Содержание
- 2. Geography of United Kingdoom and Northern Island .Geography of USA.
- 3. United Kingdom Official Name: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- 4. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, or UK, is a sovereign state, is
- 5. PROFILE Geography Area: United Kingdom 243,820 km² (94,600 sq mi) comprising of the island of Great
- 6. Cities: Capital--London (metropolitan pop. about 7.56 million). Other cities--Birmingham, Glasgow, Leeds, Sheffield, Liverpool, Bradford, Manchester, Edinburgh,
- 7. The area of the countries of the United Kingdom is set out in the table below.
- 9. People Nationality: Noun--Briton(s). Adjective--British. Population (2010 est.): 62.2 million. Annual population growth rate (2010 est.): 0.7%.
- 10. Government Type: Constitutional monarchy. Constitution: Unwritten; partly statutes, partly common law and practice. Branches: Executive--monarch (head
- 11. Economy GDP (at current market prices, 2009): $2.184 trillion. Annual growth rate (2009): -4.8%. Per capita
- 12. Mountains and hills:- Mountains of the United Kingdom The ten tallest mountains in the UK are
- 13. Rivers and lakes Main articles List of lakes in the United Kingdom; Rivers of the United
- 14. Artificial waterways Waterways in the United KingdomWaterways in the United Kingdom, Canals of Great BritainWaterways in
- 15. Natural resources AgricultureAgriculture is intensiveAgriculture is intensive, highly mechanisedAgriculture is intensive, highly mechanised, and efficient by
- 16. The United States Physical Geography
- 19. The United StatesThe United States is a countryThe United States is a country in the Western
- 20. Area:- From 1989 through 1996, the total area of the US was listed as 9,372,610 km2
- 21. Landforms The U.S. and Canada have several major mountain ranges: The Rocky Mountains The Appalachian Mountains
- 22. The Rocky Mountains The Rocky Mountains extend about 3,000 miles from Alaska south to New Mexico.
- 24. The Appalachian Mountains The Appalachian Mountains extend about 1,600 miles north to south from Newfoundland in
- 25. Pacific Coastal Ranges A series of small mountain ranges stretch from southern California to Washington. These
- 27. Other Landforms The Canadian Shield Interior Lowlands Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plains Basin and Range Great
- 28. Canadian Shield The Canadian Shield is a rocky, mainly flat area around Hudson Bay.
- 30. Interior Lowlands An area that spreads from the Appalachian Mountains to the Mississippi River. This area
- 31. Arctic and Gulf Coastal Plains These are flat areas that stretch along the Gulf of Mexico
- 32. Basin and Range This area is mostly in Nevada and it consists of rocky outcroppings of
- 34. Great Plains A largely treeless flat area that extends from Canada down to Mexico. The soil
- 36. Grand Canyon The Grand Canyon was formed by water erosion from the Colorado River. The canyon
- 38. Groups of Islands Hawaiian archipelago - A group of 19 islands and islets in the Pacific
- 41. Rivers Some major rivers in the United States are: Mississippi St. Lawrence Colorado Columbia Rio Grande
- 42. Mississippi River The Mississippi River is the second longest river in the United States with a
- 44. St. Lawrence River The St. Lawrence River connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean. The
- 48. Colorado River The Colorado River flows from Colorado to the Gulf of California. The river formed
- 52. Other Water Features Some other important water features are: Gulf of Mexico Great Lakes Arctic Ocean
- 53. Climate Canada and the United States are in the middle and high latitudes. The most common
- 54. Climate Most of the Eastern United States is humid subtropical. This climate zone has a mild
- 55. The tundra is a flat treeless plain with lichens, shrubs, and some flowers.
- 57. Скачать презентацию
Geography of United Kingdoom and Northern Island .Geography of USA.
Geography of United Kingdoom and Northern Island .Geography of USA.
