Содержание
- 2. HPAI IN-SITU COMBUSTION
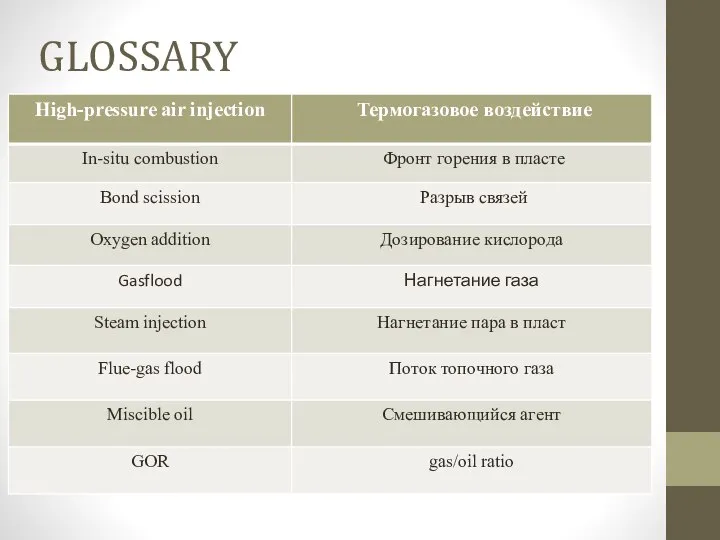
- 3. GLOSSARY
- 4. INTRODUCTION High-pressure air injection (HPAI) is an enhanced oil recovery process in which compressed air is
- 5. HISTORY 1979, Buffalo, USA, recovery – 64% 2002, North Ceder Hills, USA, recovery – 60% 2003,
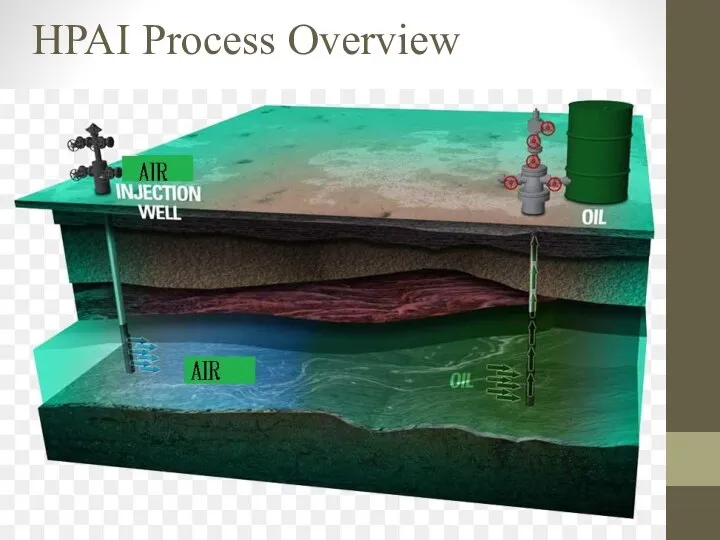
- 6. HPAI Process Overview
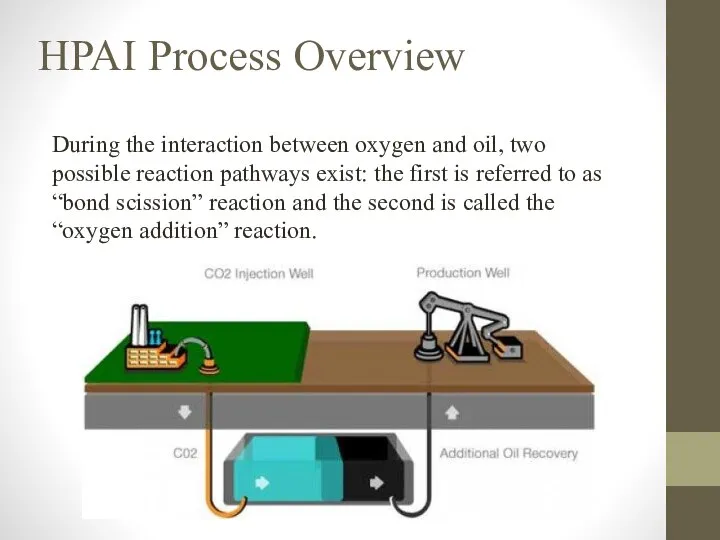
