Содержание
- 2. Table of Contents Web Sites and Web Applications Web 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 Web Browsers Hardware Servers
- 3. Web Page Document or information resource that is suitable for the World Wide Web Can be
- 4. Web Site Collection of related web pages containing web resources (web pages, images, videos, CSS files,
- 5. Web Application Next level web sites High interactivity High accessibility (Cloud) AJAX, Silverlight, Flash, Flex, etc.
- 6. Web Browsers and Layout Engines
- 7. Web Browsers Program designed to enable users to access, retrieve and view documents and other resources
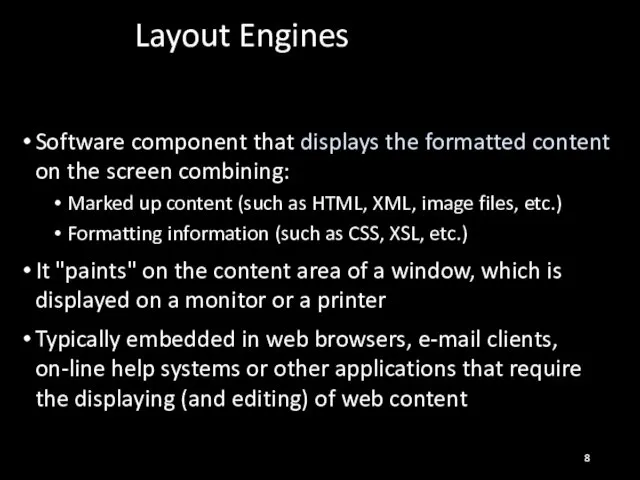
- 8. Layout Engines Software component that displays the formatted content on the screen combining: Marked up content
- 9. Layout Engines and Web Browsers Trident-based Internet Explorer, Netscape, Maxthon, etc. Gecko-based Firefox, Netscape, SeaMonkey, etc.
- 10. User Agent Strings Identify web browsers and their version Can have some additional information like layout