United Kingdom
Official Name:
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern
United Kingdom
Official Name:
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, or UK,
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, or UK,
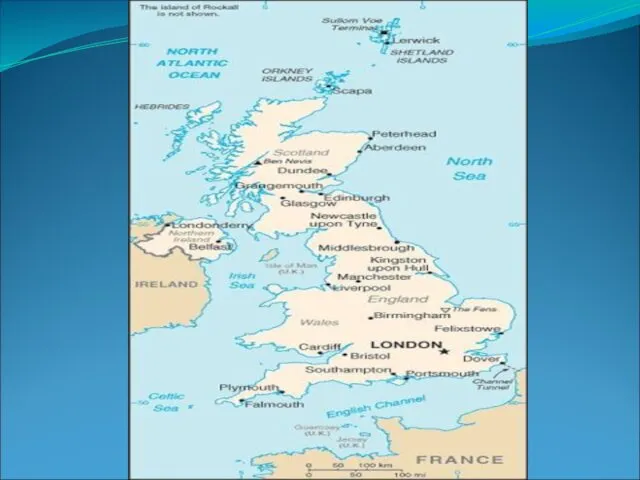
The UK lies between the North AtlanticThe UK lies between the North Atlantic and the North SeaThe UK lies between the North Atlantic and the North Sea, and comes within 35 km (22 mi) of the northwest coast of FranceThe UK lies between the North Atlantic and the North Sea, and comes within 35 km (22 mi) of the northwest coast of France, from which it is separated by the English ChannelThe UK lies between the North Atlantic and the North Sea, and comes within 35 km (22 mi) of the northwest coast of France, from which it is separated by the English Channel. Northern Ireland shares a 360 km international land boundary with the Republic of IrelandThe UK lies between the North Atlantic and the North Sea, and comes within 35 km (22 mi) of the northwest coast of France, from which it is separated by the English Channel. Northern Ireland shares a 360 km international land boundary with the Republic of Ireland. The Channel Tunnel bored beneath the English Channel, now links the UK with France.
PROFILE
Geography
Area: United Kingdom 243,820 km² (94,600 sq mi) comprising of the island of
Cities: Capital--London (metropolitan pop. about 7.56 million). Other cities--Birmingham, Glasgow, Leeds,
Cities: Capital--London (metropolitan pop. about 7.56 million). Other cities--Birmingham, Glasgow, Leeds,
The area of the countries of the United Kingdom is set
Rank Name Area 1 England 130,427 km² -
South West - 23,837 km² East of England- 19,120 km²
South East-19,096 km² East Midlands- 15,627 km²
Yorkshire and the Humber-15,420 km²
North West - 14,165 km² West Midlands-12,998 km² North East 8,592 km² London-1,572 km²
2 Scotland [8] 78,772 km² 3 Wales [9] 20,778 km²
4 Northern Ireland 13,843 km² United Kingdom 243,820 km²
People
Nationality: Noun--Briton(s). Adjective--British.
Population (2010 est.): 62.2 million.
Annual population growth rate (2010
People Nationality: Noun--Briton(s). Adjective--British. Population (2010 est.): 62.2 million. Annual population growth rate (2010
Government
Type: Constitutional monarchy.
Constitution: Unwritten; partly statutes, partly common law and
Government Type: Constitutional monarchy. Constitution: Unwritten; partly statutes, partly common law and
Economy
GDP (at current market prices, 2009): $2.184 trillion.
