Содержание
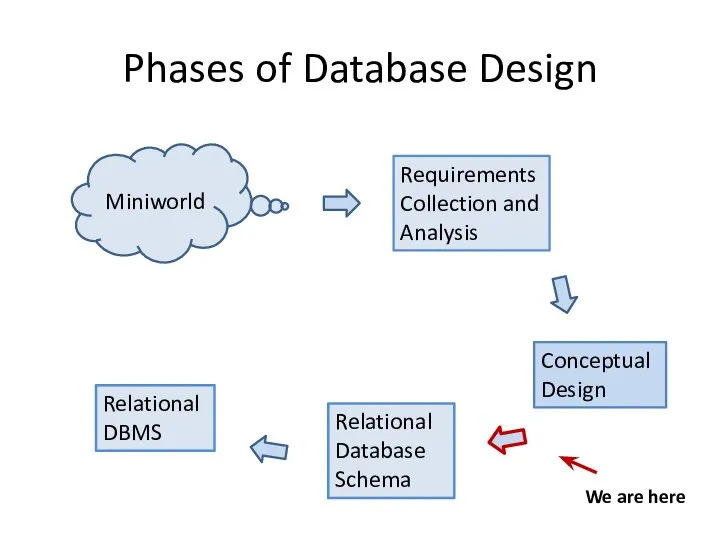
- 2. Phases of Database Design Miniworld Requirements Collection and Analysis Conceptual Design Relational Database Schema Relational DBMS
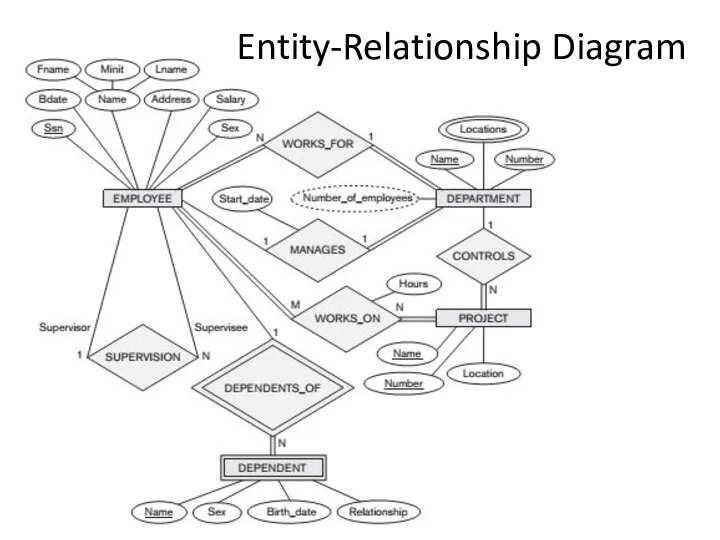
- 3. Entity-Relationship Diagram
- 4. Relational Database Schema
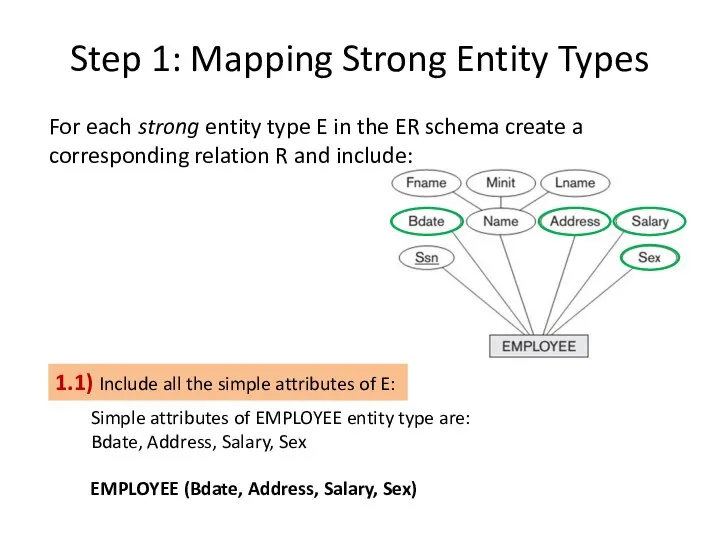
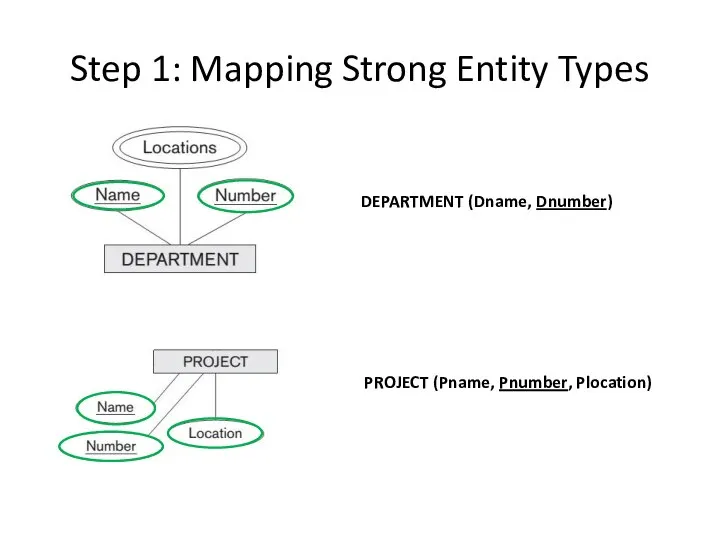
- 5. Step 1: Mapping Strong Entity Types 1.1) Include all the simple attributes of E: For each
- 6. Step 1: Mapping Strong Entity Types 1.2) Include only the simple component attributes of a composite
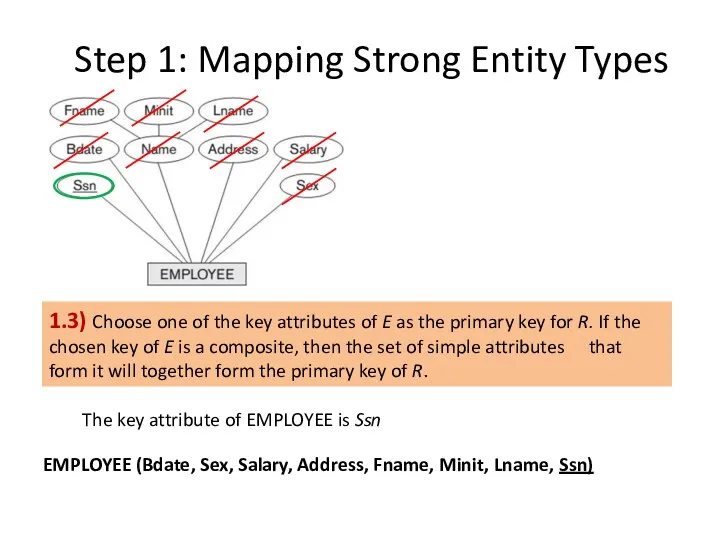
- 7. Step 1: Mapping Strong Entity Types 1.3) Choose one of the key attributes of E as
- 8. Step 1: Mapping Strong Entity Types DEPARTMENT (Dname, Dnumber) PROJECT (Pname, Pnumber, Plocation)
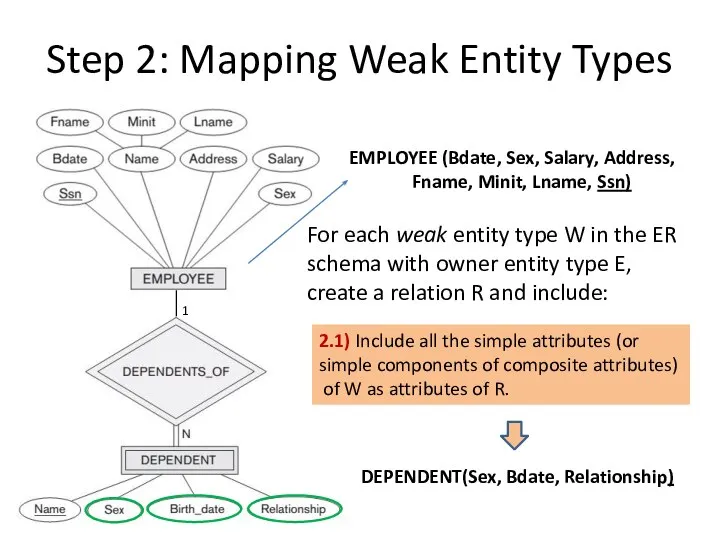
- 9. Step 2: Mapping Weak Entity Types 1 EMPLOYEE (Bdate, Sex, Salary, Address, Fname, Minit, Lname, Ssn)
- 10. Step 2: Mapping Weak Entity Types 1 EMPLOYEE (Bdate, Sex, Salary, Address, Fname, Minit, Lname, Ssn)
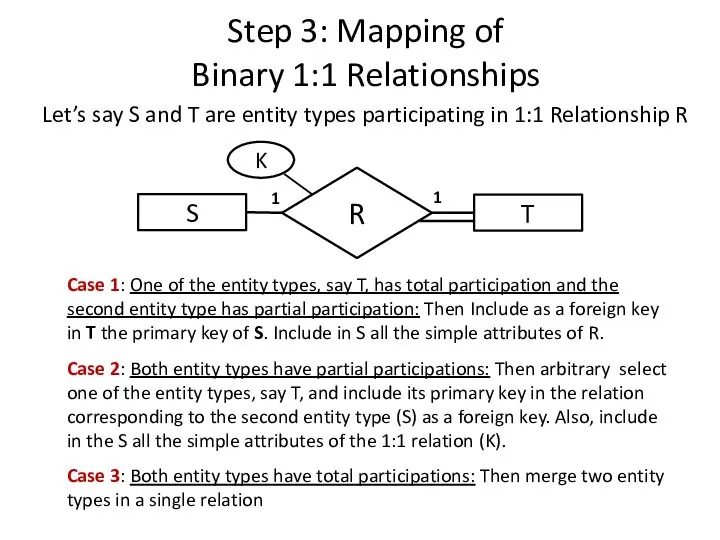
- 11. Let’s say S and T are entity types participating in 1:1 Relationship R T S R
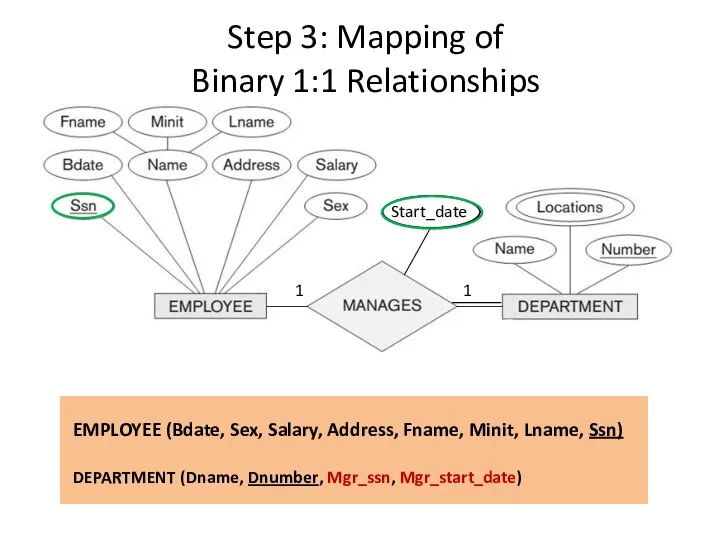
