОГИЧЕСКОГО И ГЕОФИЗИЧЕСКОГО ИЗУЧЕНИЯ ГОРНЫХ ПОРОД И ИХ ВЗАИМООТНОШЕНИЙ - презентация к уроку Географии
ПОЛЕВЫЕ МЕТОДЫ ГЕОЛОГИЧЕСКОГО И ГЕОФИЗИЧЕСКОГО ИЗУЧЕНИЯ ГОРНЫХ ПОРОД И ИХ ВЗАИМООТНОШЕНИЙ - презентация к уроку Географии Природный комплекс - это закономерное сочетание компонентов природы
Природный комплекс - это закономерное сочетание компонентов природы