Annual growth rate
Economy GDP (at current market prices, 2009): $2.184 trillion. Annual growth rate
Mountains and hills:-
Mountains of the United Kingdom
The ten tallest mountains
Mountains and hills:-
Mountains of the United Kingdom
The ten tallest mountains
Scotland: Ben NevisScotland: Ben Nevis (Aonach Mòr, 1,344 metres)
Wales: SnowdonWales: Snowdon (Snowdonia, 1,085 metres)
England: Scafell PikeEngland: Scafell Pike (Cumbrian Mountains, 977 metres)
Northern Ireland: Slieve DonardNorthern Ireland: Slieve Donard (Mourne Mountains, 852 metres)
The ranges of mountains and hills in the UK include:
Scotland: CairngormsScotland: Cairngorms, Cheviot HillsScotland: Cairngorms, Cheviot Hills, Scottish HighlandsScotland: Cairngorms, Cheviot Hills, Scottish Highlands, Southern UplandsScotland: Cairngorms, Cheviot Hills, Scottish Highlands, Southern Uplands, Grampian Mountains
Wales: Brecon BeaconsWales: Brecon Beacons, Cambrian MountainsWales: Brecon Beacons, Cambrian Mountains, SnowdoniaWales: Brecon Beacons, Cambrian Mountains, Snowdonia, Black MountainsWales: Brecon Beacons, Cambrian Mountains, Snowdonia, Black Mountains, Preseli Hills
England: ChilternsEngland: Chilterns, CotswoldsEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, DartmoorEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire WoldsEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, ExmoorEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake DistrictEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern HillsEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip HillsEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip Hills, North DownsEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip Hills, North Downs, Peak DistrictEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip Hills, North Downs, Peak District, PenninesEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip Hills, North Downs, Peak District, Pennines, Salisbury PlainEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip Hills, North Downs, Peak District, Pennines, Salisbury Plain, South DownsEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip Hills, North Downs, Peak District, Pennines, Salisbury Plain, South Downs, Shropshire HillsEngland: Chilterns, Cotswolds, Dartmoor, Lincolnshire Wolds, Exmoor, Lake District, Malvern Hills, Mendip Hills, North Downs, Peak District, Pennines, Salisbury Plain, South Downs, Shropshire Hills, Yorkshire Wolds
Northern Ireland: Mourne MountainsNorthern Ireland: Mourne Mountains, Antrim PlateauNorthern Ireland: Mourne Mountains, Antrim Plateau, Sperrin Mountains
The lowest point of the UK is in the FensThe lowest point of the UK is in the Fens of East AngliaThe lowest point of the UK is in the Fens of East Anglia, in England, parts of which lie up to 4 metres below sea level.
Rivers and lakes
Main articles List of lakes in the United Kingdom;
Rivers
Rivers and lakes
Main articles List of lakes in the United Kingdom;
Rivers
Waterfalls of the United Kingdom.
The longest river in the UK is the River Severn (220 mi, 354 km) which flows through both Wales and England.
The longest rivers in the UK by country are:
England: River Thames (215 mi, 346 km)
Scotland: River Tay (117 mi, 188 km)
N. Ireland: River Bann (76 mi, 122 km)
Wales: River Tywi (64 mi, 103 km)
The largest lakes in the UK by country are:
N. Ireland: Lough Neagh (147.39 sq mi, 381.74 km²)
Scotland: Loch Lomond (27.46 sq mi, 71.12 km²)
England: Windermere (5.69 sq mi, 14.74 km²)
Wales: Llyn Tegid (Bala Lake) (1.87 sq mi, 4.84 km²)
The deepest lake in the UK is Loch MorarThe deepest lake in the UK is Loch Morar with a maximum depth of 309 metres (Loch NessThe deepest lake in the UK is Loch Morar with a maximum depth of 309 metres (Loch Ness is second at 228 metres deep). The deepest lake in England is WastwaterThe deepest lake in the UK is Loch Morar with a maximum depth of 309 metres (Loch Ness is second at 228 metres deep). The deepest lake in England is Wastwater which descends to 79 metres (258 feet).
