Содержание
- 2. Data analysis is a process of inspecting, cleansing, transforming and modeling data with the goal of
- 3. Data mining is a particular data analysis technique that focuses on statistical modeling and knowledge discovery
- 4. Stage 1: Exploration. This stage usually starts with data preparation which may involve cleaning data, data
- 5. Stage 2: Model building and validation. This stage involves considering various models and choosing the best
- 6. Stage 3: Deployment. That final stage involves using the model selected as best in the previous
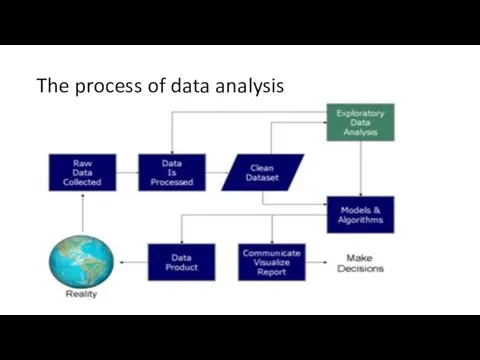
- 7. The process of data analysis
- 8. Data requirements The data are necessary as inputs to the analysis, which is specified based upon
- 9. Data collection Data are collected from a variety of sources. The requirements may be communicated by
- 10. Data processing Data initially obtained must be processed or organized for analysis. For instance, these may
- 11. Data cleaning Once processed and organised, the data may be incomplete, contain duplicates, or contain errors.
- 12. Exploratory data analysis Once the data are cleaned, it can be analyzed. Analysts may apply a
- 13. Modeling and algorithms Mathematical formulas or models called algorithms may be applied to the data to
- 14. Data product A data product is a computer application that takes data inputs and generates outputs,
- 15. Communication Once the data are analyzed, it may be reported in many formats to the users
- 17. Скачать презентацию













 Информация. Кодирование информации
Информация. Кодирование информации Разработка мер по защите информации в АИС «Сетевой край. Образование»
Разработка мер по защите информации в АИС «Сетевой край. Образование» Технологии программирования
Технологии программирования Программы, используемые при автоматизации салона красоты
Программы, используемые при автоматизации салона красоты Системы управления базами данных. PL/SQL. (Часть 2)
Системы управления базами данных. PL/SQL. (Часть 2) Презентация "Работа с объектами текстового документа" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Работа с объектами текстового документа" - скачать презентации по Информатике Разработка элементов фирменного стиля образовательной организации с использованием специализированного программного обеспечения
Разработка элементов фирменного стиля образовательной организации с использованием специализированного программного обеспечения Обеспечение эффективности банковского сектора Юрлова Виктория, МЭ-102
Обеспечение эффективности банковского сектора Юрлова Виктория, МЭ-102 Язык новостной журналистики
Язык новостной журналистики Операционные системы
Операционные системы Триггеры. Триггеры в презентации. Применение. Создание слайдов с триггерами
Триггеры. Триггеры в презентации. Применение. Создание слайдов с триггерами Моделирование как метод познания
Моделирование как метод познания Лекция 2. Основы программной инженерии. Основные этапы разработки программ, их назначение и характеристики
Лекция 2. Основы программной инженерии. Основные этапы разработки программ, их назначение и характеристики Объектная модель Excel
Объектная модель Excel Компьютерная этика
Компьютерная этика Средства защиты информации в ОС Windows
Средства защиты информации в ОС Windows Троянские программы
Троянские программы Бази даних. Система управління базами даних Microsoft Access
Бази даних. Система управління базами даних Microsoft Access Деревья Хаффмана (продолжение)
Деревья Хаффмана (продолжение) Регистрация несовершеннолетних на ЕЦПСЗ
Регистрация несовершеннолетних на ЕЦПСЗ Проектирование трансляторов языков программирования. Схема работы компилятора. (Глава 1)
Проектирование трансляторов языков программирования. Схема работы компилятора. (Глава 1) Презентация на тему Кодирование информации в компьютере
Презентация на тему Кодирование информации в компьютере Областная детско-юношеская библиотека. Культурный статус, устойчивость и значение в развитии региона
Областная детско-юношеская библиотека. Культурный статус, устойчивость и значение в развитии региона Мистецтво написання проекту
Мистецтво написання проекту Двоичная, восьмеричная и шестнадцатеричная системы счисления. 10 класс
Двоичная, восьмеричная и шестнадцатеричная системы счисления. 10 класс Технология REST
Технология REST ИНЖЕНЕРНАЯ ГРАФИКА - ВЧЕРА, СЕГОДНЯ, ЗАВТРА Инженерная графика – профессиональный язык инженеров прошлого и современности.
ИНЖЕНЕРНАЯ ГРАФИКА - ВЧЕРА, СЕГОДНЯ, ЗАВТРА Инженерная графика – профессиональный язык инженеров прошлого и современности. Винни-Пух и пчелы
Винни-Пух и пчелы