- 12. Step 3: Mapping of Binary 1:1 Relationships 1 1 DEPARTMENT (Dname, Dnumber, Mgr_ssn, Mgr_start_date) EMPLOYEE (Bdate,
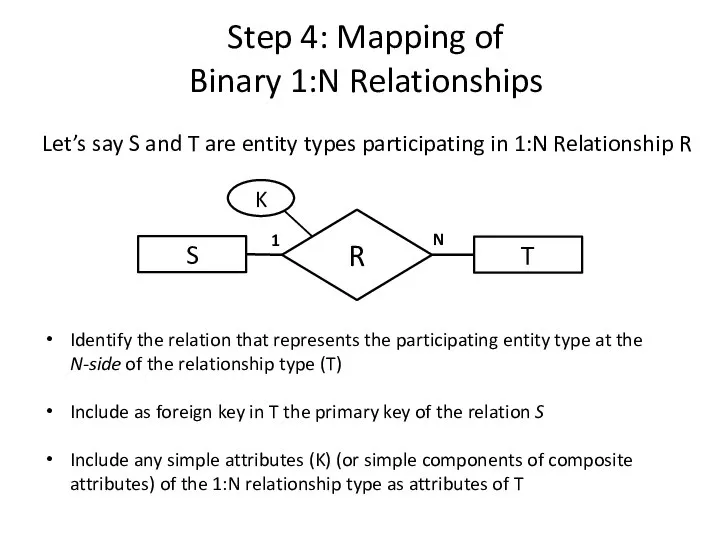
- 13. Step 4: Mapping of Binary 1:N Relationships Let’s say S and T are entity types participating
- 14. Step 4: Mapping of Binary 1:N Relationships N 1 DEPARTMENT (Dname, Dnumber, Mgr_ssn, Mgr_start_date) EMPLOYEE (Bdate,
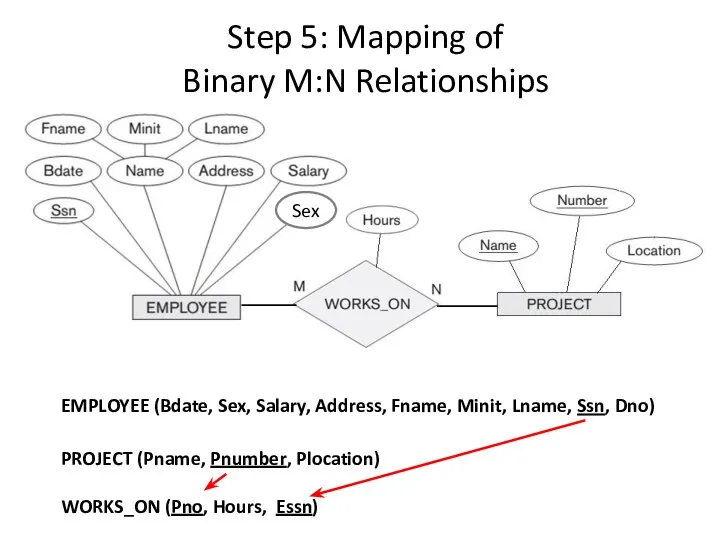
- 15. Step 5: Mapping of Binary M:N Relationships T S R M N K For each binary
- 16. Step 5: Mapping of Binary M:N Relationships Sex PROJECT (Pname, Pnumber, Plocation) EMPLOYEE (Bdate, Sex, Salary,
- 17. Step 6: Mapping of Multivalued Attributes S A For each multivalued attribute A, create a new
- 18. Step 6: Mapping of Multivalued Attributes DEPT_LOCATIONS (Dnumber, Dlocation)
- 19. Step 7: Mapping of N-ary Relationships For each n-ary relationship type R, where n > 2,
- 21. Скачать презентацию








 Презентация "Проектная деятельность" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Проектная деятельность" - скачать презентации по Информатике Презентация "Мышь. Меню – возможность выбора" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Мышь. Меню – возможность выбора" - скачать презентации по Информатике Программное обеспечение компьютеров