Artificial waterways
Waterways in the United KingdomWaterways in the United Kingdom, Canals
Artificial waterways
Waterways in the United KingdomWaterways in the United Kingdom, Canals
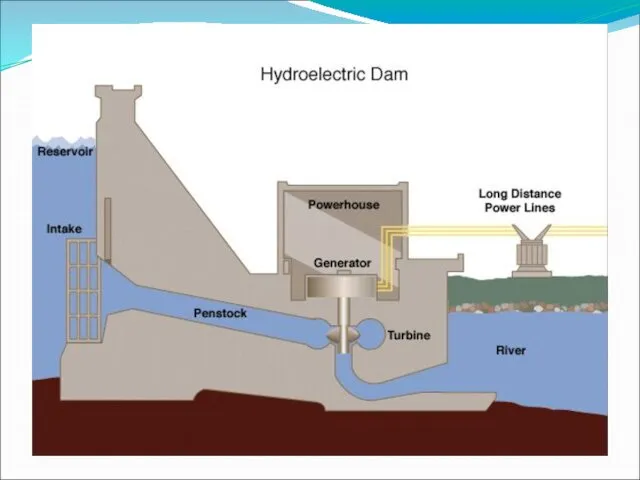
As a result of its industrial history, the United Kingdom has an extensive system of canalsAs a result of its industrial history, the United Kingdom has an extensive system of canals, mostly built in the early years of the Industrial RevolutionAs a result of its industrial history, the United Kingdom has an extensive system of canals, mostly built in the early years of the Industrial Revolution, before the rise of competition from the railwaysAs a result of its industrial history, the United Kingdom has an extensive system of canals, mostly built in the early years of the Industrial Revolution, before the rise of competition from the railways. The United Kingdom also has numerous damsAs a result of its industrial history, the United Kingdom has an extensive system of canals, mostly built in the early years of the Industrial Revolution, before the rise of competition from the railways. The United Kingdom also has numerous dams and reservoirsAs a result of its industrial history, the United Kingdom has an extensive system of canals, mostly built in the early years of the Industrial Revolution, before the rise of competition from the railways. The United Kingdom also has numerous dams and reservoirs to store water for drinking and industry. The generation of hydroelectric power is rather limited, supplying less than 2% of British electricity mainly from the Scottish Highlands.
Natural resources
AgricultureAgriculture is intensiveAgriculture is intensive, highly mechanisedAgriculture is intensive, highly
Natural resources
AgricultureAgriculture is intensiveAgriculture is intensive, highly mechanisedAgriculture is intensive, highly
In 1993, it was estimated that land use was:
Arable land: 25 %
Permanent crops: 0 %
Permanent pastures: 46 %
ForestsForests and Woodland: 10 %
Other: 19 %
Irrigated: 1,080 km²
The UK has a variety of natural resources including:
Geological: coalGeological: coal, petroleumGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gasGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestoneGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalkGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsumGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silicaGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silica, rock saltGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silica, rock salt, china clayGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silica, rock salt, china clay, iron oreGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silica, rock salt, china clay, iron ore, tinGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silica, rock salt, china clay, iron ore, tin, silverGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silica, rock salt, china clay, iron ore, tin, silver, goldGeological: coal, petroleum, natural gas, limestone, chalk, gypsum, silica, rock salt, china clay, iron ore, tin, silver, gold, lead.
Agricultural: arable landAgricultural: arable land, wheatAgricultural: arable land, wheat, barleyAgricultural: arable land, wheat, barley, sheep
The UK has large coalThe UK has large coal, natural gasThe UK has large coal, natural gas, and oilThe UK has large coal, natural gas, and oil reserves; primary energy production accounts for 10% of GDPThe UK has large coal, natural gas, and oil reserves; primary energy production accounts for 10% of GDP, one of the highest shares of any industrial nationThe UK has large coal, natural gas, and oil reserves; primary energy production accounts for 10% of GDP, one of the highest shares of any industrial nation. Due to the island location of the UK, the country has great potential for generating electricity from wave powerThe UK has large coal, natural gas, and oil reserves; primary energy production accounts for 10% of GDP, one of the highest shares of any industrial nation. Due to the island location of the UK, the country has great potential for generating electricity from wave power and tidal power, although these have not yet been exploited on a commercial basis.
The United States
Physical Geography
The United States
Physical Geography
The United StatesThe United States is a countryThe United States is
The United StatesThe United States is a countryThe United States is
Area:-
From 1989 through 1996, the total area of the US was
Area:-
From 1989 through 1996, the total area of the US was
The listed total area changed to 9,629,091 km2 (3,717,813 sq mi) in 1997 (Great Lakes area and coastal waters added), to 9,631,418 km2 (3,718,711 sq mi) in 2004, to 9,631,420 km2 (3,718,710 sq mi) in 2006, and to 9,826,630 km2 (3,794,080 sq mi) in 2007 (territorial waters added).
Currently, the CIA World Factbook gives 9,826,675 km2 (3,794,100 sq mi), the United Nations Statistics Division gives 9,629,091 km2 (3,717,813 sq mi), and the Encyclopædia Britannica gives 9,522,055 km2 (3,676,486 sq mi).
