Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives Identify health claims associated with St. John’s Wort. Name the two substances in St.
- 3. Learning Objectives Describe the effect of St. John’s Wort on mild to moderate depression compared to
- 4. St. John’s Wort Hypericum Perforatum Claims: Treatment of mild to moderate depression. Relieves anxiety, insomnia, and
- 5. History Native to Europe & Asia. Called St. John’s Wort because it flowers around St. John’s
- 6. Composition Contains at least 10 substances including hypericin & hyperforin, which are shown to have biological
- 7. Formulation & Dosage Colorado Nutrition 900 mg .3% hypericin – take 2 daily. Nature’s Way 350
- 8. Depression Criteria DSM-IV Criteria for major depression Period of at least 2 weeks during which there
- 9. Depression Criteria Dysthymia – mild to moderate Chronic disturbance involving depressed mood and at least 2
- 10. Prevalence of Depression Effects estimated 17 million Americans every year. Twice as common in women than
- 11. Mechanism of controlling depression Depression is caused by a deficiency of serotonin or norepinephrine Substances having
- 12. Mechanism of action MAO inhibition occurs with high concentrations of SJW. Inhibits serotonin uptake in post-synaptic
- 14. SJW vs. prescription anti-depressants Anti-depressant side effects: Headache, GI upset, nervousness, sexual dysfunction, fatigue, and insomnia.
- 15. Hypericum Treatment of Mild-Moderate Depression in a Placebo-Controlled Study. A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized, Multicentre Study Human
- 16. Hypericum Treatment of Mild-Moderate Depression in a Placebo-Controlled Study. A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized, Multicentre Study Human
- 17. Hypericum Treatment of Mild-Moderate Depression in a Placebo-Controlled Study. A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized, Multicentre Study Human
- 18. Efficacy of St. John’s wort extract WS 5570 in major depression: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial The
- 19. Efficacy of St. John’s wort extract WS 5570 in major depression: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial The
- 20. Efficacy of St. John’s wort extract WS 5570 in major depression: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial The
- 21. Effect of Hypericum perforatum in Major Depressive Disorder A Randomized Controlled Trial JAMA (2002) 287:14 Specific
- 22. Effect of Hypericum perforatum in Major Depressive Disorder A Randomized Controlled Trial JAMA (2002) 287:14 Treatment
- 23. Effect of Hypericum perforatum in Major Depressive Disorder A Randomized Controlled Trial JAMA (2002) 287:14 Results
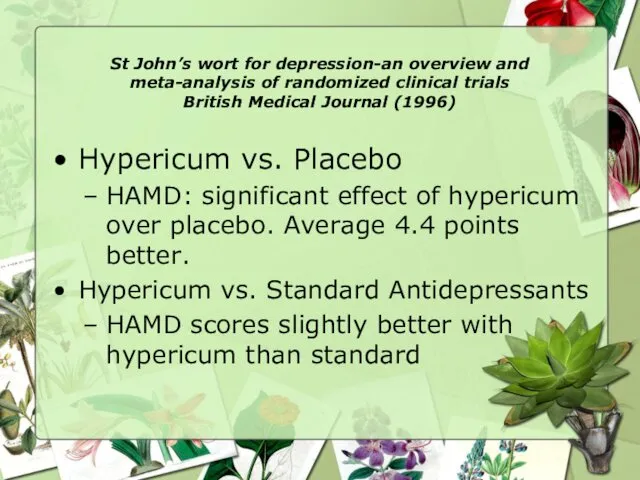
- 24. St John’s wort for depression-an overview and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials British Medical Journal (1996)
- 25. St John’s wort for depression-an overview and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials British Medical Journal (1996)
- 26. St John’s wort for depression-an overview and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials British Medical Journal (1996)
- 27. St John’s wort for depression-an overview and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials British Medical Journal (1996)
- 28. Adverse Effects Increased sensitivity to light Dry mouth Dizziness GI symptoms Fatigue Headache Sexual dysfunction
- 29. Herb-drug Interactions St. John’s Wort inducer of various drug metabolizing enzymes Urgent bulletin to physicians from
- 30. Herb-drug Interactions: Committee on Safety of Medicine HIV Medications Reduced blood levels with possible loss of
- 31. Herb-drug Interactions: Committee on Safety of Medicine Oral Contraceptives Reduced blood levels with risk of unintended
- 32. Herb-drug Interactions: Committee on Safety of Medicine Theophylline Reduced blood levels and loss of control of
- 34. Скачать презентацию




























 მარკეტინგის საფუძვლები. (ტრენინგი 2)
მარკეტინგის საფუძვლები. (ტრენინგი 2) Business Markets and Buying Behavior. (Chapter 7)
Business Markets and Buying Behavior. (Chapter 7) Компания Аспект Окна
Компания Аспект Окна Развитие направления силовых сборок ЗАО ПРОТОН-ЭЛЕКТРОТЕКС на базе СПП собственного производства
Развитие направления силовых сборок ЗАО ПРОТОН-ЭЛЕКТРОТЕКС на базе СПП собственного производства Санаторий - профилакторий Связист
Санаторий - профилакторий Связист Как навсегда обогнать конкурентов. Презентаци
Как навсегда обогнать конкурентов. Презентаци ICE Robotics Russia
ICE Robotics Russia Описание преимуществ моделей ТМ Валерия для покупателя
Описание преимуществ моделей ТМ Валерия для покупателя Модульное оборудование
Модульное оборудование Интернет-магазин Bookmarks. Закладки для книг
Интернет-магазин Bookmarks. Закладки для книг ЖК Светлоград
ЖК Светлоград Продукция DOUBLE LUXURY
Продукция DOUBLE LUXURY Коммерческое предложение по seo продвижению сайта
Коммерческое предложение по seo продвижению сайта Яндекс таланты
Яндекс таланты ООО “Пульсар Лимитед”. Один из ведущих поставщиков промышленных аккумуляторов в Украине
ООО “Пульсар Лимитед”. Один из ведущих поставщиков промышленных аккумуляторов в Украине Презентер на два девайса
Презентер на два девайса Презентация новой LADA Granta. ООО АвтоГрад
Презентация новой LADA Granta. ООО АвтоГрад Сравнение услуг торговли
Сравнение услуг торговли Faberlic и корпорация Денас МС. Денс-терапия
Faberlic и корпорация Денас МС. Денс-терапия Презентация SPAR
Презентация SPAR Национальная новогодняя промо-кампания 2017 - 2018
Национальная новогодняя промо-кампания 2017 - 2018 Тренинг по промо-акции Nivea Подарок за покупку
Тренинг по промо-акции Nivea Подарок за покупку PR инструменты в системе продвижения салона красоты
PR инструменты в системе продвижения салона красоты Как стать звездой. Аудиошкола для вокалистов
Как стать звездой. Аудиошкола для вокалистов Гарри Поттер Вики
Гарри Поттер Вики Social media marketing. Анализ использования на региональном рынке
Social media marketing. Анализ использования на региональном рынке Компания Тойота Мотор
Компания Тойота Мотор Изготовление мебели на заказ
Изготовление мебели на заказ