- 11. Hardware Servers Physical computer (a hardware system) dedicated to running one or more such services Servers
- 12. Web Servers Apache, IIS, nginx, lighttpd, etc.
- 13. What Do the Web Servers Do? All physical servers have hardware The hardware is controlled by
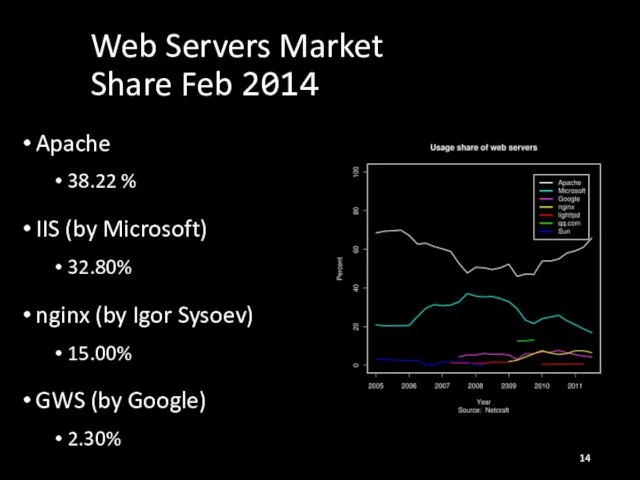
- 14. Web Servers Market Share Feb 2014 Apache 38.22 % IIS (by Microsoft) 32.80% nginx (by Igor
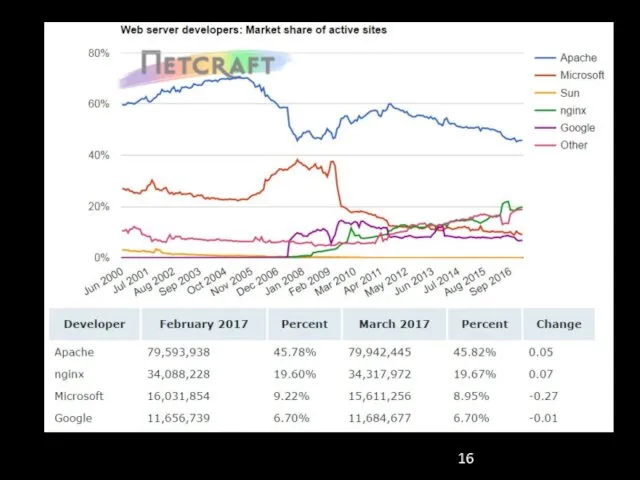
- 15. Most popular web servers in different countries Источник: W3Tech.com
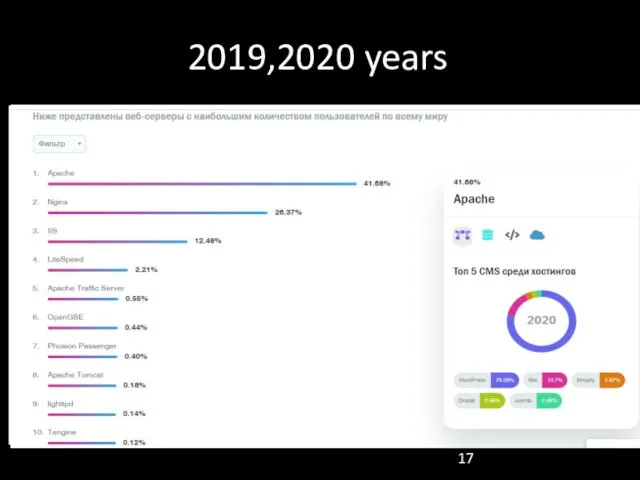
- 17. 2019,2020 years
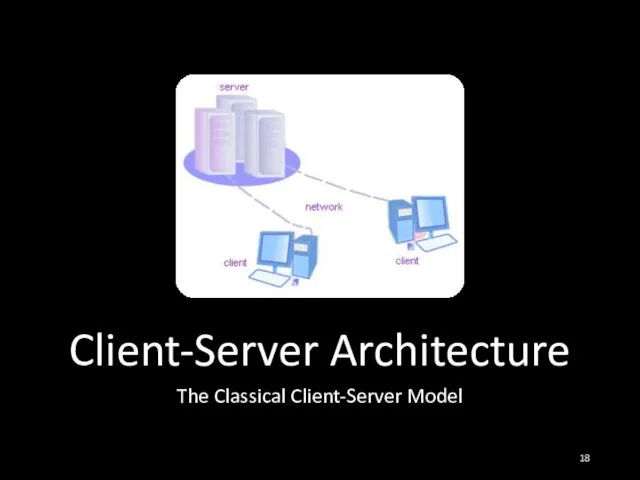
- 18. Client-Server Architecture The Classical Client-Server Model
- 19. Client-Server Architecture The client-server model consists of: Server – a single machine or cluster of machines
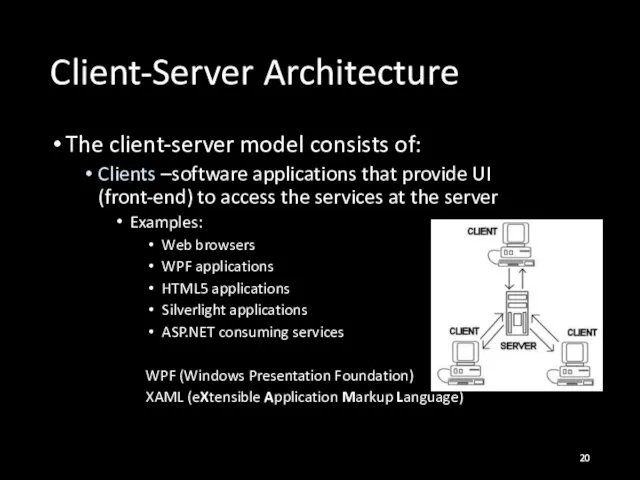
- 20. Client-Server Architecture The client-server model consists of: Clients –software applications that provide UI (front-end) to access
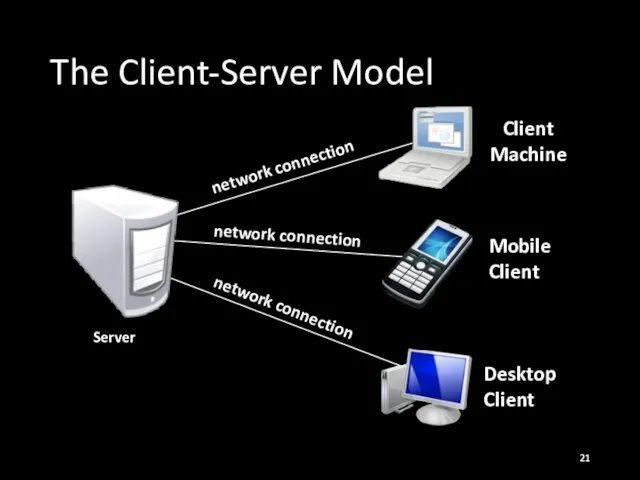
- 21. The Client-Server Model