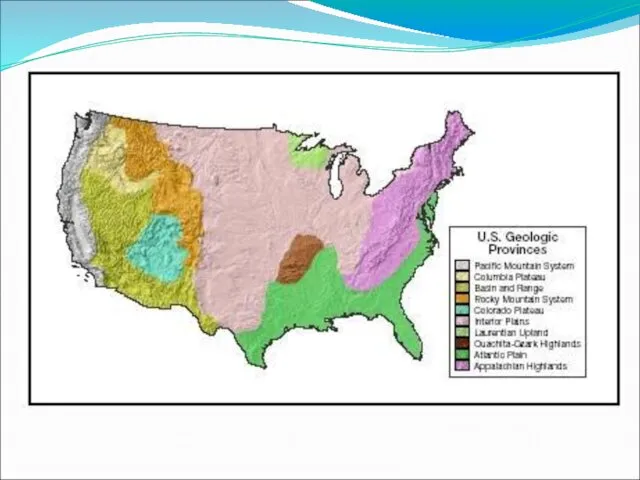
Landforms
The U.S. and Canada have several major mountain ranges:
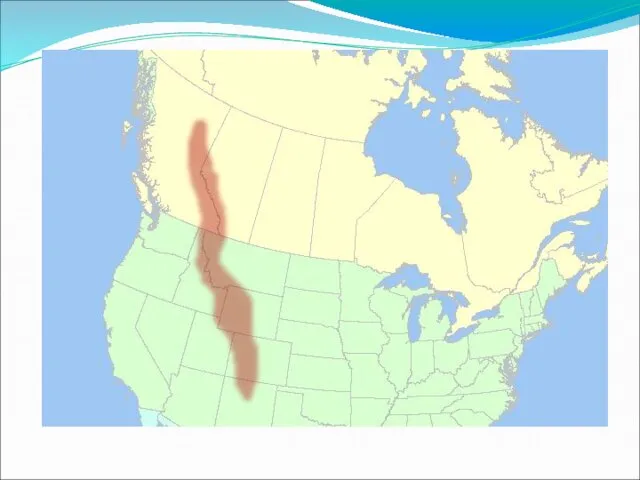
The Rocky Mountains
The
Landforms
The U.S. and Canada have several major mountain ranges:
The Rocky Mountains
The
Pacific Coastal Ranges
The Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains extend about 3,000 miles from Alaska
The Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains extend about 3,000 miles from Alaska
The Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains extend about 1,600 miles north to
The Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains extend about 1,600 miles north to
Pacific Coastal Ranges
A series of small mountain ranges
stretch from southern California
Pacific Coastal Ranges
A series of small mountain ranges
stretch from southern California
Other Landforms
The Canadian Shield
Interior Lowlands
Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plains
Basin and Range
Great
Other Landforms
The Canadian Shield
Interior Lowlands
Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plains
Basin and Range
Great
Grand Canyon
Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield is a rocky, mainly flat area around
Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield is a rocky, mainly flat area around
Interior Lowlands
An area that spreads from the Appalachian Mountains to the
Interior Lowlands
An area that spreads from the Appalachian Mountains to the
Arctic and Gulf Coastal Plains
These are flat areas that stretch along
Arctic and Gulf Coastal Plains
These are flat areas that stretch along
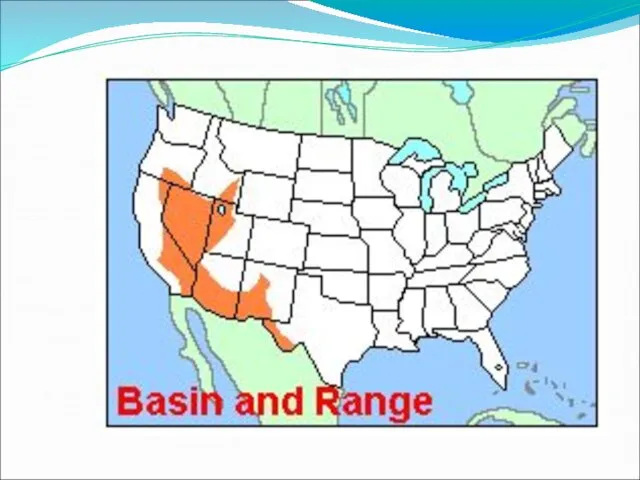
Basin and Range
This area is mostly in Nevada and it consists
Basin and Range
This area is mostly in Nevada and it consists
Great Plains
A largely treeless flat area that extends from Canada down
Great Plains
A largely treeless flat area that extends from Canada down
Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon was formed by water erosion from the
Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon was formed by water erosion from the
See the Grand Canyon skywalk at youtube!
