Содержание
- 2. Outline Introduction Body Conclusion
- 3. Introduction A network is a combination of hardware and software that sends data from one location
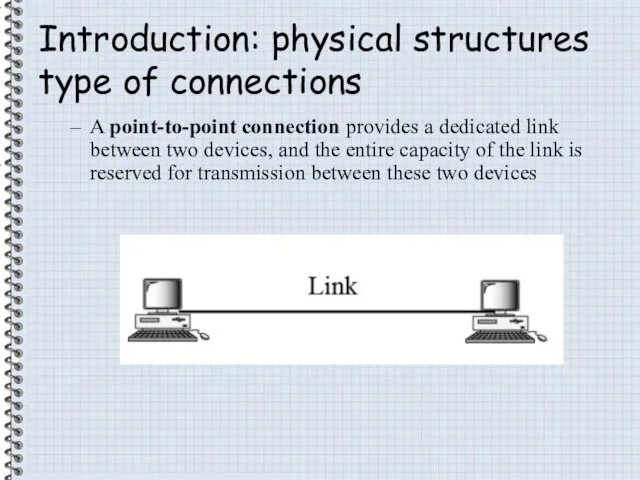
- 4. Introduction: physical structures type of connections A point-to-point connection provides a dedicated link between two devices,
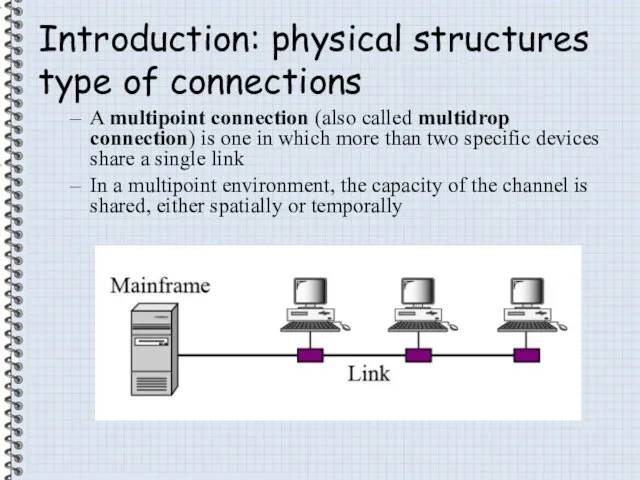
- 5. Introduction: physical structures type of connections A multipoint connection (also called multidrop connection) is one in
- 6. Introduction: physical structures physical topology The term physical topology refers to the way in which a
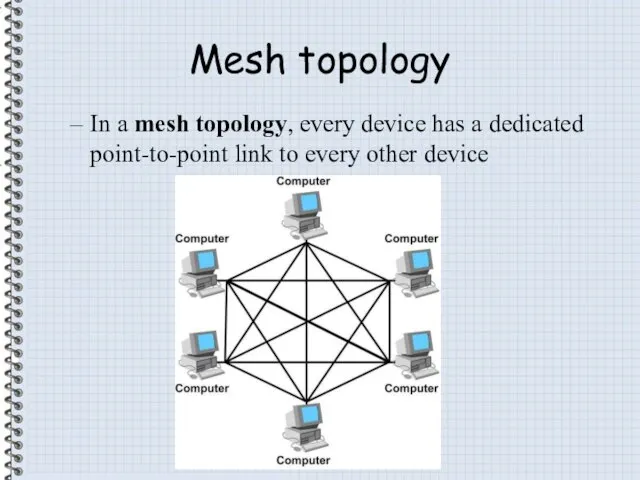
- 7. Mesh topology In a mesh topology, every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other
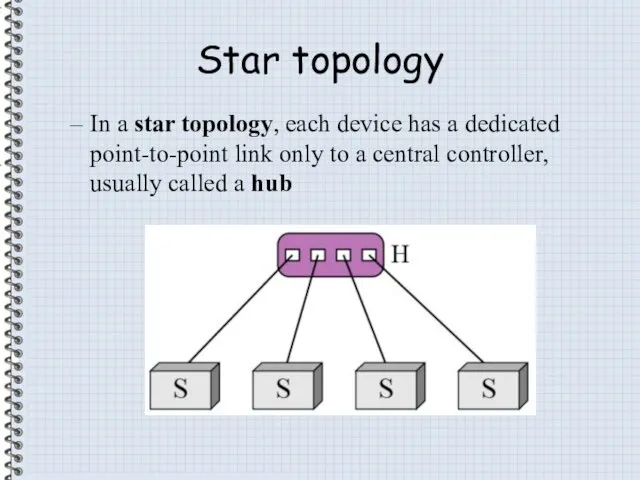
- 8. Star topology In a star topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a
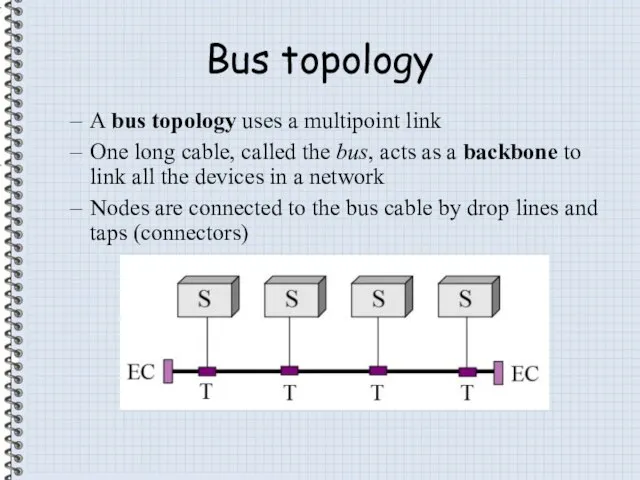
- 9. Bus topology A bus topology uses a multipoint link One long cable, called the bus, acts
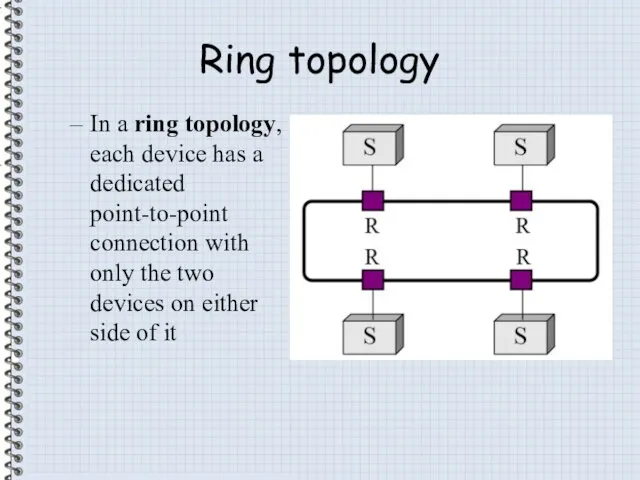
- 10. Ring topology In a ring topology, each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection with only the
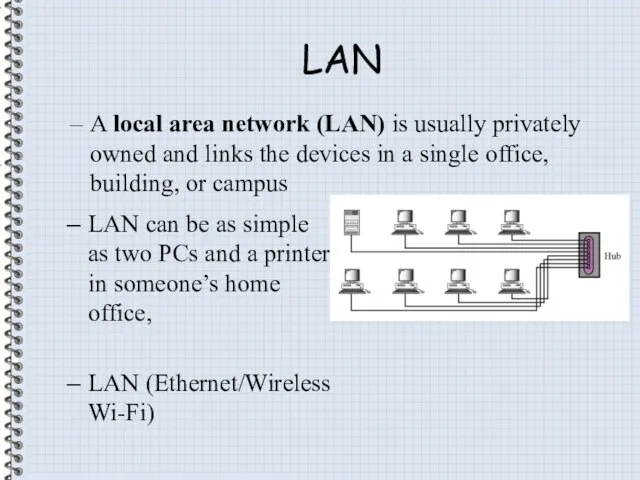
- 11. LAN A local area network (LAN) is usually privately owned and links the devices in a
- 12. MAN A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network with a size between a LAN and
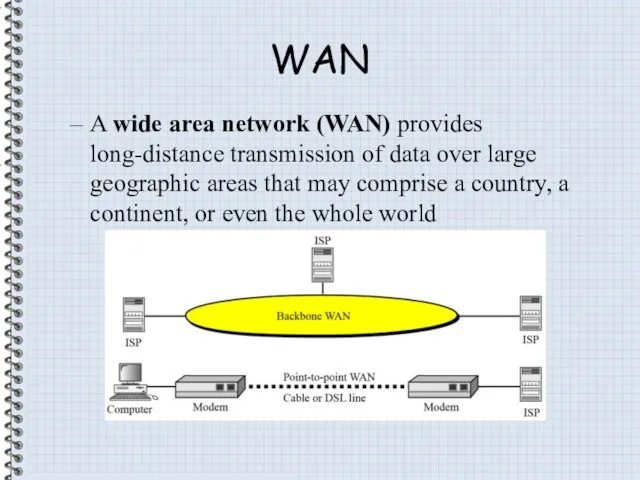
- 13. WAN A wide area network (WAN) provides long-distance transmission of data over large geographic areas that
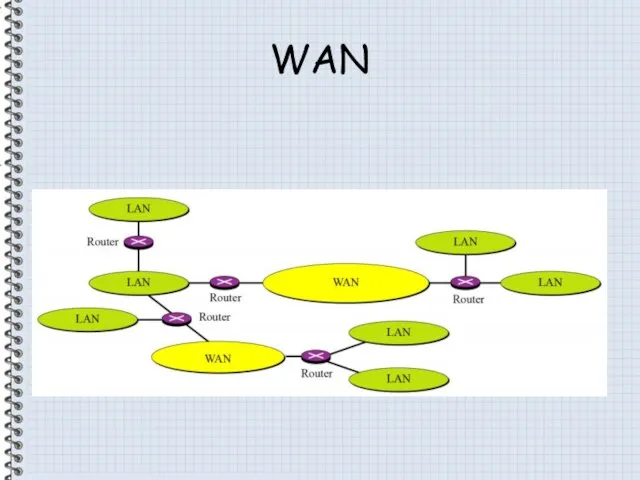
- 14. WAN