- 7. HPAI Process Overview During the interaction between oxygen and oil, two possible reaction pathways exist: the
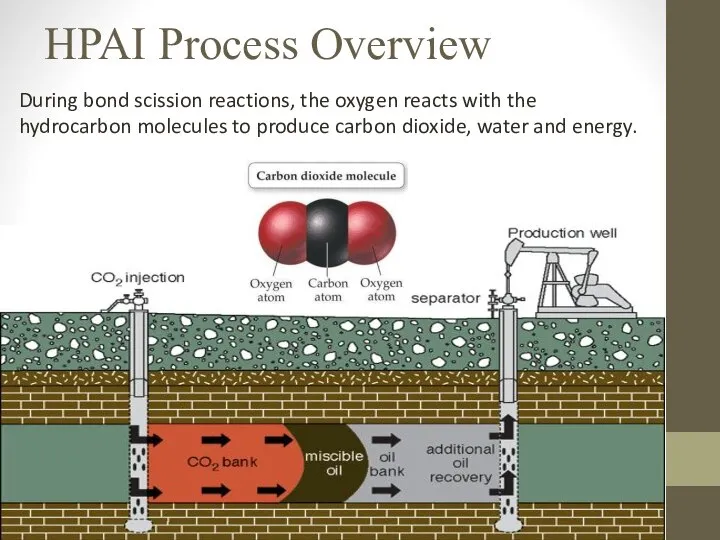
- 8. HPAI Process Overview During bond scission reactions, the oxygen reacts with the hydrocarbon molecules to produce
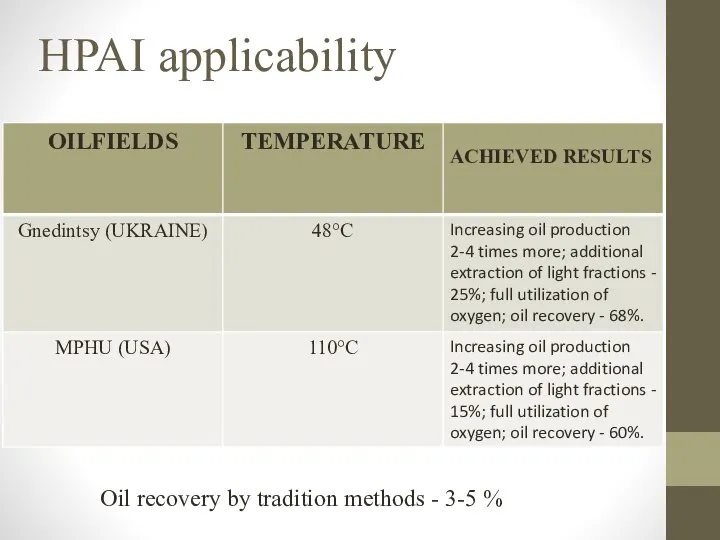
- 9. HPAI applicability Oil recovery by tradition methods - 3-5 %
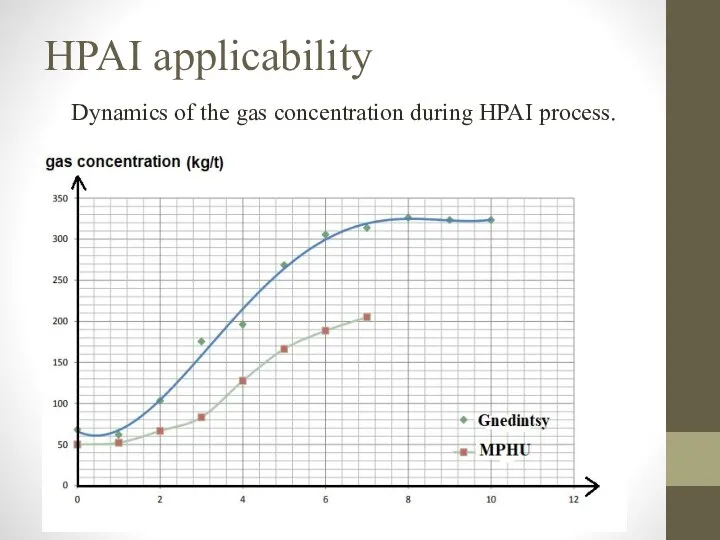
- 10. HPAI applicability Dynamics of the gas concentration during HPAI process.