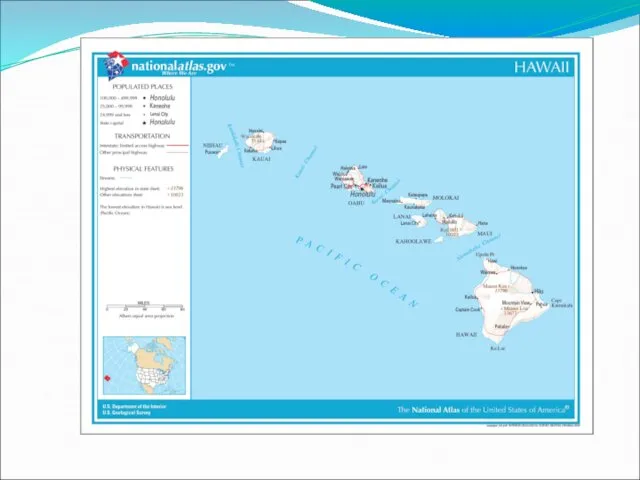
Groups of Islands
Hawaiian archipelago - A group of 19 islands and
Groups of Islands
Hawaiian archipelago - A group of 19 islands and
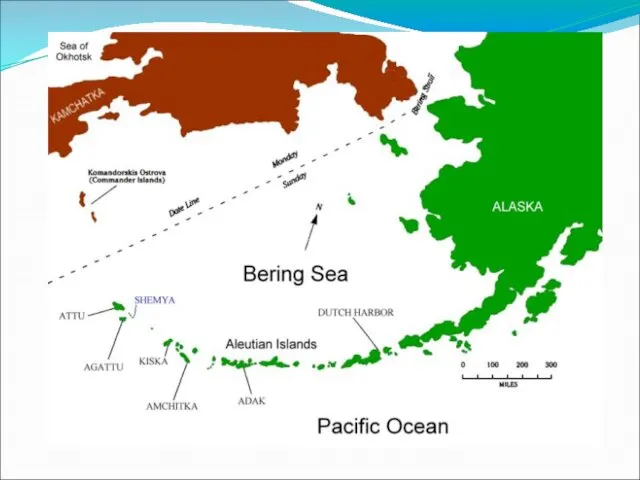
Aleutian Islands - A chain of over 300 small volcanic islands that extend from Alaska to Russia.