- 15. TCP/IP protocol suite To divide the services required to perform a task, the Internet has created
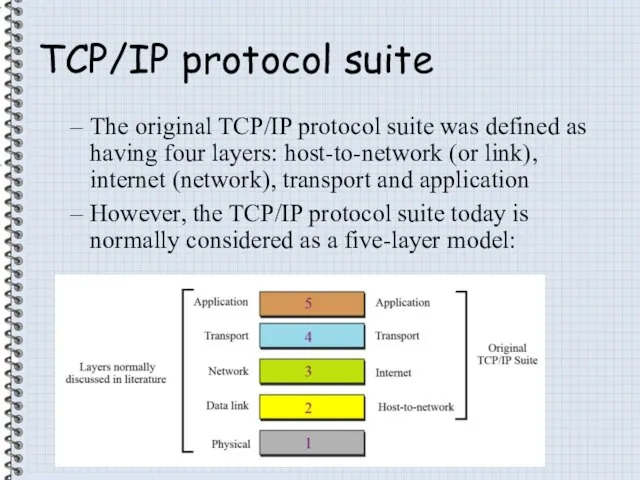
- 16. TCP/IP protocol suite The original TCP/IP protocol suite was defined as having four layers: host-to-network (or
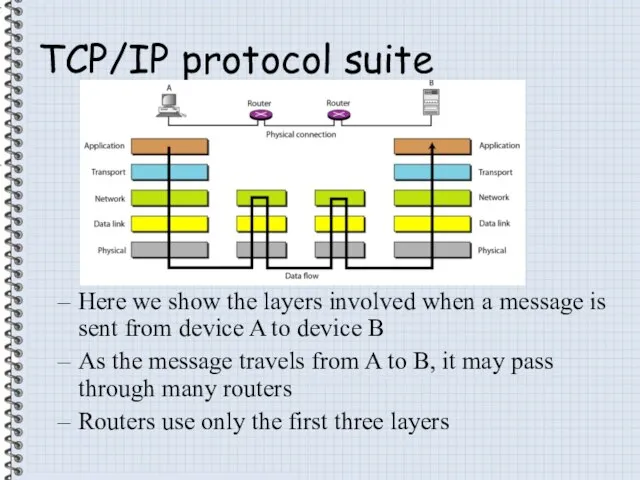
- 17. TCP/IP protocol suite Here we show the layers involved when a message is sent from device
- 18. Transport layer address (port numbers) The IP address of the server is necessary for communication, but
- 19. Transport layer protocols: TCP Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) supports all the duties of a transport layer
- 20. Network layer: IP The TCP/IP protocol suite supports one main protocol (IP) and several auxiliary protocols
- 21. Network layer: network layer protocols The notation divides the 32-bit address into four 8-bit sections and
- 22. Network layer: network layer protocols At a message’s source the IPv4 protocol adds the source and
- 23. Data link layer addresses The Ethernet protocol, the most prevalent LAN in the use today, uses
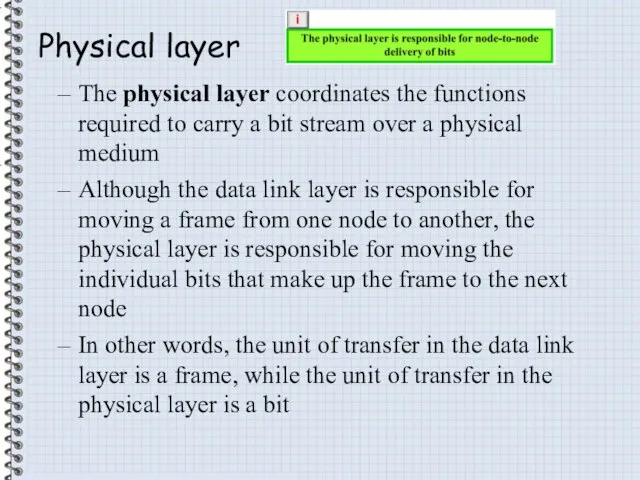
- 24. Physical layer The physical layer coordinates the functions required to carry a bit stream over a
- 25. Read the IT news!!! L3 IP-address, router/роутер/маршрутизатор transmits packets (host-to-host communication) L2 MAC-address, hub/switch/коммутатор transmits frames
- 26. Read the IT news!!! G - generation (Поколение) 1G - 2G - GSM (CSD 9.6Kbit/s) 2.5G
- 27. Read the IT news!!! PAN (BlueTooth) LAN (Ethernet/Wireless) MAN (ADSL/FTTB/GPON) WAN ()
- 28. Read the IT news!!! Win8.1 change Public Network profile to Private Win+R --> regEdit HKLM/Software/Microsoft/Windows NT/CurrentVersion/NetworkList/Profiles