- 11. HPAI advantages • Reservoir pressurization • Production response within a short time period • Consumption of
- 12. HPAI disadvantages • Air compression and operation could be expensive • Complex process: multiphase flow, heat
- 13. Why reconsider HPAI today? • Thermally, it is the most efficient oil recovery process • Availability
- 17. ISC advantages 1. Transition to the gas phase of some (lightest) components of oil saturating the
- 18. ISC disadvantages to take measures to protect the environment and disposal of combustion products to prevent
- 20. Скачать презентацию











 ОО на 825 мест (УстьСлавянка, уч.33)
ОО на 825 мест (УстьСлавянка, уч.33) Воды России
Воды России Наумовский сельсовет муниципального района Стерлитамакский район Республики Башкортостан
Наумовский сельсовет муниципального района Стерлитамакский район Республики Башкортостан Проблема использования мирового океана: новый этап.
Проблема использования мирового океана: новый этап. Тема: Экономическое районирование Задачи: Познакомиться… Определить… Изучить… Сформировать… Развивать…
Тема: Экономическое районирование Задачи: Познакомиться… Определить… Изучить… Сформировать… Развивать…  Обвалы, оползни. Осыпи. Карст, суффозия. Овраги
Обвалы, оползни. Осыпи. Карст, суффозия. Овраги ПОНЯТИЕ ПРЕСТУПЛЕНИЯ. ВИДЫ И КАТЕГОРИИ ПРЕСТУПЛЕНИЙ 9 КЛАСС
ПОНЯТИЕ ПРЕСТУПЛЕНИЯ. ВИДЫ И КАТЕГОРИИ ПРЕСТУПЛЕНИЙ 9 КЛАСС АВСТРАЛИЯ
АВСТРАЛИЯ  Куба Республикасы
Куба Республикасы Усинск
Усинск Суперконтинент Пангея - презентация к уроку Географии
Суперконтинент Пангея - презентация к уроку Географии Умеренный пояс: засушливые зоны 1.Какая основная особенность климата умеренного пояса? (наклон солнечных лучей) 2. От чего становит
Умеренный пояс: засушливые зоны 1.Какая основная особенность климата умеренного пояса? (наклон солнечных лучей) 2. От чего становит Ласкаво просимо до Херсону
Ласкаво просимо до Херсону Презентация на тему КАМЕРУН Столица: Яунде
Презентация на тему КАМЕРУН Столица: Яунде  Погода - презентация к уроку Географии_
Погода - презентация к уроку Географии_ Ул Московская г Пенза - презентация к уроку Географии
Ул Московская г Пенза - презентация к уроку Географии ТЕМПЕРАТУРА ВОЗДУХА Урок географии 6 класс
ТЕМПЕРАТУРА ВОЗДУХА Урок географии 6 класс  Основы инженерно-геологической характеристики и оценки дисперсных грунтов – рыхлые несвязные и глинистые связные породы
Основы инженерно-геологической характеристики и оценки дисперсных грунтов – рыхлые несвязные и глинистые связные породы Вред природе. - презентация к уроку Географии
Вред природе. - презентация к уроку Географии ВНУТРЕННИЕ ВОДЫ ЮЖНОЙ АМЕРИКИ _
ВНУТРЕННИЕ ВОДЫ ЮЖНОЙ АМЕРИКИ _ ДРЕВНИЙ КИЕВ ДРЕВНИЙ КИЕВ
ДРЕВНИЙ КИЕВ ДРЕВНИЙ КИЕВ Мир профессий Все профессии от людей и только три от Бога: учитель, судья и врач" - Сократ.
Мир профессий Все профессии от людей и только три от Бога: учитель, судья и врач" - Сократ. Биогеохимические циклы наиболее жизненно важных биогенных веществ
Биогеохимические циклы наиболее жизненно важных биогенных веществ Самара
Самара Германия (ФРГ). Общие сведения
Германия (ФРГ). Общие сведения Родина бывает разная, но у всех она одна!
Родина бывает разная, но у всех она одна! Бразилия 11 класс - презентация к уроку Географии
Бразилия 11 класс - презентация к уроку Географии Выполнил: Группа Преподаватель:
Выполнил: Группа Преподаватель: