Содержание
- 2. Topics covered Molecular weight and Molar Mass Representation of Compounds Types of Chemical Reactions Net ionic
- 3. Compounds Compound – pure substance that is composed of two or more elements in a fixed
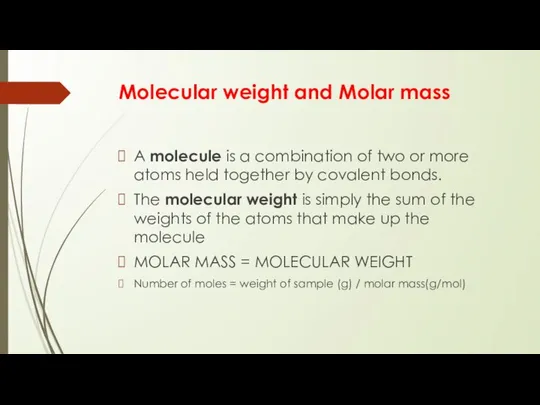
- 4. Molecular weight and Molar mass A molecule is a combination of two or more atoms held
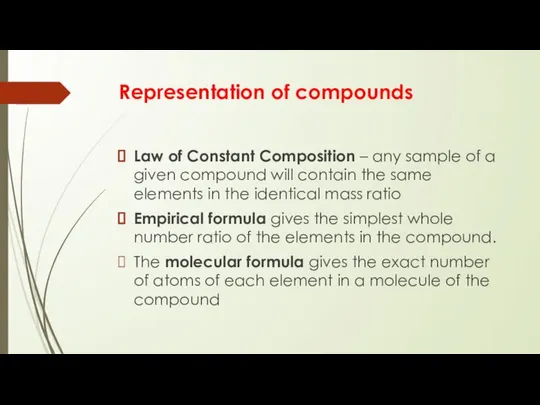
- 5. Representation of compounds Law of Constant Composition – any sample of a given compound will contain
- 6. Percent composition It is the weight percent of the element in a specific compound.
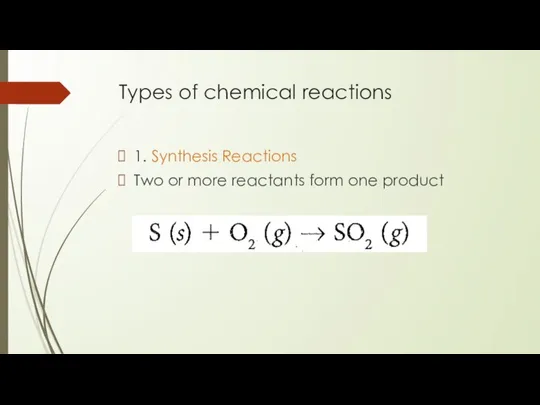
- 7. Types of chemical reactions 1. Synthesis Reactions Two or more reactants form one product
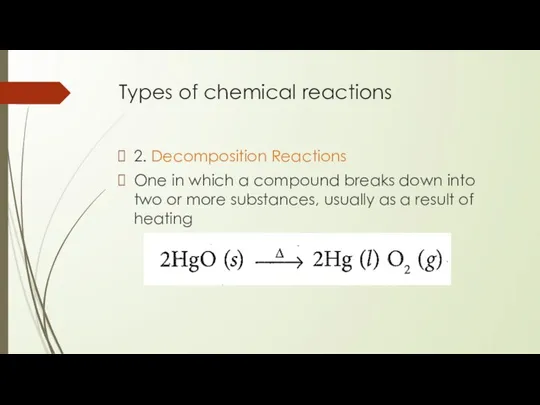
- 8. Types of chemical reactions 2. Decomposition Reactions One in which a compound breaks down into two
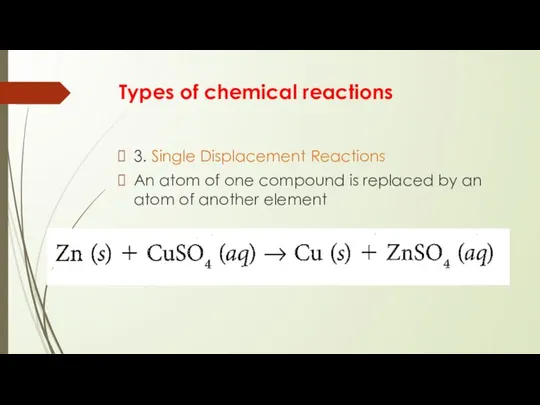
- 9. Types of chemical reactions 3. Single Displacement Reactions An atom of one compound is replaced by
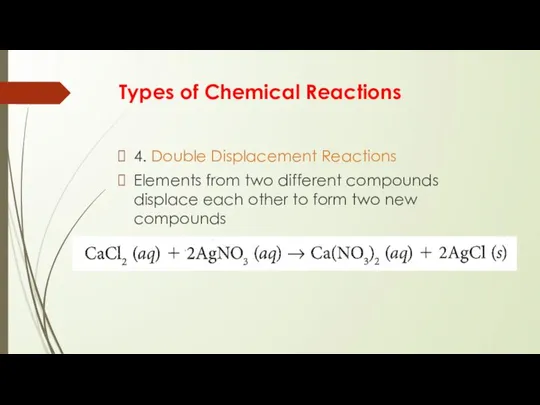
- 10. Types of Chemical Reactions 4. Double Displacement Reactions Elements from two different compounds displace each other
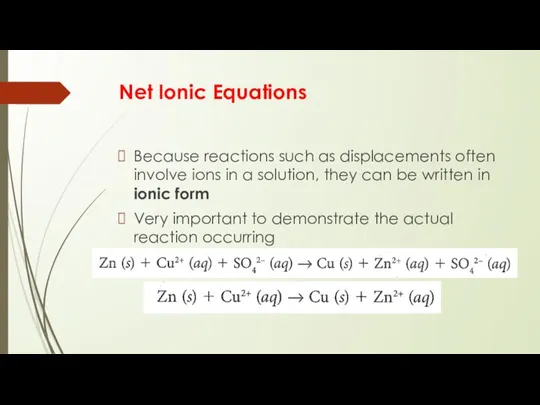
- 11. Net Ionic Equations Because reactions such as displacements often involve ions in a solution, they can
- 12. Balancing Equations From the law of conservation of mass, the mass of the reactants in a
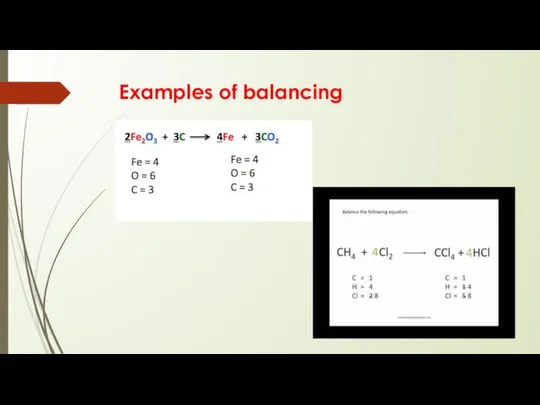
- 13. Examples of balancing
- 14. Applications of stoichiometry
- 15. Limiting Reactants Limiting reactant limits the amounts of product that can be formed in the reaction
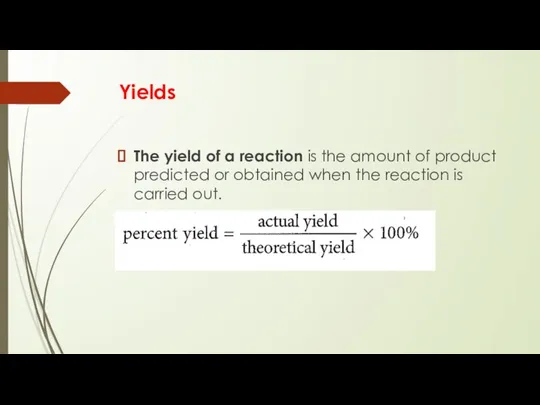
- 16. Yields The yield of a reaction is the amount of product predicted or obtained when the
- 18. Скачать презентацию






 Презентація на тему Карбонові кислоти Підготував студент групи ФК-44-I Галюк Юрій
Презентація на тему Карбонові кислоти Підготував студент групи ФК-44-I Галюк Юрій  Кислород. Применение и круговорот в природе. 8 класс
Кислород. Применение и круговорот в природе. 8 класс Минеральные вещества. Микроэлементы и макроэлементы
Минеральные вещества. Микроэлементы и макроэлементы Тема: «Бишофит – новый старый антигололедный реагент» Авторы: Гончаревич Анастасия Клокова Татьян
Тема: «Бишофит – новый старый антигололедный реагент» Авторы: Гончаревич Анастасия Клокова Татьян Горные породы и минералы. Камни-самоцветы