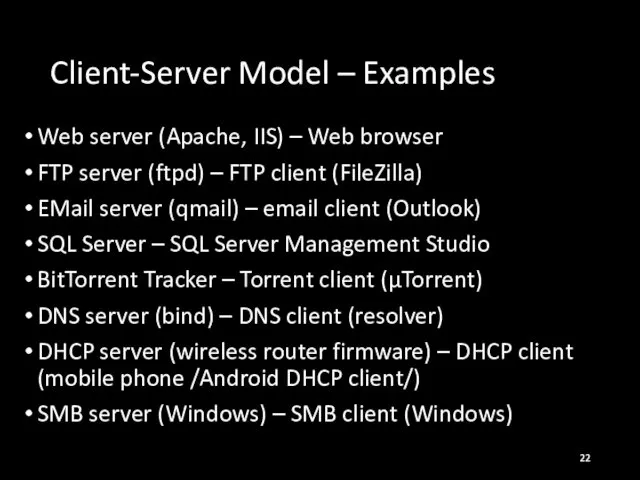
- 22. Client-Server Model – Examples Web server (Apache, IIS) – Web browser FTP server (ftpd) – FTP
- 23. FTP (File Transfer Protocol) FileZilla DNS (Domain Name System) DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) SMB (Server
- 24. 3-Tier / Multi-Tier Architectures Classical Layered Structure of Software Systems
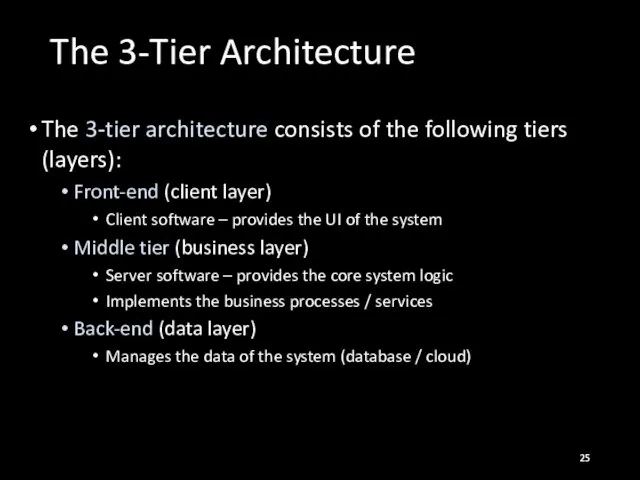
- 25. The 3-Tier Architecture The 3-tier architecture consists of the following tiers (layers): Front-end (client layer) Client
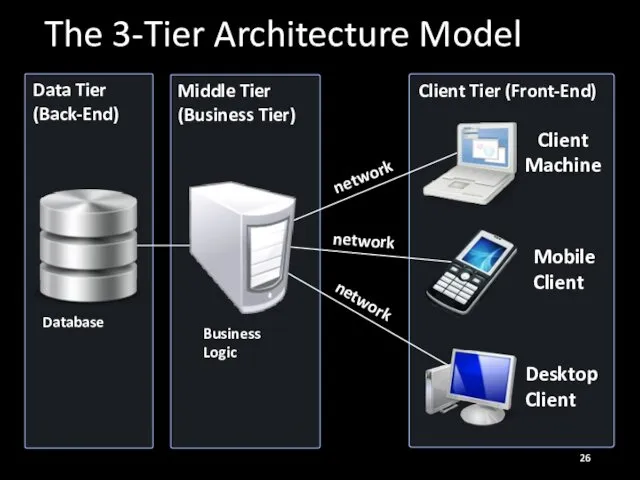
- 26. The 3-Tier Architecture Model Business Logic Desktop Client Mobile Client Client Machine network network network Database
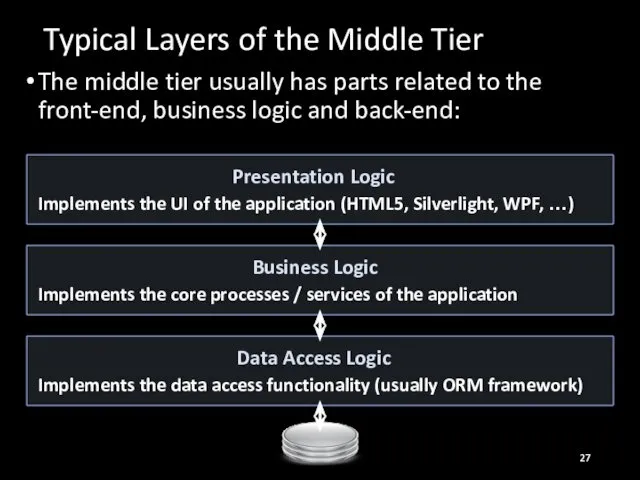
- 27. Typical Layers of the Middle Tier The middle tier usually has parts related to the front-end,
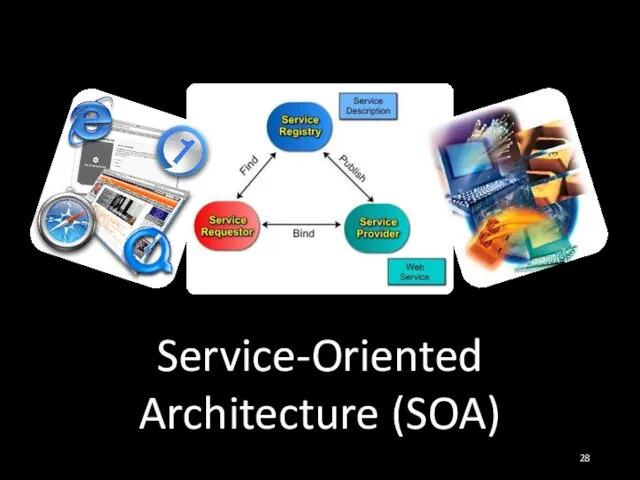
- 28. Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
- 29. What is a Service? In the real world a "service" is: A piece of work performed
- 30. What is "Cloud"?