Rivers
Some major rivers in the United States are:
Mississippi
St. Lawrence
Colorado
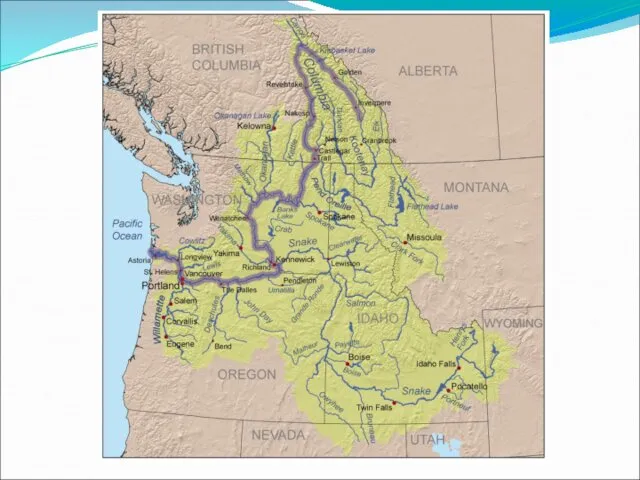
Columbia
Rio Grande
Rivers
Some major rivers in the United States are:
Mississippi
St. Lawrence
Colorado
Columbia
Rio Grande
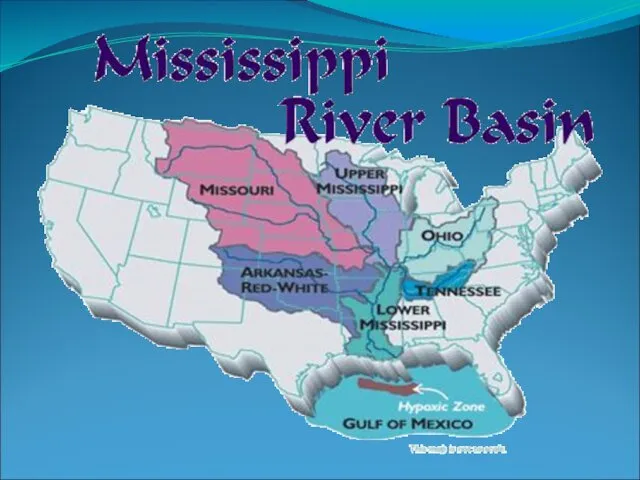
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second longest river in the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second longest river in the
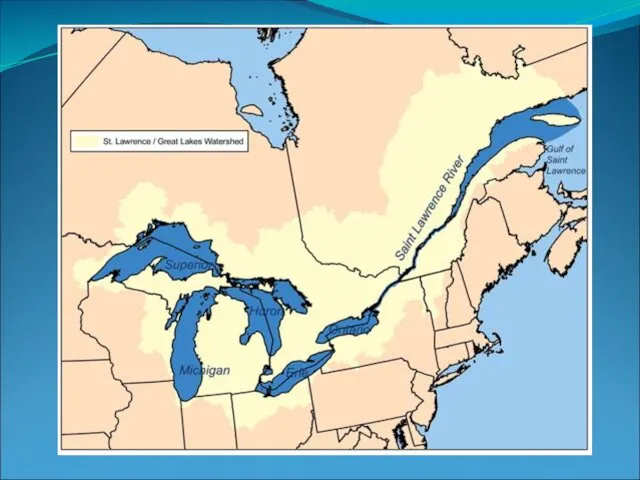
St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River connects the Great Lakes to
St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River connects the Great Lakes to
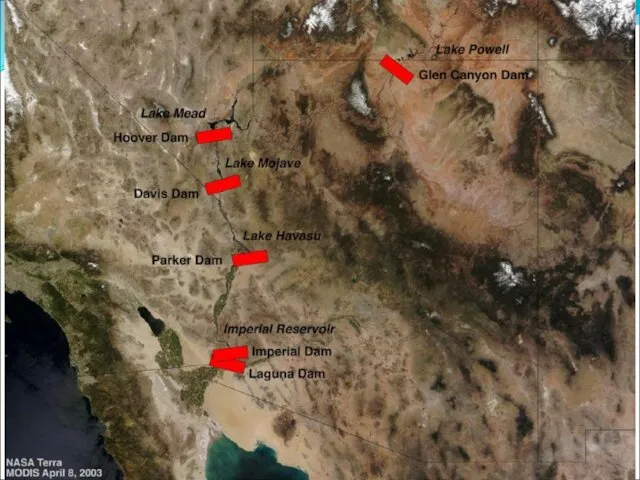
Colorado River
The Colorado River flows from Colorado to the Gulf of
Colorado River
The Colorado River flows from Colorado to the Gulf of
Other Water Features
Some other important water features are:
Gulf of Mexico
Great Lakes
Arctic
Other Water Features
Some other important water features are:
Gulf of Mexico
Great Lakes
Arctic
Pacific Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
Hudson Bay
Climate
Canada and the United States are in the middle and high
Climate
Canada and the United States are in the middle and high
Humid Subtropical and Continental
Semiarid and Arid
Marine West Coast and Mediterranean
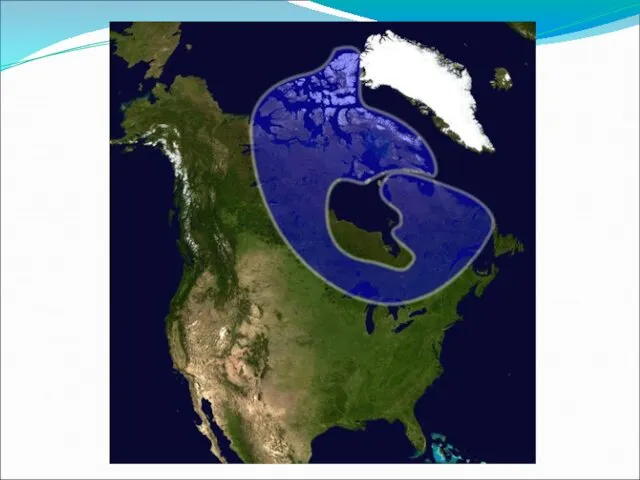
Tundra and Icecap
Climate
Most of the Eastern United States is humid subtropical. This climate
Climate
Most of the Eastern United States is humid subtropical. This climate
The tundra is a flat treeless plain with lichens, shrubs,
and some
The tundra is a flat treeless plain with lichens, shrubs,
and some








































 Новейшая история стран Юго-Восточной Азии
Новейшая история стран Юго-Восточной Азии Океания
Океания Выполнила ученица 10в класса Дубровская Юлия.
Выполнила ученица 10в класса Дубровская Юлия. Расизм и национализм – это тупиковая ветвь эволюции
Расизм и национализм – это тупиковая ветвь эволюции Смешанные леса
Смешанные леса Пермская система. Характеристика периода. (Лекция 13)