- 29. Read the IT news!!! http://profit.kz/ http://tengrinews.kz/tech/ http://www.habrahabr.ru http://www.computerworld.kz/ http://xakep.ru http://www.securitylab.ru/ http://ictmagazine.kz/ and so on… Homework every
- 31. Скачать презентацию











 Алгоритмы. Свойства алгоритмов. Формы представления алгоритмов
Алгоритмы. Свойства алгоритмов. Формы представления алгоритмов Предмет и задачи информатики
Предмет и задачи информатики Презентация "Тест "Электронные таблицы" (9 класс)" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Тест "Электронные таблицы" (9 класс)" - скачать презентации по Информатике Can computer games help to learn English?
Can computer games help to learn English? Память ЭВМ. Иерархическое построение памяти ЭВМ
Память ЭВМ. Иерархическое построение памяти ЭВМ Работа мозга. Работа с информацией
Работа мозга. Работа с информацией Свойства информации
Свойства информации ConnectKey 2017. Приложения и инструменты. Возможности Xerox ConnectKey 2017
ConnectKey 2017. Приложения и инструменты. Возможности Xerox ConnectKey 2017 Создание запросов на выборку в базе данных
Создание запросов на выборку в базе данных Перечисления и массивы
Перечисления и массивы Программное обеспечение персонального компьютера
Программное обеспечение персонального компьютера Внутренние и периферийные устройства компьютера
Внутренние и периферийные устройства компьютера Архитектурная схема ЭВМ. Состав ПК
Архитектурная схема ЭВМ. Состав ПК Книга «Дизайн логотипа». Боб Паташник
Книга «Дизайн логотипа». Боб Паташник Мониторы. Строение современного монитора. Классификация мониторов
