Содержание
- 2. Learning Objective: Create, evaluate and improve search queries that use multiple criteria and relational operators to
- 3. Success criteria know what is Queries know the purpose of the Queries can create Queries using
- 4. MySQL – RDBMS SQL stands for the Structured Query Language. It defines how to insert, retrieve,
- 5. Создание базы данных CREATE DATABASE my_first_db; DROP DATABASE: Удалить базу данных DROP TABLE: Удалить таблицу EXPLAIN:
- 6. ALTER TABLE: Изменить таблицу Удаляем столбец ALTER TABLE users DROP email; Изменение столбца ALTER TABLE users
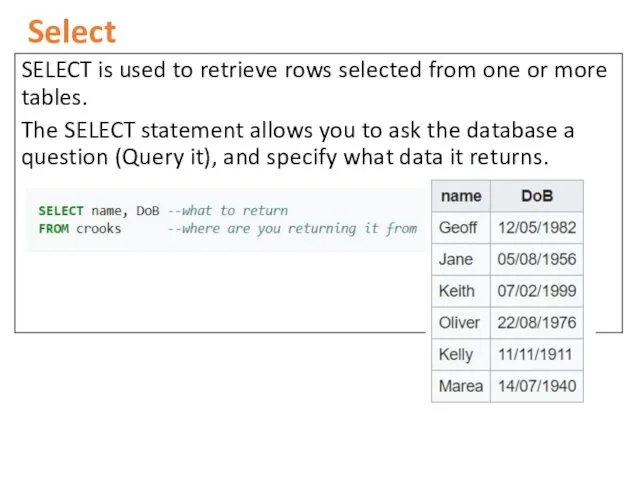
- 7. Select SELECT is used to retrieve rows selected from one or more tables. The SELECT statement
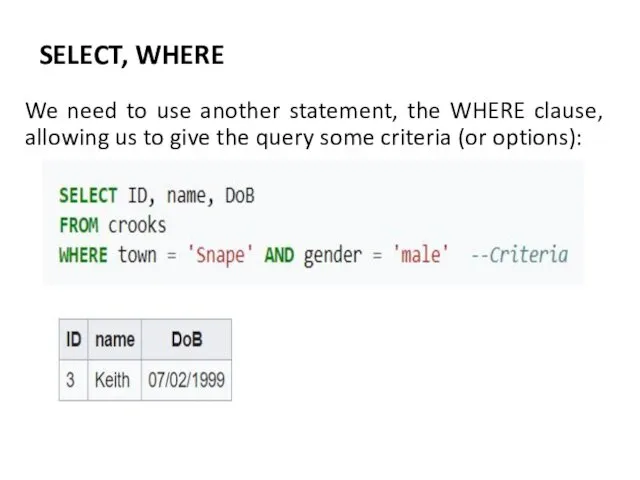
- 8. SELECT, WHERE We need to use another statement, the WHERE clause, allowing us to give the
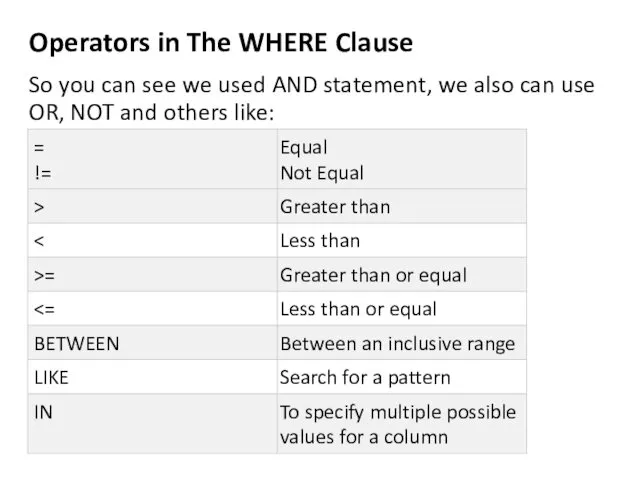
- 9. Operators in The WHERE Clause So you can see we used AND statement, we also can
- 10. Example Say the police knew that a crime had been committed by a heavily scarred woman
- 11. Example However, the police want to quickly sort through and see who is the most heavily
- 12. Select with Comparison Operators For numbers (INT, DECIMAL, FLOAT)
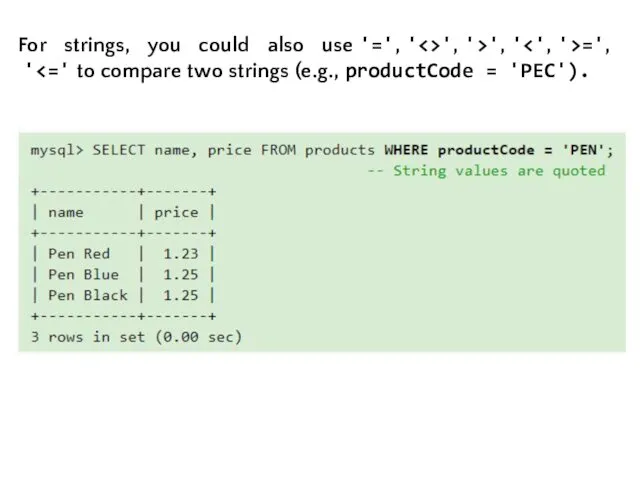
- 13. For strings, you could also use '=', ' ', '>', ' =', '
- 14. String Pattern Matching - LIKE and NOT LIKE we can perform pattern matching using operator LIKE
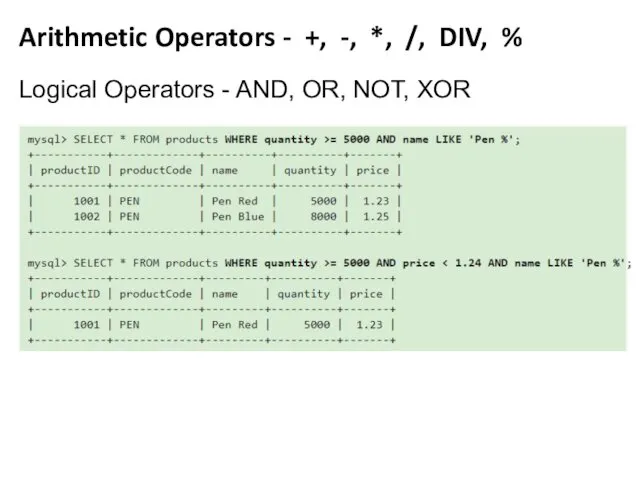
- 15. Arithmetic Operators - +, -, *, /, DIV, % Logical Operators - AND, OR, NOT, XOR
- 16. Further Reading….. IN, NOT IN BETWEEN, NOT BETWEEN IS NULL, IS NOT NULL ORDER BY Clause
- 17. create table Employee(empno int(5) primary key, ename varchar(30), job varchar(25), hiredate date, sal double(10,2), commission double(6,2),
- 19. Скачать презентацию











 Computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing Internet Technology
Internet Technology Презентация "Основные компоненты компьютера" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Основные компоненты компьютера" - скачать презентации по Информатике Безопасный интернет