Программное обеспечение компьютеров Создание 2D платформера в среде разработки Godot Engine
Создание 2D платформера в среде разработки Godot Engine Microsoft paint
Microsoft paint Пневматический манипулятор с 3-мя степенями свободы под управлением ПЛК
Пневматический манипулятор с 3-мя степенями свободы под управлением ПЛК Инструкция по заполнению анкеты TSI
Инструкция по заполнению анкеты TSI файлы и файловая система
файлы и файловая система Документирование как основа тестирования
Документирование как основа тестирования Компьютерное поколение
Компьютерное поколение Win 7 Smart Tool For Intel SKL platform
Win 7 Smart Tool For Intel SKL platform Презентация "Системный блок компьютера" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Системный блок компьютера" - скачать презентации по Информатике Разработка программ с использованием классов. C#
Разработка программ с использованием классов. C# Компьютерные сети, коммуникационные технологии. Понятие об информации
Компьютерные сети, коммуникационные технологии. Понятие об информации Компьютерные презентации с использованием мультимедиа технологии
Компьютерные презентации с использованием мультимедиа технологии Презентация "Текстовый редактор MS Word (7 класс)" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Текстовый редактор MS Word (7 класс)" - скачать презентации по Информатике Прикладне програмування
Прикладне програмування Siebel Party Business Components
Siebel Party Business Components Принципы работы и практика использования виртуальных машин
Принципы работы и практика использования виртуальных машин Трёхмерное моделирование в КОМПАС
Трёхмерное моделирование в КОМПАС Запись прошивки на USB флешку
Запись прошивки на USB флешку Разработка базы данных для учета ремонтных работ ООО «СпецНовСтрой»
Разработка базы данных для учета ремонтных работ ООО «СпецНовСтрой» Работа в Word
Работа в Word Всероссийская акция «Час кода»
Всероссийская акция «Час кода» Теория принятия решений принятие оптимальных решений методами динамического программирования
Теория принятия решений принятие оптимальных решений методами динамического программирования Системы счисления
Системы счисления Презентация "MSC.Mvision Workshop 6" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "MSC.Mvision Workshop 6" - скачать презентации по Информатике Организация администрирования компьютерных сетей
Организация администрирования компьютерных сетей