- 31. What is Cloud? Cloud ≈ multiple hardware machines combine their computing power and resources Share them
- 32. Cloud Computing Models Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Virtual machines in the cloud on demand Users
- 34. Скачать презентацию



















 Разработка программного обеспечения (Software Engineering)
Разработка программного обеспечения (Software Engineering) Аттестационная работа. Выполнение исследовательской работы по информатике в области исследования безопасности в интернет
Аттестационная работа. Выполнение исследовательской работы по информатике в области исследования безопасности в интернет Информация и автоматизация в средствах размещения
Информация и автоматизация в средствах размещения Создание программы на языке Free Pascal в среде разработки KDevelop Презентацию подготовила учитель информатики Лямина Т. М.
Создание программы на языке Free Pascal в среде разработки KDevelop Презентацию подготовила учитель информатики Лямина Т. М. Разработка в 1С
Разработка в 1С Коммерческое предложение
Коммерческое предложение Выполнила: студентка группы Ма1-07 Александрова Д.
Выполнила: студентка группы Ма1-07 Александрова Д. ОГЭ по информатике
ОГЭ по информатике Технологии управления жизненным циклом подвижного состава. CALS (Continuous Acquisition and Life-cycle Support
Технологии управления жизненным циклом подвижного состава. CALS (Continuous Acquisition and Life-cycle Support Выполнение чертежа в AutoCAD
Выполнение чертежа в AutoCAD Особенности картографического обеспечения планирования сетей связи, доступа и вещания с помощью Oneplan
Особенности картографического обеспечения планирования сетей связи, доступа и вещания с помощью Oneplan Графический редактор PAINT
Графический редактор PAINT Лекция 3-Формулы
Лекция 3-Формулы Планирование и внедрение инфраструктуры для развертывания серверов
Планирование и внедрение инфраструктуры для развертывания серверов С компьютером на "ты"
С компьютером на "ты" Презентация "Информация и информационные процессы в неживой и живой природе" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Информация и информационные процессы в неживой и живой природе" - скачать презентации по Информатике Создание сайта. Рынок. Ниша и анализ конкурентов
Создание сайта. Рынок. Ниша и анализ конкурентов Арт-студия. Тест возможности редактора Paint
Арт-студия. Тест возможности редактора Paint Измерение информации. Объёмный подход
Измерение информации. Объёмный подход Программа Stud.Update
Программа Stud.Update ИСТОРИЯ РАЗВИТИЯ КОМПЬЮТЕРОВ.
ИСТОРИЯ РАЗВИТИЯ КОМПЬЮТЕРОВ. Иерархическая и сетевая модели данных
Иерархическая и сетевая модели данных Создание мультимедийной презентации В рамках создания тематического учебного проекта
Создание мультимедийной презентации В рамках создания тематического учебного проекта  Сервис виртуальных графических рабочих станций. ActiveCloud (ООО АктивХост РУ)
Сервис виртуальных графических рабочих станций. ActiveCloud (ООО АктивХост РУ) Презентация "Интернет и Всемирная паутина. Электронная почта (8 класс)" - скачать презентации по Информатике
Презентация "Интернет и Всемирная паутина. Электронная почта (8 класс)" - скачать презентации по Информатике Тема урока: Операторы цикла. Решение задач со счетчиком. Выполнила: Троегубова Татьяна Сергеевна учитель
Тема урока: Операторы цикла. Решение задач со счетчиком. Выполнила: Троегубова Татьяна Сергеевна учитель  Биометрические криптосистемы. Лекция 5
Биометрические криптосистемы. Лекция 5 Инструкция к элементу Задание (1)
Инструкция к элементу Задание (1)