Безопасный интернет Моделирование и формализация: разработка экономических моделей в среде MS Excel. 10 класс
Моделирование и формализация: разработка экономических моделей в среде MS Excel. 10 класс Информационные технологии
Информационные технологии Программа для создания текстовых документов
Программа для создания текстовых документов Основные функции CLIPS
Основные функции CLIPS Интернет-сленг
Интернет-сленг Требования к разработке приложения на платформе 1С: Предприятие 8.3
Требования к разработке приложения на платформе 1С: Предприятие 8.3 Требования и тенденции построения ОС
Требования и тенденции построения ОС Управление реальной и виртуальной памятью. Основные понятия. Схема динамического преобразования адресов. (Лекция 12)
Управление реальной и виртуальной памятью. Основные понятия. Схема динамического преобразования адресов. (Лекция 12) Примеры для задания Бизнес-идея
Примеры для задания Бизнес-идея Операции соединения. Виды оператора JOIN
Операции соединения. Виды оператора JOIN Как самостоятельно оформить компьютерную презентацию, если ты не дизайнер
Как самостоятельно оформить компьютерную презентацию, если ты не дизайнер Презентация "Алгоритмы" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Алгоритмы" - скачать презентации по Информатике Фірмовий знак
Фірмовий знак Антивирус и защита операционной системы от несанкционированного взлома. Бесплатные антивирусы
Антивирус и защита операционной системы от несанкционированного взлома. Бесплатные антивирусы База данных. Таблицы
База данных. Таблицы Структуры, перечисления
Структуры, перечисления Информация и знания. Информационные процессы
Информация и знания. Информационные процессы Методы объектов. (Занятие 8)
Методы объектов. (Занятие 8) Макет. Архитекту́рный маке́т
Макет. Архитекту́рный маке́т Lecture 01. The basic concepts of SQL
Lecture 01. The basic concepts of SQL Проектирование параметрических запросов
Проектирование параметрических запросов Создание сайта IT и IKT - будущее человечества
Создание сайта IT и IKT - будущее человечества Архивация файлов
Архивация файлов Сортировка и поиск данных
Сортировка и поиск данных