Содержание
- 2. Canada was hit hard by the Great Depression. The international Great Depression, which began in the
- 3. Economic result.By 1930, 30% of the labor force was inactive, and one-fifth of the population became
- 4. Impact. The economy of Canada at this time was just beginning to shift from primary industry
- 5. Unemployment Urban unemployment nationally was 19%; Toronto's rate was 17%, according to the 1931 census. Farmers
- 6. The liberals are coming back. The onset of the Depression led to a Liberal defeat in
- 7. The Bank has played an important role to help regulate government spending in the right direction.
- 9. Скачать презентацию
Canada was hit hard by the Great Depression. The international Great
Canada was hit hard by the Great Depression. The international Great
Economic result.By 1930, 30% of the labor force was inactive, and
Economic result.By 1930, 30% of the labor force was inactive, and
Impact.
The economy of Canada at this time was just beginning to
Impact.
The economy of Canada at this time was just beginning to
Unemployment
Urban unemployment nationally was 19%; Toronto's rate was 17%, according to
Unemployment
Urban unemployment nationally was 19%; Toronto's rate was 17%, according to
Recovery
The canadian recovery from the great Depression continued slowly. Economists Pedro Amaral and James McGee find that the canadian recovery has important differences with the United States. In American productivity, recovered quickly, while the labor force remained depressed for a decade. In Canadian employment, quickly recovered, but productivity remained well below trend. Amaral and McGee suggest that this decline is due to a long decline in international trade during the 1930s.In the middle of the great Depression, the Crown in Council tried to raise people and created two national corporations: the Canadian Radio Broadcasting Commission (CRBC) and the Bank of Canada. The former, established in 1932, was seen as a means to keep the country United and uplifted in these harsh economic times. Many poor citizens found radio as a salvation and used it to restore their own faith in a brighter future. Broadcasting coast to coast primarily in English, with some French primarily in Quebec, CRBC played a vital role in continuing morale for Canadians everywhere. The latter was used to regulate currency and credit, which was horribly managed among canadian citizens in previous years. It was also set up to serve as a private banker's Bank and help and advise the canadian government on its own debts and financial matters.
The liberals are coming back.
The onset of the Depression led
The liberals are coming back. The onset of the Depression led
The Bank has played an important role to help regulate government
The Bank has played an important role to help regulate government
It took the sudden start of world war II to pull Canada out of the depression. Since 1939, increased demand in Europe for materials and increased spending by the canadian government have created a strong boost for the economy. Unemployed men joined the armed forces. By 1939, Canada was in its first period of prosperity in the business cycle in a decade. This coincided with a recovery in the us economy, which has created a better market for exports and a new influx of capital that is much needed.






 День Народного Единства
День Народного Единства История Древнего мира
История Древнего мира Столетняя война
Столетняя война Российский государственный архив научно-технической документации (РГАНТД)
Российский государственный архив научно-технической документации (РГАНТД) Презентация на тему "Политическое развитие России в 1894-1904 гг" - презентации по Истории скачать
Презентация на тему "Политическое развитие России в 1894-1904 гг" - презентации по Истории скачать  Александр II. Личность. Начало правления. Фёдорова И.А.
Александр II. Личность. Начало правления. Фёдорова И.А. Легенды о короле Артуре: правда и вымысел
Легенды о короле Артуре: правда и вымысел Александро-Невская Лавра
Александро-Невская Лавра Россия в XVI веке. Время Ивана Грозного. 3. Внешняя политика России при Иване Грозном.
Россия в XVI веке. Время Ивана Грозного. 3. Внешняя политика России при Иване Грозном. Военно-исторический журнал Они несли с собой любовь и милосердие
Военно-исторический журнал Они несли с собой любовь и милосердие Київська Русь за часів роздробленості. Галицько-Волинська держава
Київська Русь за часів роздробленості. Галицько-Волинська держава Переезд или внезапная находка. Блокада Ленинграда
Переезд или внезапная находка. Блокада Ленинграда 20170913_m.yu_._lermontov.borodino_prezentatsiya
20170913_m.yu_._lermontov.borodino_prezentatsiya Древнейшие государства и народы на территории России
Древнейшие государства и народы на территории России Аттестационная работа. Эссе. Организация проектной и исследовательской деятельности учащихся начальной школы
Аттестационная работа. Эссе. Организация проектной и исследовательской деятельности учащихся начальной школы Лжедмитрий I – Григорий Отрепьев
Лжедмитрий I – Григорий Отрепьев Постиндустриальное общество в Европе и США после Второй Мировой войны
Постиндустриальное общество в Европе и США после Второй Мировой войны Музеи в жизни города
Музеи в жизни города История города — Енакиево
История города — Енакиево Воплощенные в бронзе и на холсте образы освободителей Отечества – Кузьмы Минина и князя Дмитрия Пожарского
Воплощенные в бронзе и на холсте образы освободителей Отечества – Кузьмы Минина и князя Дмитрия Пожарского Национальная и религиозная политика Александра
Национальная и религиозная политика Александра Гісторыя Беларусі
Гісторыя Беларусі Военная Операция ,,Буря в Пустыне”
Военная Операция ,,Буря в Пустыне” Древняя Месопотамия
Древняя Месопотамия Государства Юго-Восточной Европы в XI – XV вв
Государства Юго-Восточной Европы в XI – XV вв Устройство Римской республики
Устройство Римской республики История 1598-1605
История 1598-1605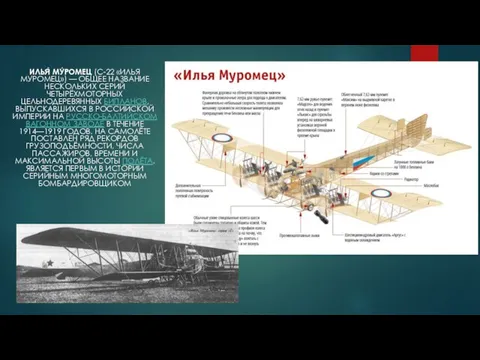 Боевая техника Первой Мировой войны
Боевая техника Первой Мировой войны