Горные породы и минералы. Камни-самоцветы Минералы горных пород
Минералы горных пород Липиды. Классификация липидов
Липиды. Классификация липидов Повышение эффективности вакуумной перегонки мазута
Повышение эффективности вакуумной перегонки мазута Кремний и его соединения (9 класс)
Кремний и его соединения (9 класс) Происхождение жизни на Земле
Происхождение жизни на Земле Неорганические полимеры
Неорганические полимеры Диаграмма состояния системы железо – углерод
Диаграмма состояния системы железо – углерод Минералогия. Кристаллохимия
Минералогия. Кристаллохимия Качественный анализ дубильных веществ
Качественный анализ дубильных веществ Химия и повседневная жизнь человека
Химия и повседневная жизнь человека Жидкие кристаллы в технике
Жидкие кристаллы в технике Общая и неорганическая химия. Классы неорганических соединений. Способы выражения состава растворов
Общая и неорганическая химия. Классы неорганических соединений. Способы выражения состава растворов Презентация Благородные газы
Презентация Благородные газы Графическое представление газовых процессов. (10 класс)
Графическое представление газовых процессов. (10 класс) Биологическая роль липидов. Транспортные формы липидов
Биологическая роль липидов. Транспортные формы липидов Пурин нуклеозидтері (аденозии 3-фосфор қышқылы, рибоксии). Сапасына Қойылантын талаптар, талдау әдістері
Пурин нуклеозидтері (аденозии 3-фосфор қышқылы, рибоксии). Сапасына Қойылантын талаптар, талдау әдістері Формирование навыков научно-исследовательской деятельности школьников 5-7 классов
Формирование навыков научно-исследовательской деятельности школьников 5-7 классов Вещества молекулярного и немолекулярного строения
Вещества молекулярного и немолекулярного строения 2.3. Матричные синтезы. Часть 1
2.3. Матричные синтезы. Часть 1 Менделєєв Дмитро Іванович Роботу виконав: Учень 11 - Б класу Вдовіченко І. Вчитель інформатики: Трибко О.Б.
Менделєєв Дмитро Іванович Роботу виконав: Учень 11 - Б класу Вдовіченко І. Вчитель інформатики: Трибко О.Б.  Rectification. Difference between the rectification and distillation
Rectification. Difference between the rectification and distillation Природные полимеры. Белки и нуклеиновые кислоты
Природные полимеры. Белки и нуклеиновые кислоты Средства для борьбы с бытовыми насекомыми
Средства для борьбы с бытовыми насекомыми