Пермская система. Характеристика периода. (Лекция 13) Исследования Мирового океана. Задачи и возможности
Исследования Мирового океана. Задачи и возможности Народы, языки и религии География 7 класс
Народы, языки и религии География 7 класс Франция
Франция Литосфера. Обучающий урок
Литосфера. Обучающий урок Природа Европейского Севера
Природа Европейского Севера Литосферные плиты Литосферная плита — это крупный стабильный участок земной коры, часть литосферы. Согласно теории тектоники
Литосферные плиты Литосферная плита — это крупный стабильный участок земной коры, часть литосферы. Согласно теории тектоники  Достопримечательности Крыма
Достопримечательности Крыма Кругосветные путешествия
Кругосветные путешествия Doing Business in the United Arab Emirates 2012 Mierta Capaul & Aikaterini Leris
Doing Business in the United Arab Emirates 2012 Mierta Capaul & Aikaterini Leris Тайны бермудского треугольника Выполнила: ученица 11 «А» класса МБОУ СОШ №99 Бочарова Лилия Александровна Научный руководител
Тайны бермудского треугольника Выполнила: ученица 11 «А» класса МБОУ СОШ №99 Бочарова Лилия Александровна Научный руководител Физико-географическая характеристика Азербайджана
Физико-географическая характеристика Азербайджана Градусная сеть. Географические координаты
Градусная сеть. Географические координаты Зелёный луч
Зелёный луч Реки в природе и на географических картах
Реки в природе и на географических картах Физико-географическая характеристика Грузии
Физико-географическая характеристика Грузии Otradnoe. The location on the map
Otradnoe. The location on the map Южная Америка
Южная Америка Знатоки географии 10,11 классы - презентация к уроку Географии
Знатоки географии 10,11 классы - презентация к уроку Географии Форма и размеры Земли. Географическая карта. 6-й класс - презентация к уроку Географии
Форма и размеры Земли. Географическая карта. 6-й класс - презентация к уроку Географии Инновационные технологии в ТЭК и ЖКХ. Опыт и перспективы - презентация к уроку Географии
Инновационные технологии в ТЭК и ЖКХ. Опыт и перспективы - презентация к уроку Географии Как люди заселяли Землю
Как люди заселяли Землю Вулканы
Вулканы