Содержание
- 2. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (the UK) occupies most of the territory
- 3. It consists of four main parts: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. London is the capital
- 4. The population of the United Kingdom is over 57 million people. Foreigners often call British people
- 5. The Parliament of Great Britain
- 6. The Parliament was formed in 1707 by the Acts of Union The oldest Parliament Upper House
- 7. Parliament has three main functions: Examining and challenging the work of the government To debate the
- 8. The business of Parliament takes place in two Houses: the House of Commons Their work is
- 9. The House of Commons Meets at the Palace of Westminster The Commons is publicly elected MPs
- 10. Speaker The House of Commons elects a speaker Doesn't take part in debate nor vote John
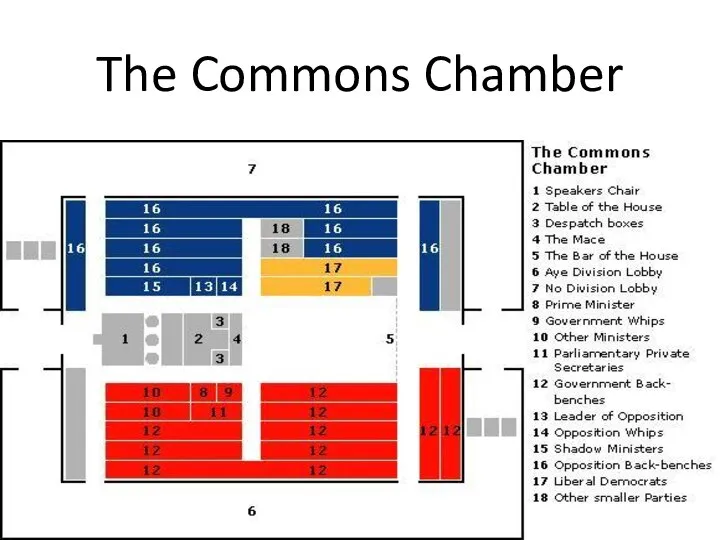
- 11. The Commons Chamber
- 12. The House of Lords Members are appointed by the Queen Life Peers Baron or Baroness, ¼
- 13. The House of Lords is the upper chamber of Great Britain’s bicameral legislature. Originating in the
- 14. The House of Lords consists of over 670 numbers . Which includes : Hereditary peers Life
- 15. The Sovereign’s throne is in the House of Lords. Queen sits on it once a year
- 16. Traditionally the House of Lords did not elect its own speaker, unlike the House of Commons;
- 17. This reform of the post of Lord Chancellor was made due to the perceived constitutional anomalies
- 18. The powers of the modern House of Lords are extremely limited The House of Lords’ powers
- 19. Under the 1911 act, all bills specified by the speaker of the House of Commons as
- 20. Despite these limitations, the House of Lords plays a significant role in Parliament. The main functions
- 21. In 1998 the Labour government of Tony Blair introduced legislation to deprive hereditary peers (by then
- 22. The measure, which went into effect in late 1999, was seen as a prelude to wider
- 23. To become law … A Bill must be agreed by both Houses The members of Parliament
- 24. The Queen Elizabeth II Queen Elizabeth II was born Princess Elizabeth Alexandra Mary on April 21,
- 25. As the longest-serving monarch in British history, she has tried to make her reign more modern
- 27. Скачать презентацию























 Трюдо, Кларк, Малруни. Буржуазные правительства и проблемы развития страны
Трюдо, Кларк, Малруни. Буржуазные правительства и проблемы развития страны Политическая реклама Матросова М
Политическая реклама Матросова М Политические события в Восточной Европе во второй половине 80-ых гг
Политические события в Восточной Европе во второй половине 80-ых гг Природа и сущность государственного управления
Природа и сущность государственного управления Реализация государственной демографической политики в Минской
Реализация государственной демографической политики в Минской Политическая система
Политическая система Политология как наука и учебная дисциплина
Политология как наука и учебная дисциплина Государство, как элемент политической системы общества. Признаки и функции государства
Государство, как элемент политической системы общества. Признаки и функции государства Политическая система общества
Политическая система общества Террористическая организация Аль-Каида
Террористическая организация Аль-Каида Выступления, интервью, публикации по вопросам разработки и реализации государственной политики
Выступления, интервью, публикации по вопросам разработки и реализации государственной политики Виды и формы государства
Виды и формы государства Введение в основы идеологии. Тема 1
Введение в основы идеологии. Тема 1 Коррупция и борьба с ней в России. Нормативно-правовое обеспечение
Коррупция и борьба с ней в России. Нормативно-правовое обеспечение Структура управления в областях на примерах разных стран
Структура управления в областях на примерах разных стран Ю.В. Андропов и Н.А. Щеколов
Ю.В. Андропов и Н.А. Щеколов Специфика и разновидности монопартизма
Специфика и разновидности монопартизма О деятельности Федерации Независимых Профсоюзов России
О деятельности Федерации Независимых Профсоюзов России Масштабные теракты на планете в конце 20 - начале 21 веков
Масштабные теракты на планете в конце 20 - начале 21 веков Топ 5 горячих точек мира
Топ 5 горячих точек мира Миротворческий контроль внутригосударственных конфликтов
Миротворческий контроль внутригосударственных конфликтов Wybory do Sejmu Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej i do Senatu Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej 13 października 2019 r
Wybory do Sejmu Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej i do Senatu Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej 13 października 2019 r Диссидент. Диссидентство
Диссидент. Диссидентство Политика как социальное явление
Политика как социальное явление Политические партии и движения
Политические партии и движения Политическая система общества и политический режим
Политическая система общества и политический режим Основы конституционного строя. Государственное устройство России
Основы конституционного строя. Государственное устройство России Вопросы по теме Коррупция в Тайланде
Вопросы по теме Коррупция в Тайланде