Мониторы. Строение современного монитора. Классификация мониторов Назначение модулей РВ (административные модули, технологические модули, модули записи архивов)
Назначение модулей РВ (административные модули, технологические модули, модули записи архивов) Презентация к уроку информатики 6 класс тема «Алгоритмы» Подготовила: Никитина Ирина.
Презентация к уроку информатики 6 класс тема «Алгоритмы» Подготовила: Никитина Ирина.  СУБД Access. Создание базы данных
СУБД Access. Создание базы данных Блогерство как социальный феномен
Блогерство как социальный феномен Общие сведения о языке программирования python
Общие сведения о языке программирования python Изучение фейковых сообщений и вредоносного по в сети интернет и с помощью системы крибрум
Изучение фейковых сообщений и вредоносного по в сети интернет и с помощью системы крибрум Презентация "Математические модели информационных потоков" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Математические модели информационных потоков" - скачать презентации по Информатике Создание Телеграмм - бота для покупок авиабилетов
Создание Телеграмм - бота для покупок авиабилетов ФАЙЛЫ и ПАПКИ
ФАЙЛЫ и ПАПКИ Информация и информационные процессы
Информация и информационные процессы Программная платформа. Аппаратное обеспечение компьютера
Программная платформа. Аппаратное обеспечение компьютера Программное обеспечение компьютера. Операционная система
Программное обеспечение компьютера. Операционная система Презентация на тему: «Налаживаем взаимодействие между компьютерами: настройка IP-адресации и маршрутизации.» Выполнила ученица 10
Презентация на тему: «Налаживаем взаимодействие между компьютерами: настройка IP-адресации и маршрутизации.» Выполнила ученица 10